Configure EC2Launch v2 settings for Windows instances
This section contains information about how to configure settings for EC2Launch v2.
Topics include:
Change settings using the EC2Launch v2 settings dialog box
The following procedure describes how to use the EC2Launch v2 settings dialog box to enable or disable settings.
Note
If you improperly configure custom tasks in the agent-config.yml file, and you attempt to open the Amazon EC2Launch settings dialog box, you will receive an error. For example schema, see Example: agent-config.yml.
-
Launch and connect to your Windows instance.
-
From the Start menu, choose All Programs, and then navigate to EC2Launch settings. Before you choose Shutdown with Sysprep or Shutdown without Sysprep, make sure that you save any changes that you want to apply when you run the shutdown.
-
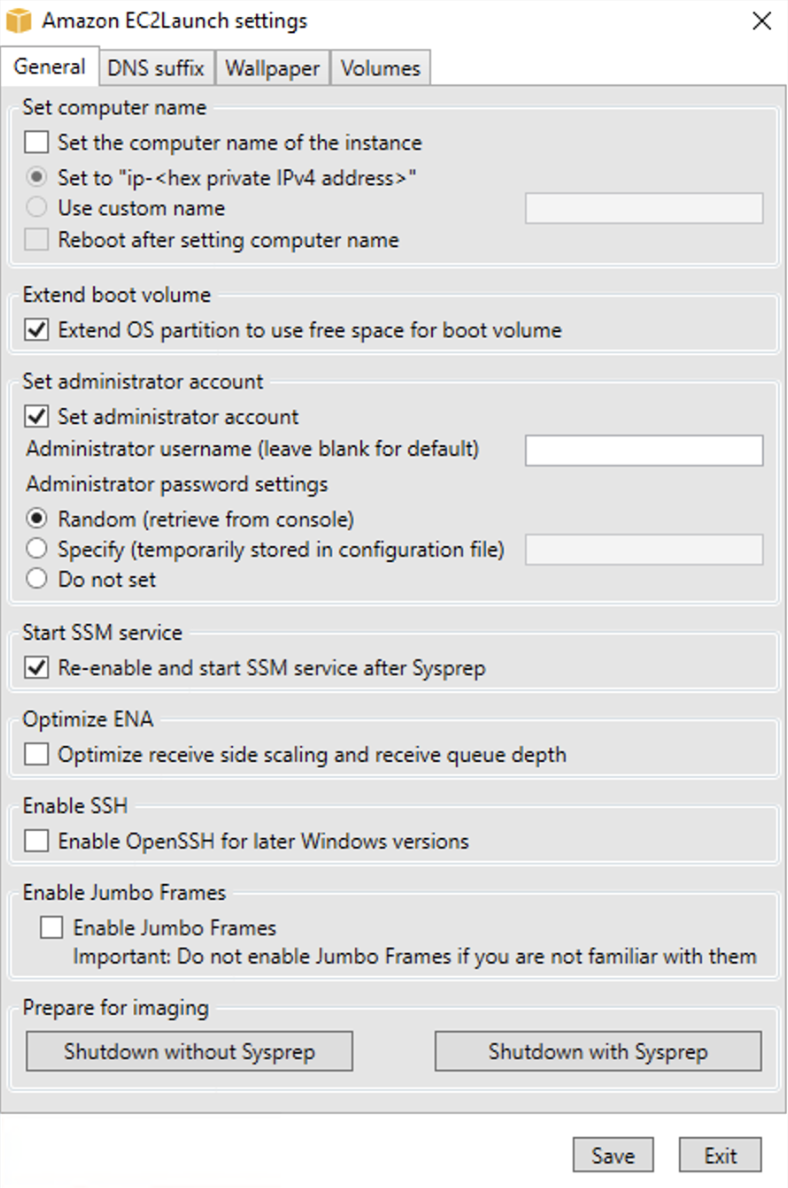
On the General tab of the EC2Launch settings dialog box, you can enable or disable the following settings.
