High throughput for FIFO queues in Amazon SQS
High throughput FIFO queues in Amazon SQS efficiently manage high message throughput while maintaining strict message order, ensuring reliability and scalability for applications processing numerous messages. This solution is ideal for scenarios demanding both high throughput and ordered message delivery.
Amazon SQS high throughput FIFO queues are not necessary in scenarios where strict message ordering is not crucial and where the volume of incoming messages is relatively low or sporadic. For instance, if you have a small-scale application that processes infrequent or non-sequential messages, the added complexity and cost associated with high throughput FIFO queues may not be justified. Additionally, if your application does not require the enhanced throughput capabilities provided by high throughput FIFO queues, opting for a standard Amazon SQS queue might be more cost-effective and simpler to manage.
To enhance request capacity in high throughput FIFO queues, increasing the number of message groups is recommended. For more information on high throughput message quotas, see Amazon SQS service quotas in the Amazon Web Services General Reference.
For information per-queue quotas and data distribution strategies, see Amazon SQS message quotas and Partitions and data distribution for high throughput for SQS FIFO queues.
Use cases for high throughput for Amazon SQS FIFO queues
The following use cases highlight the diverse applications of high throughput FIFO queues, showcasing their effectiveness across industries and scenarios:
-
Real-time data processing: Applications dealing with real-time data streams, such as event processing or telemetry data ingestion, can benefit from high throughput FIFO queues to handle the continuous influx of messages while preserving their order for accurate analysis.
-
E-commerce order processing: In e-commerce platforms where maintaining the order of customer transactions is critical, high throughput FIFO queues ensure that orders are processed sequentially and without delays, even during peak shopping seasons.
-
Financial services: Financial institutions handling high-frequency trading or transactional data rely on high throughput FIFO Queues to process market data and transactions with minimal latency while adhering to strict regulatory requirements for message ordering.
-
Media streaming: Streaming platforms and media distribution services utilize high throughput FIFO queues to manage the delivery of media files and streaming content, ensuring smooth playback experiences for users while maintaining the correct order of content delivery.
Partitions and data distribution for high throughput for SQS FIFO queues
Amazon SQS stores FIFO queue data in partitions. A partition is an allocation of storage for a queue that is automatically replicated across multiple Availability Zones within an AWS Region. You don't manage partitions. Instead, Amazon SQS handles partition management.
For FIFO queues, Amazon SQS modifies the number of partitions in a queue in the following situations:
-
If the current request rate approaches or exceeds what the existing partitions can support, additional partitions are allocated until the queue reaches the regional quota. For information on quotas, see Amazon SQS message quotas.
-
If the current partitions have low utilization, the number of partitions may be reduced.
Partition management occurs automatically in the background and is transparent to your applications. Your queue and messages are available at all times.
Distributing data by message group IDs
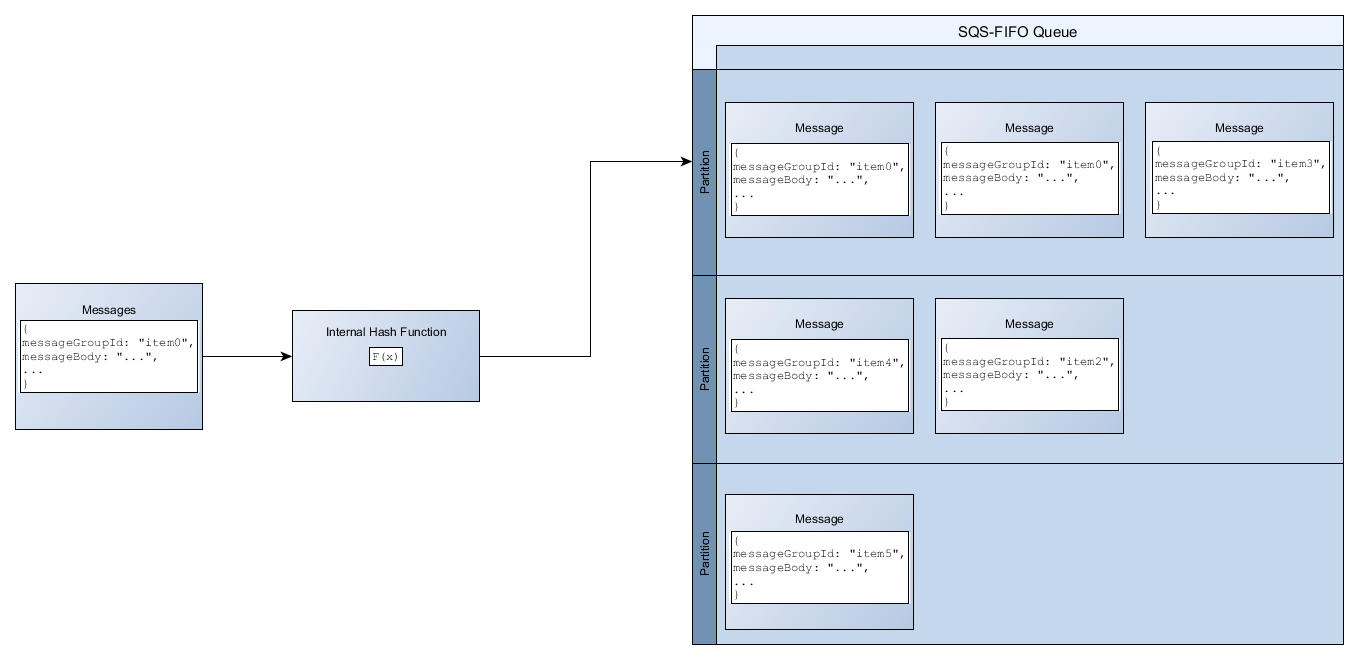
To add a message to a FIFO queue, Amazon SQS uses the value of each message’s message group ID as input to an internal hash function. The output value from the hash function determines which partition stores the message.
