Enable federated access to the Athena API
This section discusses federated access that allows a user or client application in your
organization to call Amazon Athena API operations. In this case, your organization's users don't
have direct access to Athena. Instead, you manage user credentials outside of AWS in
Microsoft Active Directory. Active Directory supports SAML 2.0
To authenticate users in this scenario, use the JDBC or ODBC driver with SAML.2.0 support to access Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) 3.0 and enable a client application to call Athena API operations.
For more information about SAML 2.0 support on AWS, see About SAML 2.0 federation in the IAM User Guide.
Note
Federated access to the Athena API is supported for a particular type of identity provider (IdP), the Active Directory Federation Service (ADFS 3.0), which is part of Windows Server. Federated access is not compatible with the IAM Identity Center trusted identity propagation feature. Access is established through the versions of JDBC or ODBC drivers that support SAML 2.0. For information, see Connect to Amazon Athena with JDBC and Connect to Amazon Athena with ODBC.
Topics
Before you begin
Before you begin, complete the following prerequisites:
-
Inside your organization, install and configure the ADFS 3.0 as your IdP.
-
Install and configure the latest available versions of JDBC or ODBC drivers on clients that are used to access Athena. The driver must include support for federated access compatible with SAML 2.0. For information, see Connect to Amazon Athena with JDBC and Connect to Amazon Athena with ODBC.
Understand the authentication process
The following diagram illustrates the authentication process of federated access to the Athena API.
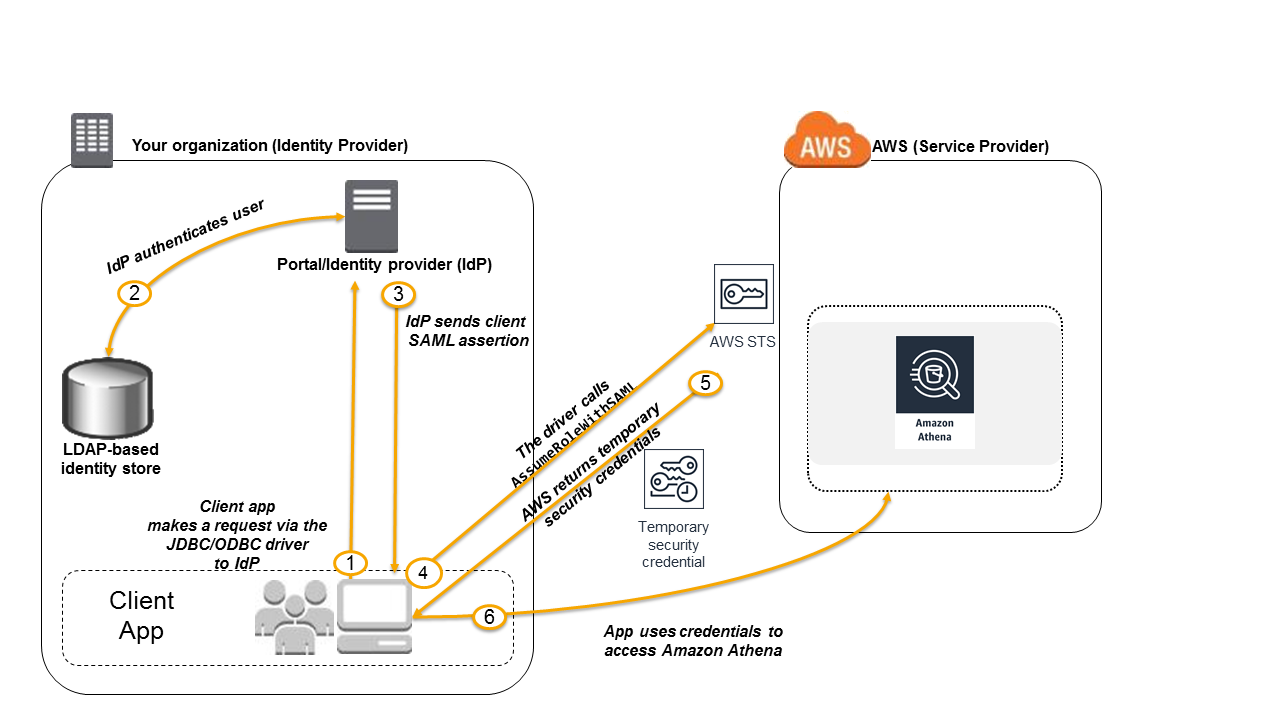
-
A user in your organization uses a client application with the JDBC or ODBC driver to request authentication from your organization's IdP. The IdP is ADFS 3.0.
-
The IdP authenticates the user against Active Directory, which is your organization's Identity Store.