-
Set Computer Name
If this setting is enabled (it is disabled by default), the current host name is compared to the desired host name at each boot. If the host names do not match, the host name is reset, and the system then optionally reboots to pick up the new host name. If a custom host name is not specified, it is generated using the hexadecimal-formatted private IPv4 address, for example,
ip-AC1F4E6. To prevent your existing host name from being modified, do not enable this setting. -
Extend Boot Volume
This setting dynamically extends
Disk 0/Volume 0to include any unpartitioned space. This can be useful when the instance is booted from a root device volume that has a custom size. -
Set Administrator Account
When enabled, you can set the username and password attributes for the administrator account that is created on your local machine. If this feature is not enabled, an administrator account is not created on the system following Sysprep. Provide a password in
adminPasswordonly ifadminPasswordtypeisSpecify.The password types are defined as follows:
-
RandomEC2Launch generates a password and encrypts it using the user's key. The system disables this setting after the instance is launched so that this password persists if the instance is rebooted or stopped and started.
-
SpecifyEC2Launch uses the password that you specify in
adminPassword. If the password does not meet the system requirements, EC2Launch generates a random password instead. The password is stored inagent-config.ymlas clear text and is deleted after Sysprep sets the administrator password. EC2Launch encrypts the password using the user's key. -
Do not setEC2Launch uses the password that you specify in the unattend.xml file. If you don't specify a password in unattend.xml, the administrator account is disabled.
-
-
Start SSM Service
When selected, the Systems Manager service is enabled to start following Sysprep. EC2Launch v2 performs all of the tasks described earlier, and the SSM Agent processes requests for Systems Manager capabilities, such as Run Command and State Manager.
You can use Run Command to upgrade your existing instances to use the latest version of the EC2Launch v2 service and SSM Agent. For more information, see Update SSM Agent using Run Command in the AWS Systems Manager User Guide.
-
Optimize ENA
When selected, ENA settings are configured to ensure that ENA Receive Side Scaling and Receive Queue Depth settings are optimized for AWS. For more information, see Configure Receive side scaling CPU affinity.
-
Enable SSH
This setting enables OpenSSH for later Windows versions to allow for remote system administration.
-
Enable Jumbo Frames
Select to enable Jumbo Frames. Jumbo Frames can have unintended effects on your network communications, so ensure you understand how Jumbo Frames will impact your system before enabling. For more information about Jumbo Frames, see Jumbo frames (9001 MTU).
-
Prepare for Imaging
Select whether you want your EC2 instance to shut down with or without Sysprep. When you want to run Sysprep with EC2Launch v2, choose Shutdown with Sysprep.
-
-
On the DNS Suffix tab, you can select whether you want to add a DNS suffix list for DNS resolution of servers running in EC2, without providing the fully qualified domain name. DNS suffixes can contain the variables
$REGIONand$AZ. Only suffixes that do not already exist will be added to the list.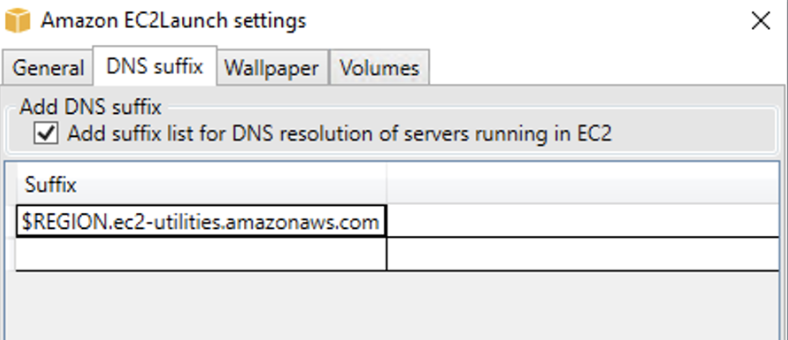
-
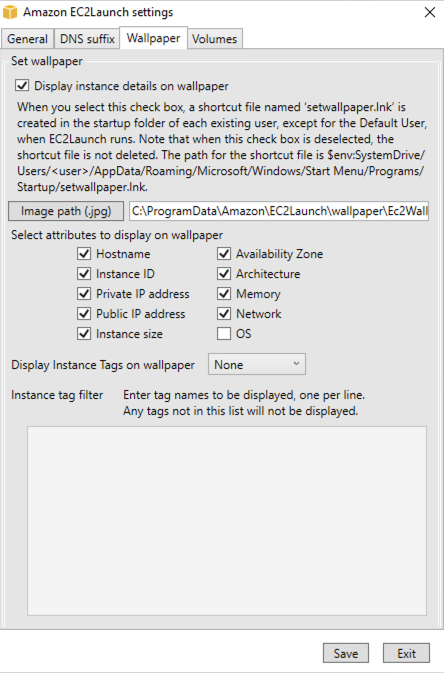
On the Wallpaper tab, you can configure your instance wallpaper with a background image, and specify instance details for the wallpaper to display. Amazon EC2 generates the details each time you log in.