The following diagram shows a queue that spans multiple partitions. The queue’s message
group ID is based on item number. Amazon SQS uses its hash function to determine where to store a
new item; in this case, it's based on the hash value of the string item0. Note
that the items are stored in the same order in which they are added to the queue. Each item's
location is determined by the hash value of its message group ID.
Note
Amazon SQS is optimized for uniform distribution of items across a FIFO queue's partitions, regardless of the number of partitions. AWS recommends that you use message group IDs that can have a large number of distinct values.
Optimizing partition utilization
Each partition supports up to 3,000 messages per second with batching, or up to 300 messages per second for send, receive, and delete operations in supported regions. For more information on high throughput message quotas, see Amazon SQS service quotas in the Amazon Web Services General Reference.
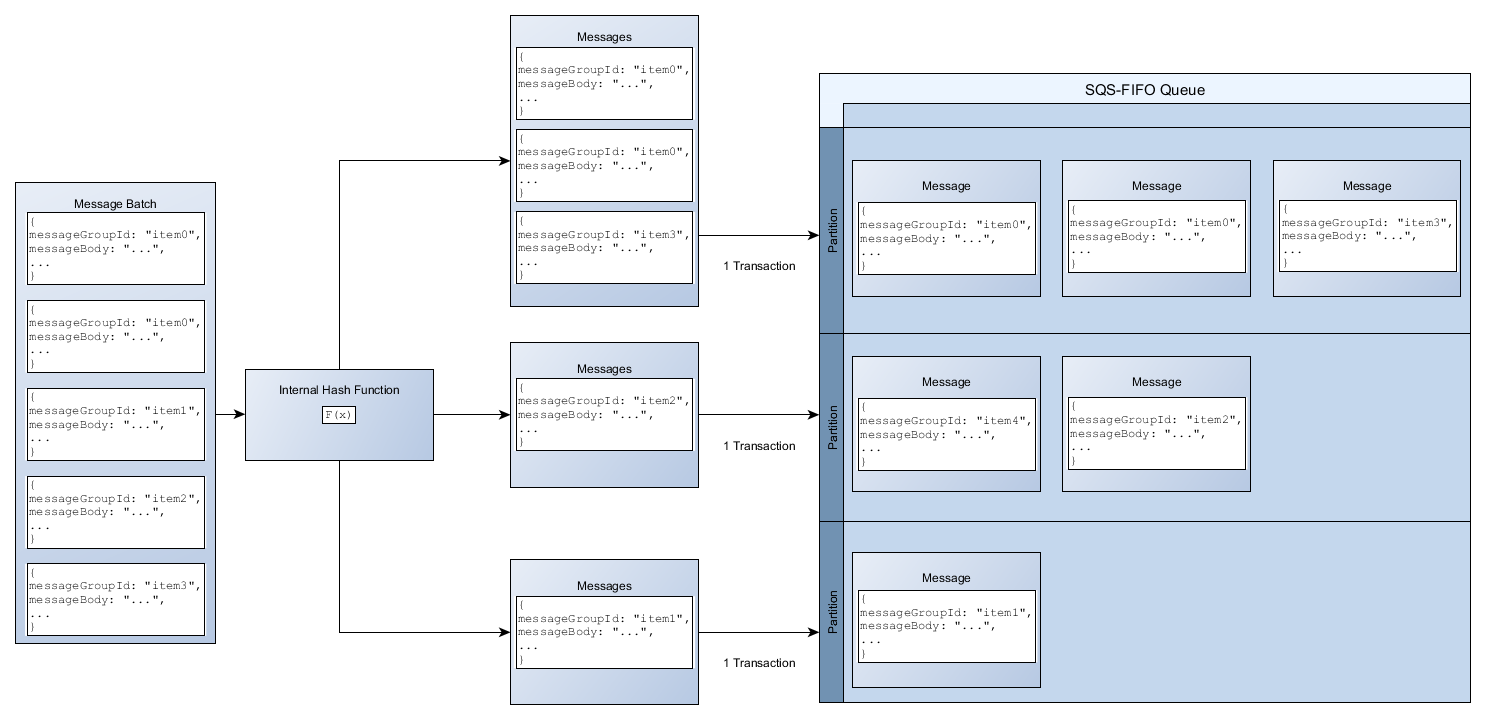
When using batch APIs, each message is routed based on the process described in Distributing data by message group IDs. Messages that are routed to the same partition are grouped and processed in a single transaction.
To optimize partition utilization for the SendMessageBatch API, AWS recommends batching
messages with the same message group IDs when possible.
To optimize partition utilization for the DeleteMessageBatch and
ChangeMessageVisibilityBatch APIs, AWS recommends using
ReceiveMessage requests with the MaxNumberOfMessages parameter set
to 10, and batching the receipt-handles returned by a single ReceiveMessage
request.
In the following example, a batch of messages with various message group IDs is sent. The batch is split into three groups, each of which counts against the quota for the partition.
Note
Amazon SQS only guarantees that messages with the same message group ID's internal hash function are grouped within a batch request. Depending on the output of the internal hash function and the number of partitions, messages with different message group IDs might be grouped. Since the hash function or number of partitions can change at any time, messages that are grouped at one point may not be grouped later.