Store instance launch parameters in Amazon EC2 launch templates
You can use an Amazon EC2 launch template to store instance launch parameters so that you don't have to specify them every time you launch an Amazon EC2 instance. For example, you can create a launch template that stores the AMI ID, instance type, and network settings that you typically use to launch instances. When you launch an instance using the Amazon EC2 console, an AWS SDK, or a command line tool, you can specify the launch template instead of entering the parameters again.
For each launch template, you can create one or more numbered launch template versions. Each version can have different launch parameters. When you launch an instance from a launch template, you can use any version of the launch template. If you don't specify a version, the default version is used. You can set any version of the launch template as the default version—by default, it's the first version of the launch template.
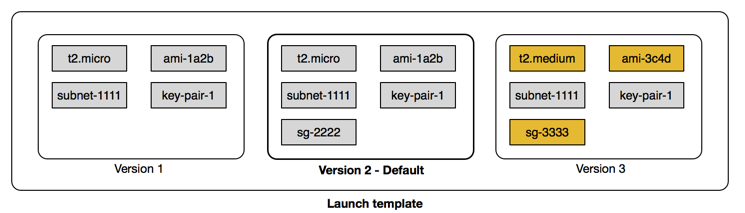
The following diagram shows a launch template with three versions. The first version specifies the instance type, AMI ID, subnet, and key pair to use to launch the instance. The second version is based on the first version and also specifies a security group for the instance. The third version uses different values for some of the parameters. Version 2 is set as the default version. If you launched an instance from this launch template, the launch parameters from version 2 would be used if no other version were specified.