Create a target tracking scaling policy using metric math
Using metric math, you can query multiple CloudWatch metrics and use math expressions to create new time series based on these metrics. You can visualize the resulting time series in the CloudWatch console and add them to dashboards. For more information about metric math, see Using metric math in the Amazon CloudWatch User Guide.
The following considerations apply to metric math expressions:
-
You can query any available CloudWatch metric. Each metric is a unique combination of metric name, namespace, and zero or more dimensions.
-
You can use any arithmetic operator (+ - * / ^), statistical function (such as AVG or SUM), or other function that CloudWatch supports.
-
You can use both metrics and the results of other math expressions in the formulas of the math expression.
-
Any expressions used in a metric specification must eventually return a single time series.
-
You can verify that a metric math expression is valid by using the CloudWatch console or the CloudWatch GetMetricData API.
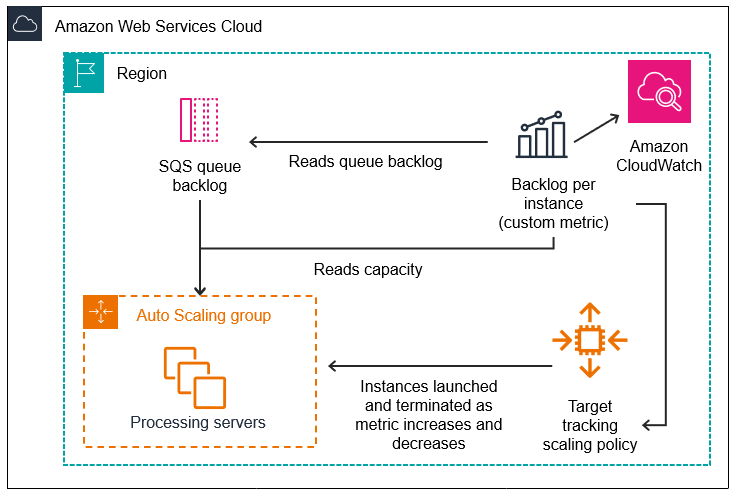
Example: Amazon SQS queue backlog per instance
To calculate the Amazon SQS queue backlog per instance, take the approximate
number of messages available for retrieval from the queue and divide that
number by the Auto Scaling group's running capacity, which is the number of
instances in the InService state. For more information, see
Scaling policy based on Amazon SQS.
The logic for the expression is this:
sum of (number of messages in the queue)/(number of
InService instances)
Then your CloudWatch metric information is the following.
| ID | CloudWatch metric | Statistic | Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| m1 | ApproximateNumberOfMessagesVisible | Sum | 1 minute |
| m2 | GroupInServiceInstances | Average | 1 minute |
Your metric math ID and expression are the following.
| ID | Expression |
|---|---|
| e1 | (m1)/(m2) |
The following diagram illustrates the architecture for this metric:
To use this metric math to create a target tracking scaling policy (AWS CLI)
-
Store the metric math expression as part of a customized metric specification in a JSON file named
config.json.Use the following example to help you get started. Replace each
user input placeholderwith your own information.{ "CustomizedMetricSpecification": { "Metrics": [ { "Label": "Get the queue size (the number of messages waiting to be processed)", "Id": "m1", "MetricStat": { "Metric": { "MetricName": "ApproximateNumberOfMessagesVisible", "Namespace": "AWS/SQS", "Dimensions": [ { "Name": "QueueName", "Value": "my-queue" } ] }, "Stat": "Sum" }, "ReturnData": false }, { "Label": "Get the group size (the number of InService instances)", "Id": "m2", "MetricStat": { "Metric": { "MetricName": "GroupInServiceInstances", "Namespace": "AWS/AutoScaling", "Dimensions": [ { "Name": "AutoScalingGroupName", "Value": "my-asg" } ] }, "Stat": "Average" }, "ReturnData": false }, { "Label": "Calculate the backlog per instance", "Id": "e1", "Expression": "m1 / m2", "ReturnData": true } ] }, "TargetValue":100}For more information, see TargetTrackingConfiguration in the Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling API Reference.
Note
Following are some additional resources that can help you find metric names, namespaces, dimensions, and statistics for CloudWatch metrics:
-
For information about the available metrics for AWS services, see AWS services that publish CloudWatch metrics in the Amazon CloudWatch User Guide.
-
To get the exact metric name, namespace, and dimensions (if applicable) for a CloudWatch metric with the AWS CLI, see list-metrics
.
-
-
To create this policy, run the put-scaling-policy
command using the JSON file as input, as demonstrated in the following example. aws autoscaling put-scaling-policy --policy-namesqs-backlog-target-tracking-scaling-policy\ --auto-scaling-group-namemy-asg--policy-type TargetTrackingScaling \ --target-tracking-configurationfile://config.jsonIf successful, this command returns the policy's Amazon Resource Name (ARN) and the ARNs of the two CloudWatch alarms created on your behalf.
{ "PolicyARN": "arn:aws:autoscaling:us-west-2:123456789012:scalingPolicy:228f02c2-c665-4bfd-aaac-8b04080bea3c:autoScalingGroupName/my-asg:policyName/sqs-backlog-target-tracking-scaling-policy", "Alarms": [ { "AlarmARN": "arn:aws:cloudwatch:us-west-2:123456789012:alarm:TargetTracking-my-asg-AlarmHigh-fc0e4183-23ac-497e-9992-691c9980c38e", "AlarmName": "TargetTracking-my-asg-AlarmHigh-fc0e4183-23ac-497e-9992-691c9980c38e" }, { "AlarmARN": "arn:aws:cloudwatch:us-west-2:123456789012:alarm:TargetTracking-my-asg-AlarmLow-61a39305-ed0c-47af-bd9e-471a352ee1a2", "AlarmName": "TargetTracking-my-asg-AlarmLow-61a39305-ed0c-47af-bd9e-471a352ee1a2" } ] }Note
If this command throws an error, make sure that you have updated the AWS CLI locally to the latest version.