You can configure your wallpaper with the following controls.
-
Display instance details on wallpaper – This checkbox activates or deactivates instance detail display on the wallpaper.
-
Image path (.jpg) – Specify the path to the image to use as the wallpaper background.
-
Select attributes to display on wallpaper – Select the check boxes for the instance details that you want to appear on the wallpaper. Clear the check boxes for previously selected instance details that you want to remove from the wallpaper.
-
Display Instance Tags on wallpaper – Select one of the following settings to display instance tags on the wallpaper:
-
None – Don't display any instance tags on the wallpaper.
-
Show all – Display all instance tags on the wallpaper.
-
Show filtered – Display specified instance tags on the wallpaper. When you select this setting, you can add instance tags that you want to display on your wallpaper in the Instance tag filter box.
Note
You must enable tags in metadata to show tags on the wallpaper. For more information about instance tags and metadata, see View tags for your EC2 instances using instance metadata.
-
-
-
On the Volumes tab, select whether you want to initialize the volumes that are attached to the instance. Enabling sets drive letters for any additional volumes and extends them to use available space. If you select All, all of the storage volumes are initialized. If you select Devices, only devices that are specified in the list are initialized. You must enter the device for each device to be initialized. Use the devices listed on the EC2 console, for example,
xvdbor/dev/nvme0n1. The dropdown list displays the storage volumes that are attached to the instance. To enter a device that is not attached to the instance, enter it in the text field.Name, Letter, and Partition are optional fields. If no value is specified for Partition, storage volumes larger than 2 TB are initialized with the
gptpartition type, and those smaller than 2 TB are initialized with thembrpartition type. If devices are configured, and a non-NTFS device either contains a partition table, or the first 4 KB of the disk contain data, then the disk is skipped and the action logged.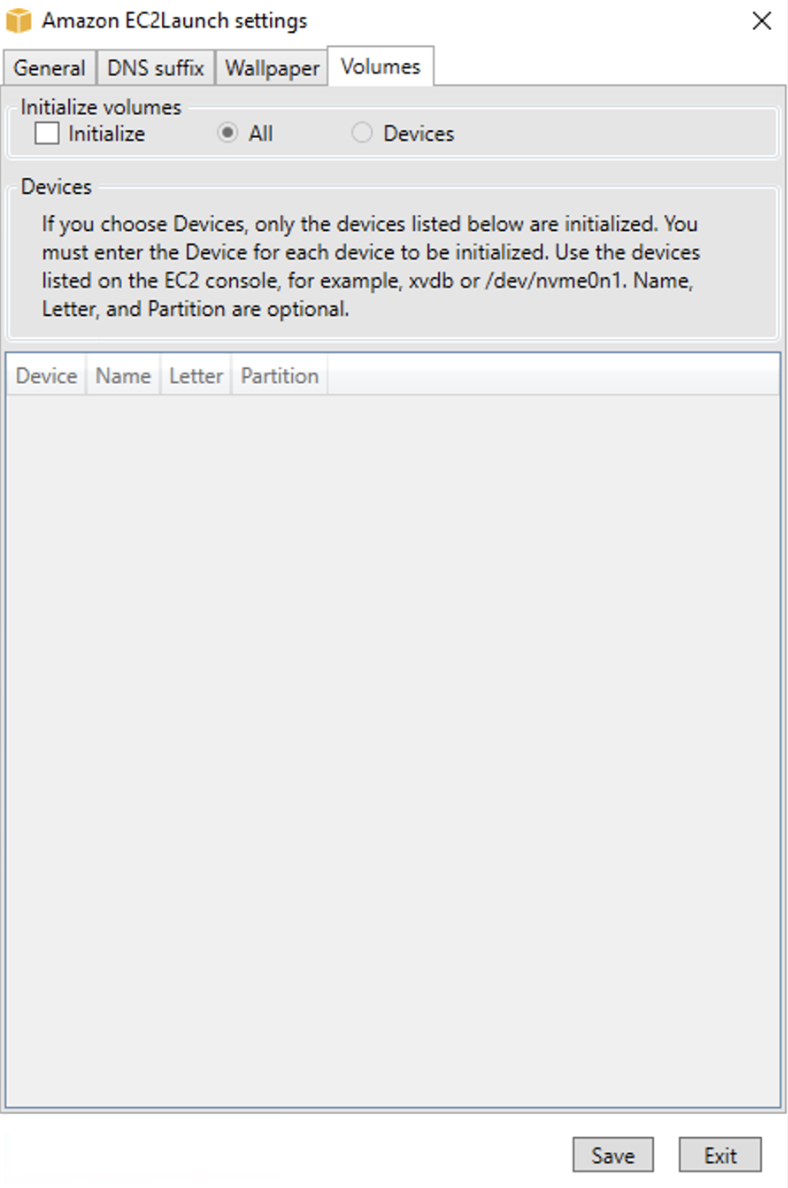
The following is an example configuration YAML file created from the settings entered in the EC2Launch dialog.