-
The IdP constructs a SAML assertion with information about the user and sends the assertion to the client application via the JDBC or ODBC driver.
-
The JDBC or ODBC driver calls the AWS Security Token Service AssumeRoleWithSAML API operation, passing it the following parameters:
-
The ARN of the SAML provider
-
The ARN of the role to assume
-
The SAML assertion from the IdP
For more information, see AssumeRoleWithSAML, in the AWS Security Token Service API Reference.
-
-
The API response to the client application via the JDBC or ODBC driver includes temporary security credentials.
-
The client application uses the temporary security credentials to call Athena API operations, allowing your users to access Athena API operations.
Procedure: Enable SAML-based federated access to the Athena API
This procedure establishes trust between your organization's IdP and your AWS account to enable SAML-based federated access to the Amazon Athena API operation.
To enable federated access to the Athena API:
-
In your organization, register AWS as a service provider (SP) in your IdP. This process is known as relying party trust. For more information, see Configuring your SAML 2.0 IdP with relying party trust in the IAM User Guide. As part of this task, perform these steps:
-
Obtain the sample SAML metadata document from this URL: https://signin.aws.amazon.com/static/saml-metadata.xml
. -
In your organization's IdP (ADFS), generate an equivalent metadata XML file that describes your IdP as an identity provider to AWS. Your metadata file must include the issuer name, creation date, expiration date, and keys that AWS uses to validate authentication responses (assertions) from your organization.
-
-
In the IAM console, create a SAML identity provider entity. For more information, see Creating SAML identity providers in the IAM User Guide. As part of this step, do the following:
Open the IAM console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/
. -
Upload the SAML metadata document produced by the IdP (ADFS) in Step 1 in this procedure.
-
In the IAM console, create one or more IAM roles for your IdP. For more information, see Creating a role for a third-party Identity Provider (federation) in the IAM User Guide. As part of this step, do the following:
-
In the role's permission policy, list actions that users from your organization are allowed to do in AWS.
-
In the role's trust policy, set the SAML provider entity that you created in Step 2 of this procedure as the principal.
This establishes a trust relationship between your organization and AWS.
-
-
In your organization's IdP (ADFS), define assertions that map users or groups in your organization to the IAM roles. The mapping of users and groups to the IAM roles is also known as a claim rule. Note that different users and groups in your organization might map to different IAM roles.
For information about configuring the mapping in ADFS, see the blog post: Enabling federation to AWS using Windows Active Directory, ADFS, and SAML 2.0
. -
Install and configure the JDBC or ODBC driver with SAML 2.0 support. For information, see Connect to Amazon Athena with JDBC and Connect to Amazon Athena with ODBC.
-
Specify the connection string from your application to the JDBC or ODBC driver. For information about the connection string that your application should use, see the topic "Using the Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) Credentials Provider" in the JDBC Driver Installation and Configuration Guide, or a similar topic in the ODBC Driver Installation and Configuration Guide available as PDF downloads from the Connect to Amazon Athena with JDBC and Connect to Amazon Athena with ODBC topics.
Following is a high-level summary of configuring the connection string to the drivers:
-
In the
AwsCredentialsProviderClass configuration, set thecom.simba.athena.iamsupport.plugin.AdfsCredentialsProviderto indicate that you want to use SAML 2.0 based authentication via ADFS IdP. -
For
idp_host, provide the host name of the ADFS IdP server. -
For
idp_port, provide the port number that the ADFS IdP listens on for the SAML assertion request. -
For
UIDandPWD, provide the AD domain user credentials. When using the driver on Windows, ifUIDandPWDare not provided, the driver attempts to obtain the user credentials of the user logged in to the Windows machine. -
Optionally, set
ssl_insecuretotrue. In this case, the driver does not check the authenticity of the SSL certificate for the ADFS IdP server. Setting totrueis needed if the ADFS IdP's SSL certificate has not been configured to be trusted by the driver. -
To enable mapping of an Active Directory domain user or group to one or more IAM roles (as mentioned in step 4 of this procedure), in the
preferred_rolefor the JDBC or ODBC connection, specify the IAM role (ARN) to assume for the driver connection. Specifying thepreferred_roleis optional, and is useful if the role is not the first role listed in the claim rule.
As a result of this procedure, the following actions occur:
-
The JDBC or ODBC driver calls the AWS STS AssumeRoleWithSAML API, and passes it the assertions, as shown in step 4 of the architecture diagram.
-
AWS makes sure that the request to assume the role comes from the IdP referenced in the SAML provider entity.
-
If the request is successful, the AWS STS AssumeRoleWithSAML API operation returns a set of temporary security credentials, which your client application uses to make signed requests to Athena.
Your application now has information about the current user and can access Athena programmatically.
-