Call an API with an API Gateway Lambda authorizer
Having configured the Lambda authorizer (formerly known as the custom authorizer) and deployed the API, you
should test the API with the Lambda authorizer enabled. For this, you need a REST client, such as cURL or Postman
Note
When calling an authorizer-enabled method, API Gateway does not log the call to CloudWatch if the required token for
the TOKEN authorizer is not set, is null, or is invalidated by the specified Token
validation expression. Similarly, API Gateway does not log the call to CloudWatch if any of the required
identity sources for the REQUEST authorizer are not set, are null, or are empty.
In the following, we show how to use Postman to call or test an API with a Lambda TOKEN
authorizer. The method can be applied to calling an API with a Lambda REQUEST authorizer, if you
specify the required path, header, or query string parameters explicitly.
To call an API with the custom TOKEN authorizer
-
Open Postman, choose the GET method, and paste the API's Invoke URL into the adjacent URL field.
Add the Lambda authorization token header and set the value to
allow. Choose Send.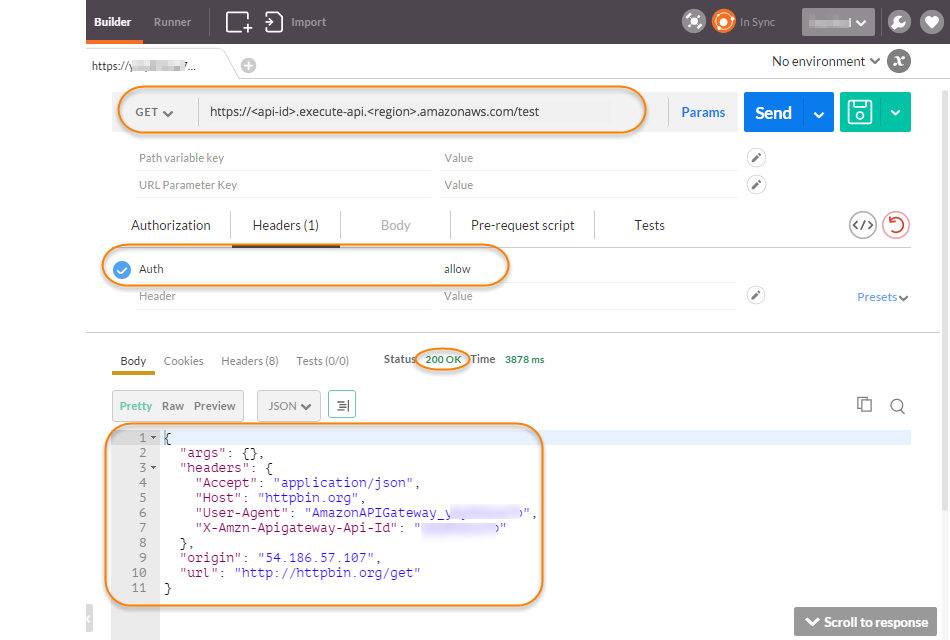
The response shows that the API Gateway Lambda authorizer returns a 200 OK response and successfully authorizes the call to access the HTTP endpoint (http://httpbin.org/get) integrated with the method.
-
Still in Postman, change the Lambda authorization token header value to
deny. Choose Send.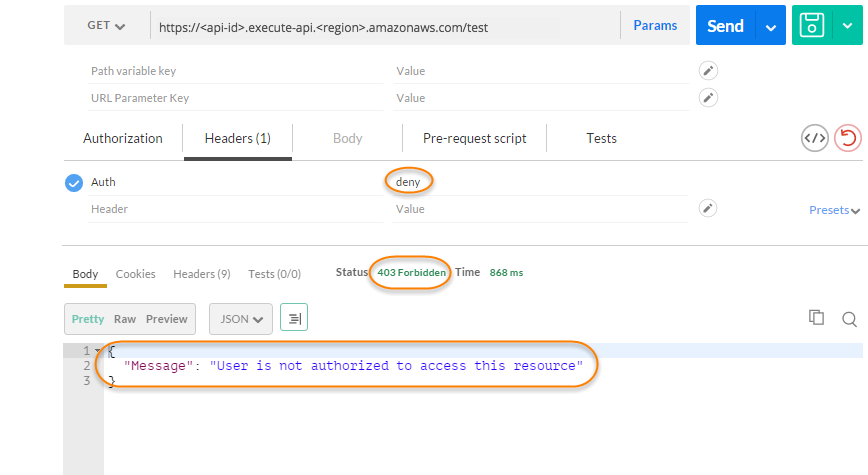
The response shows that the API Gateway Lambda authorizer returns a 403 Forbidden response without authorizing the call to access the HTTP endpoint.
-
In Postman, change the Lambda authorization token header value to
unauthorizedand choose Send.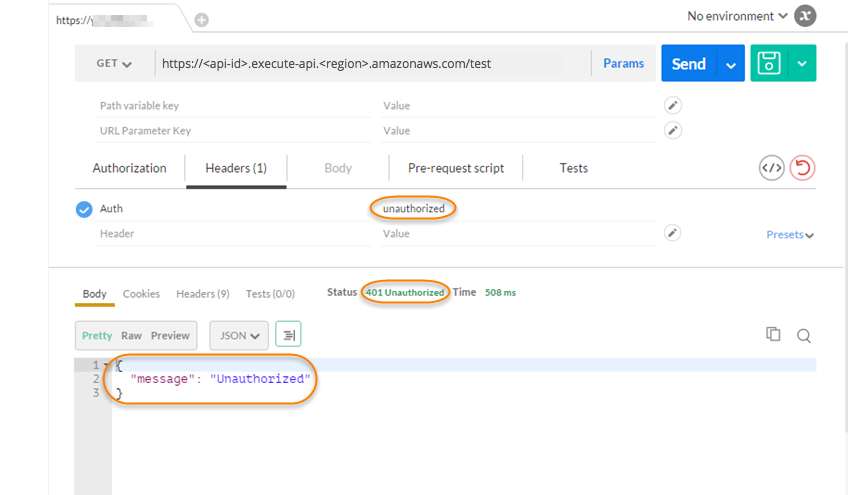
The response shows that API Gateway returns a 401 Unauthorized response without authorizing the call to access the HTTP endpoint.
-
Now, change the Lambda authorization token header value to
fail. Choose Send.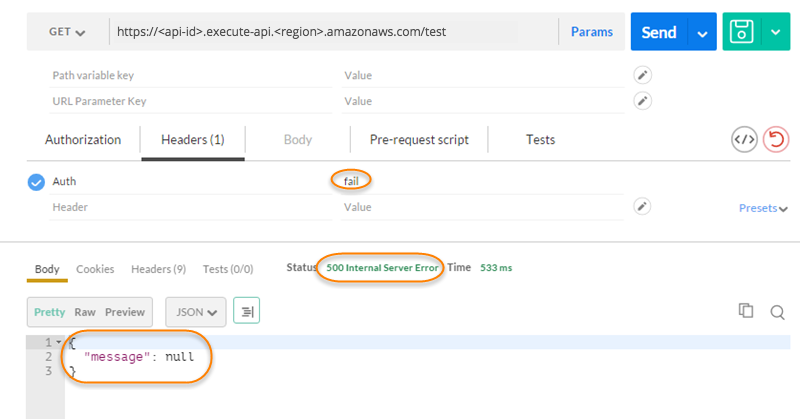
The response shows that API Gateway returns a 500 Internal Server Error response without authorizing the call to access the HTTP endpoint.