version: 1.0 config: - stage: boot tasks: - task: extendRootPartition - stage: preReady tasks: - task: activateWindows inputs: activation: type: amazon - task: setDnsSuffix inputs: suffixes: - $REGION.ec2-utilities.amazonaws.com - task: setAdminAccount inputs: password: type: random - task: setWallpaper inputs: path: C:\ProgramData\Amazon\EC2Launch\wallpaper\Ec2Wallpaper.jpg attributes: - hostName - instanceId - privateIpAddress - publicIpAddress - instanceSize - availabilityZone - architecture - memory - network - stage: postReady tasks: - task: startSsm
Configure EC2Launch v2 using the CLI
You can use the Command Line Interface (CLI) to configure your EC2Launch settings and manage the service. The following section contains descriptions and usage information for the CLI commands that you can use to manage EC2Launch v2.
collect-logs
Collects log files for EC2Launch, zips the files, and places them in a specified directory.
Example
ec2launch collect-logs -o C:\Mylogs.zip
Usage
ec2launch collect-logs [flags]
Flags
-h, --help
help for collect-logs
-o, --output string
path to zipped output log files
get-agent-config
Prints agent-config.yml in the format specified (JSON or YAML).
If no format is specified, agent-config.yml is printed in the
format previously specified.
Example
ec2launch get-agent-config -f json
Usage
ec2launch get-agent-config [flags]
Flags
-h, --help
help for get-agent-config
-f, --format string
output format of agent-config file: json,
yaml
list-volumes
Lists all of the storage volumes attached to the instance, including ephemeral and EBS volumes.
Example
ec2launch list-volumes
Usage
ec2launch list-volumes
Flags
-h, --help
help for list-volumes
reset
The main goal of this task is to reset the agent for the next time that it
runs. To do that, the reset command deletes all of the agent
state data for EC2Launch v2 from the local EC2Launch directory
(see EC2Launch v2 directory structure). Reset optionally deletes the
service and Sysprep logs.
Script behavior depends on what mode the agent runs the scripts in – inline, or detached.
- Inline (default)
-
The EC2Launch v2 agent runs scripts one at a time (
detach: false). This is the default setting.Note
When your inline script issues a reset or sysprep command, it runs immediately and resets the agent. The current task finishes, then the agent shuts down without running any further tasks.
For example, if the task that issues the command would have been followed by a
startSsmtask (included by default after user data runs), the task doesn't run and the Systems Manager service never starts. - Detached
-
The EC2Launch v2 agent runs scripts concurrently with other tasks (
detach: true).Note
When your detached script issues a reset or sysprep command, those commands wait for the agent to finish before they run. Tasks after the executeScript will still run.
Example
ec2launch reset -c
Usage
ec2launch reset [flags]
Flags
-c, --clean
cleans instance logs before reset
-h, --help
help for reset
run
Runs EC2Launch v2.
Example
ec2launch run
Usage
ec2launch run [flags]
Flags
-h, --help
help for run
status
Gets the status of the EC2Launch v2 agent. Optionally blocks the process until the agent is finished. The process exit code determines the agent state:
-
0–the agent ran and was successful. -
1– the agent ran and failed. -
2– the agent is still running. -
3– the agent is in an unknown state. The agent state is not running or stopped. -
4– an error occurred when attempting to retrieve the agent state. -
5– the agent is not running and the status of the last known run is unknown. This could mean one of the following:-
both the
state.jsonandprevious-state.jsonare deleted. -
the
previous-state.jsonis corrupted.
