What is Amazon Elastic Container Service?
Tip
Join our upcoming container workshop series to learn best
practices for Amazon ECS and AWS Fargate. Click
here
Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) is a fully managed container orchestration service that helps you easily deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications. As a fully managed service, Amazon ECS comes with AWS configuration and operational best practices built-in. It's integrated with both AWS tools, such as Amazon Elastic Container Registry, and third-party tools, such as Docker. This integration makes it easier for teams to focus on building the applications, not the environment. You can run and scale your container workloads across AWS Regions in the cloud, and on-premises, without the complexity of managing a control plane.
Terminology and components
There are three layers in Amazon ECS:
-
Capacity - The infrastructure where your containers run
-
Controller - Deploy and manage your applications that run on the containers
-
Provisioning - The tools that you can use to interface with the scheduler to deploy and manage your applications and containers
The following diagram shows the Amazon ECS layers.
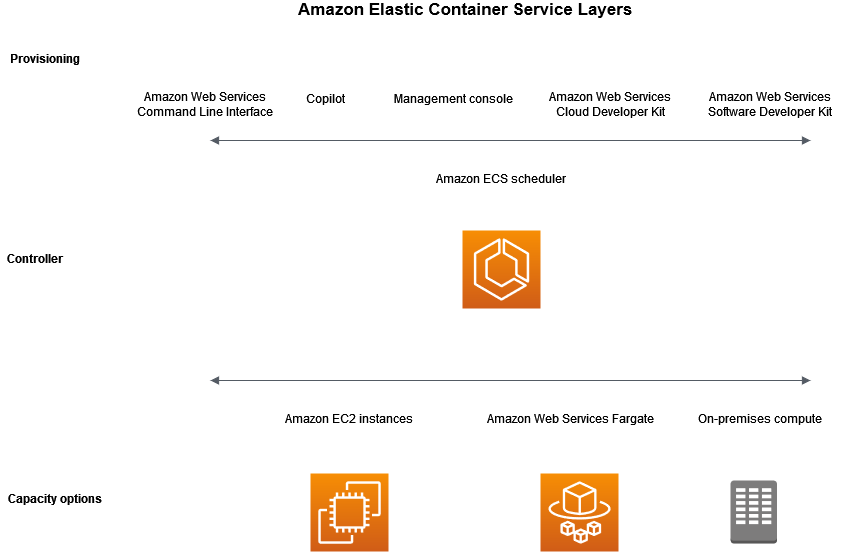
The capacity is the infrastructure where your containers run. The following is an overview of the capacity options:
-
Amazon ECS Managed Instances is a compute option for Amazon ECS that enables you to run containerized workloads on a range of Amazon EC2 instance types while offloading infrastructure management to AWS. With Amazon ECS Managed Instances, you can access specific compute capabilities such as GPU acceleration, specific CPU architectures, high network performance, and specialized instances types, while AWS handles provisioning, patching, scaling, and maintenance of the underlying infrastructure.
-
Amazon EC2 instances in the AWS cloud
You choose the instance type, the number of instances, and manage the capacity.
-
Serverless in the AWS cloud
Fargate is a serverless, pay-as-you-go compute engine. With Fargate you don't need to manage servers, handle capacity planning, or isolate container workloads for security.
-
On-premises virtual machines (VM) or servers
Amazon ECS Anywhere provides support for registering an external instance such as an on-premises server or virtual machine (VM), to your Amazon ECS cluster.
The Amazon ECS scheduler is the software that manages your applications.
Features
Amazon ECS provides the following high-level features:
- Task definition
-
The blueprint for the application.
- Cluster
-
The infrastructure your application runs on.
- Task
-
An application such as a batch job that performs work, and then stops.
- Service
-
A long running stateless application.
- Account Setting
-
Allows access to features.
- Cluster Auto Scaling
-
Amazon ECS manages the scaling of Amazon EC2 instances that are registered to your cluster.
- Service Auto Scaling
-
Amazon ECS increases or decreases the desired number of tasks in your service automatically.
Provisioning
There are multiple options for provisioning Amazon ECS:
-
AWS Management Console — Provides a web interface that you can use to access your Amazon ECS resources.
-
AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) — Provides commands for a broad set of AWS services, including Amazon ECS. It's supported on Windows, Mac, and Linux. For more information, see AWS Command Line Interface
. -
AWS SDKs — Provides language-specific APIs and takes care of many of the connection details. These include calculating signatures, handling request retries, and error handling. For more information, see AWS SDKs
. -
AWS CDK — Provides an open-source software development framework that you can use to model and provision your cloud application resources using familiar programming languages. The AWS CDK provisions your resources in a safe, repeatable manner through AWS CloudFormation.
Pricing
Amazon ECS pricing depends on the capacity option you choose for your containers.
-
Amazon ECS pricing
– Pricing information for Amazon ECS. -
AWS Fargate pricing
– Pricing information for Fargate.
Related services
Services to use with Amazon ECS
You can use other AWS services to help you deploy yours tasks and services on Amazon ECS.
- Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling
-
Helps ensure you have the correct number of Amazon EC2 instances available to handle the load for your application.
- Amazon CloudWatch
-
Monitor your services and tasks.
- Amazon Elastic Container Registry
-
Store and manage container images.
- Elastic Load Balancing
-
Automatically distribute incoming service traffic.
- Amazon GuardDuty
-
Detect potentially unauthorized or malicious use of your container instances and workloads.