Connect Amazon ECS applications to the internet
Most containerized applications have a least some components that need outbound access to the internet. For example, the backend for a mobile app requires outbound access to push notifications.
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud has two main methods for facilitating communication between your VPC and the internet.
Public subnet and internet gateway
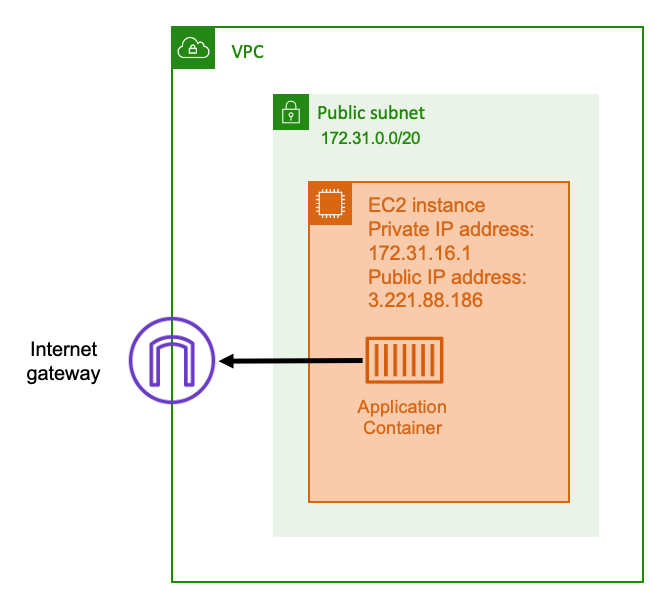
When you use a public subnet that has a route to an internet gateway, your containerized application can run on a host inside a VPC on a public subnet. The host that runs your container is assigned a public IP address. This public IP address is routable from the internet. For more information, see Internet gateways in the Amazon VPC User Guide.
This network architecture facilitates direct communication between the host that runs your application and other hosts on the internet. The communication is bi-directional. This means that not only can you establish an outbound connection to any other host on the internet, but other hosts on the internet might also attempt to connect to your host. Therefore, you should pay close attention to your security group and firewall rules. This ensures that other hosts on the internet can’t open any connections that you don't want to be opened.
For example, if your application runs on Amazon EC2, make sure that port 22 for SSH access is not open. Otherwise, your instance could receive constant SSH connection attempts from malicious bots on the internet. These bots trawl through public IP addresses. After they find an open SSH port, they attempt to brute-force passwords to try to access your instance. Because of this, many organizations limit the usage of public subnets and prefer to have most, if not all, of their resources inside of private subnets.
Using public subnets for networking is suitable for public applications that require large amounts of bandwidth or minimal latency. Applicable use cases include video streaming and gaming services.
This networking approach is supported both when you use Amazon ECS on Amazon EC2 and when you use it on AWS Fargate.
-
Amazon EC2 — You can launch EC2 instances on a public subnet. Amazon ECS uses these EC2 instances as cluster capacity, and any containers that are running on the instances can use the underlying public IP address of the host for outbound networking. This applies to both the
hostandbridgenetwork modes. However, theawsvpcnetwork mode doesn't provide task ENIs with public IP addresses. Therefore, they can’t make direct use of an internet gateway. -
Fargate — When you create your Amazon ECS service, specify public subnets for the networking configuration of your service, and use the Assign public IP address option. Each Fargate task is networked in the public subnet, and has its own public IP address for direct communication with the internet.
Private subnet and NAT gateway

When you use a private subnet and a NAT gateway, you can run your containerized application on a host that's in a private subnet. As such, this host has a private IP address that's routable inside your VPC, but isn't routable from the internet. This means that other hosts inside the VPC can connect to the host using its private IP address, but other hosts on the internet can't make any inbound communications to the host.
With a private subnet, you can use a Network Address Translation (NAT) gateway to allow a host inside a private subnet to connect to the internet. Hosts on the internet receive an inbound connection that appears to be coming from the public IP address of the NAT gateway that's inside a public subnet. The NAT gateway is responsible for serving as a bridge between the internet and the private subnet. This configuration is often preferred for security reasons because it means that your VPC is protected from direct access by attackers on the internet. For more information, see NAT gateways in the Amazon VPC User Guide.
This private networking approach is suitable for scenarios where you want to protect your containers from direct external access. Applicable scenarios include payment processing systems or containers storing user data and passwords. You're charged for creating and using a NAT gateway in your account. NAT gateway hourly usage and data processing rates also apply. For redundancy purposes, you should have a NAT gateway in each Availability Zone. This way, the loss in availability of a single Availability Zone doesn't compromise your outbound connectivity. Because of this, if you have a small workload, it might be more cost effective to use private subnets and NAT gateways.
This networking approach is supported both when using Amazon ECS on Amazon EC2 and when using it on AWS Fargate.
-
Amazon EC2 — You can launch EC2 instances on a private subnet. The containers that run on these EC2 hosts use the underlying hosts networking, and outbound requests go through the NAT gateway.
-
Fargate — When you create your Amazon ECS service, specify private subnets for the networking configuration of your service, and don't use the Assign public IP address option. Each Fargate task is hosted in a private subnet. Its outbound traffic is routed through any NAT gateway that you have associated with that private subnet.