This is the agent state after running the reset command.
-
Example:
ec2launch status -b
Usage
ec2launch status [flags]
Flags
-b,--block
blocks the process until the agent finishes running
-h,--help
help for status
sysprep
The main goal of this task is to reset the agent for the next time that it
runs. To do that, the sysprep command resets the agent state,
updates the unattend.xml file, disables RDP, and runs
Sysprep.
Script behavior depends on what mode the agent runs the scripts in – inline, or detached.
- Inline (default)
-
The EC2Launch v2 agent runs scripts one at a time (
detach: false). This is the default setting.Note
When your inline script issues a reset or sysprep command, it runs immediately and resets the agent. The current task finishes, then the agent shuts down without running any further tasks.
For example, if the task that issues the command would have been followed by a
startSsmtask (included by default after user data runs), the task doesn't run and the Systems Manager service never starts. - Detached
-
The EC2Launch v2 agent runs scripts concurrently with other tasks (
detach: true).Note
When your detached script issues a reset or sysprep command, those commands wait for the agent to finish before they run. Tasks after the executeScript will still run.
Example:
ec2launch sysprep
Usage
ec2launch sysprep [flags]
Flags
-c,--clean
cleans instance logs before sysprep
-h,--help
help for Sysprep
-s,--shutdown
shuts down the instance after sysprep
validate
Validates the agent-config file
C:\ProgramData\Amazon\EC2Launch\config\agent-config.yml.
Example
ec2launch validate
Usage
ec2launch validate [flags]
Flags
-h , --help
help for validate
version
Gets the executable version.
Example
ec2launch version
Usage
ec2launch version [flags]
Flags
-h, --help
help for version
wallpaper
Sets new wallpaper to the wallpaper path that is provided (.jpg file), and displays the selected instance details.
Syntax
ec2launch wallpaper ^ --path="C:\ProgramData\Amazon\EC2Launch\wallpaper\Ec2Wallpaper.jpg" ^ --all-tags ^ --attributes=hostName,instanceId,privateIpAddress,publicIpAddress,instanceSize,availabilityZone,architecture,memory,network
Inputs
Parameters
- --allowed-tags [
tag-name-1,tag-name-n] -
(Optional) Base64 encoded JSON array of instance tag names to display on the wallpaper. You can use this tag or the
--all-tags, but not both. - --attributes
attribute-string-1,attribute-string-n -
(Optional) A comma-separated list of
wallpaperattribute strings to apply settings to the wallpaper. - [--path | -p]
path-string -
(Required) Specifies the
wallpaperbackground image file path.
Flags
- --all-tags
-
(Optional) Displays all of the instance tags on the wallpaper. You can use this tag or the
--allowed-tags, but not both. - [--help | -h]
-
Displays help for the wallpaper command.
EC2Launch v2 task configuration
This section includes the configuration schema, tasks, details, and examples for
agent-config.yml and user data.
Tasks and examples
Schema:
agent-config.yml
The structure of the agent-config.yml file is shown below. Note
that a task cannot be repeated in the same stage. For task properties, see the
task descriptions that follow.
Document structure: agent-config.yml
JSON
{ "version": "1.1", "config": [ { "stage": "string", "tasks": [ { "task": "string", "inputs": { ... } }, ... ] }, ... ] }
YAML
version: 1.1 config: - stage: string tasks: - task: string inputs: ... ... ...
Example:
agent-config.yml
The following example shows settings for the agent-config.yml
configuration file.
version: 1.1 config: - stage: boot tasks: - task: extendRootPartition - stage: preReady tasks: - task: activateWindows inputs: activation: type: amazon - task: setDnsSuffix inputs: suffixes: - $REGION.ec2-utilities.amazonaws.com - task: setAdminAccount inputs: password: type: random - task: setWallpaper inputs: path: C:\ProgramData\Amazon\EC2Launch\wallpaper\Ec2Wallpaper.jpg attributes: - hostName - instanceId - privateIpAddress - publicIpAddress - instanceSize - availabilityZone - architecture - memory - network - stage: postReady tasks: - task: startSsm
Configure EC2Launch v2 user data scripts that run during launch or reboot
The following JSON and YAML examples show the document structure for user
data. Amazon EC2 parses each task named in the tasks array that you
specify in the document. Each task has its own set of properties and
requirements. For details, see the Task definitions for EC2Launch v2 startup tasks.
Note
A task must only appear once in the user data tasks array.
Document structure: user data
JSON
{ "version": "1.1", "tasks": [ { "task": "string", "inputs": { ... }, }, ... ] }
YAML
version: 1.1 tasks: - task: string inputs: ... ...
Example: user data
For more information about user data, see How Amazon EC2 handles user data for Windows instances.
The following YAML document example shows a PowerShell script that EC2Launch v2 runs as user data to create a file.
version: 1.1 tasks: - task: executeScript inputs: - frequency: always type: powershell runAs: localSystem content: |- New-Item -Path 'C:\PowerShellTest.txt' -ItemType File
You can use an XML format for the user data that's compatible with
previous versions of the launch agent. EC2Launch v2 runs the script as an
executeScript task in the UserData stage. To
conform with EC2Launch v1 and EC2Config behavior, the user data script runs as
an attached/inline process by default.
You can add optional tags to customize how your script runs. For example, to run the user data script when the instance reboots in addition to one time when the instance launches, you can use the following tag:
<persist>true</persist>
Example:
<powershell> $file = $env:SystemRoot + "\Temp" + (Get-Date).ToString("MM-dd-yy-hh-mm") New-Item $file -ItemType file </powershell> <persist>true</persist>
You can specify one or more PowerShell arguments with the
<powershellArguments> tag. If no arguments are
passed, EC2Launch v2 adds the following argument by default:
-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted.
Example:
<powershell> $file = $env:SystemRoot + "\Temp" + (Get-Date).ToString("MM-dd-yy-hh-mm") New-Item $file -ItemType file </powershell> <powershellArguments>-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -NoProfile -NonInteractive</powershellArguments>
To run an XML user data script as a detached process, add the following tag to your user data.
<detach>true</detach>
Example:
<powershell> $file = $env:SystemRoot + "\Temp" + (Get-Date).ToString("MM-dd-yy-hh-mm") New-Item $file -ItemType file </powershell> <detach>true</detach>
Note
The detach tag is not supported on previous launch agents.
Change log: user data
The following table lists changes for user data, and cross-references them to the EC2Launch v2 agent version that applies.
| User data version | Details | Introduced in |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1 |
|
EC2Launch v2 version 2.0.1245 |
| 1.0 |
|
EC2Launch v2 version 2.0.0 |
* When used with the default agent-config.yml
file.
EC2Launch v2 exit codes and reboots
You can use EC2Launch v2 to define how exit codes are handled by your scripts. By
default, the exit code of the last command that is run in a script is reported as
the exit code for the entire script. For example, if a script includes three
commands and the first command fails but the following ones succeed, the run status
is reported as success because the final command succeeded.
If you want a script to reboot an instance, then you must specify exit
3010 in your script, even when the reboot is the last step in your
script. exit 3010 instructs EC2Launch v2 to reboot the instance and call
the script again until it returns an exit code that is not 3010, or
until the maximum reboot count has been reached. EC2Launch v2 permits a maximum of 5
reboots per task. If you attempt to reboot an instance from a script by using a
different mechanism, such as Restart-Computer, then the script run
status will be inconsistent. For example, it may get stuck in a restart loop or not
perform the restart.
If you are using an XML user data format that is compatible with older agents, the user data may run more times than you intend it to. For more information, see Service runs user data more than once in the Troubleshooting section.
EC2Launch v2 and Sysprep
The EC2Launch v2 service runs Sysprep, a Microsoft tool that enables you to create a
customized Windows AMI that can be reused. When EC2Launch v2 calls Sysprep, it uses the
files in %ProgramData%\Amazon\EC2Launch to determine which operations
to perform. You can edit these files indirectly using the EC2Launch
settings dialog box, or directly using a YAML editor or a text
editor. However, there are some advanced settings that aren't available in the
EC2Launch settings dialog box, so you must edit those
entries directly.
If you create an AMI from an instance after updating its settings, the new settings are applied to any instance that's launched from the new AMI. For information about creating an AMI, see Create an Amazon EBS-backed AMI.