What is AWS Clean Rooms?
AWS Clean Rooms helps you and your partners analyze and collaborate on your collective datasets to gain new insights without revealing underlying data to one another. AWS Clean Rooms is a secure collaboration workspace, where you create your own clean rooms in minutes, and analyze your collective datasets with just a few steps. You choose the partners with whom you want to collaborate, select their datasets, and configure privacy-enhancing controls for those partners.
With AWS Clean Rooms, you can collaborate with thousands of companies already using AWS. Collaboration doesn't require moving data out of AWS or loading it into another cloud services provider. When you run queries or jobs, AWS Clean Rooms reads data from that data's original location and applies built-in analysis rules to help you maintain control over that data.
AWS Clean Rooms provides built-in data access controls and audit support controls that you can configure. These controls include:
-
Analysis rules to restrict SQL queries and provide output constraints.
-
Cryptographic Computing for Clean Rooms to keep data encrypted, even as queries are processed, to comply with stringent data handling policies.
-
Analysis logs to review queries and jobs in AWS Clean Rooms and help support audits.
-
Differential privacy to protect against user-identification attempts. AWS Clean Rooms Differential Privacy is a fully-managed capability that protects the privacy of your users with mathematically-backed techniques and intuitive controls that you can apply in a few steps.
-
AWS Clean Rooms ML to allow two parties to identify similar users in their data without the need to share their data with each other. The first party creates and configures a lookalike model from their training data. Then, seed data is brought to the collaboration to create a lookalike segment that resembles the training data.
The following video explains more about AWS Clean Rooms.
Are you a first-time AWS Clean Rooms user?
If you are a first-time user of AWS Clean Rooms, we recommend that you begin by reading the following sections:
How AWS Clean Rooms works
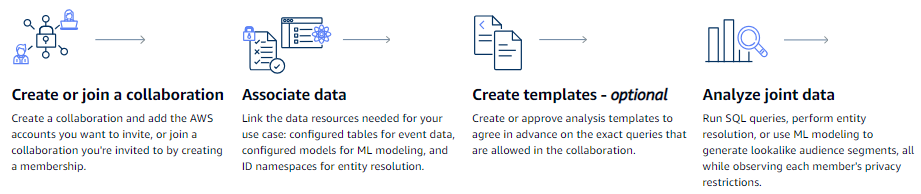
In AWS Clean Rooms, you create a collaboration and add the AWS accounts that you want to invite, or create a membership to join a collaboration that you've been invited to. You then link the data resources needed for your use case: configured tables for event data, configured models for ML modeling, or ID namespaces for entity resolution. You have the option to create or approve analysis templates to agree in advance on the exact queries and jobs that you want to allow in a collaboration. Finally, you analyze the joint data by running SQL queries or PySpark jobs on the configured tables, performing entity resolution in ID mapping tables, or using ML modeling to generate lookalike audience segments.
The following diagram shows how AWS Clean Rooms works.
Related services
AWS services
The following AWS services are related to AWS Clean Rooms:
-
Amazon Athena
Collaboration members can store data that they bring into AWS Clean Rooms as AWS Glue Data Catalog views in Amazon Athena. For more information, see the following topics:
For more information, see the following topics:
Preparing data tables for queries in AWS Clean Rooms
Creating a configured table – Amazon Athena data source
What is Amazon Athena? in the Amazon Athena User Guide
-
AWS CloudFormation
Create the following resources in AWS CloudFormation: collaborations, configured tables, configured table associations, and memberships
For more information, see Creating AWS Clean Rooms resources with AWS CloudFormation.
-
AWS CloudTrail
Use AWS Clean Rooms with CloudTrail logs to enhance your analysis of AWS service activity.
For more information, see Logging AWS Clean Rooms API calls using AWS CloudTrail.
-
AWS Entity Resolution
Use AWS Clean Rooms with AWS Entity Resolution to perform entity resolution.
For more information, see AWS Entity Resolution in AWS Clean Rooms.
-
AWS Glue
Collaboration members can create AWS Glue tables from their data in Amazon S3 for use in AWS Clean Rooms.
For more information, see the following topics:
Preparing data tables for queries in AWS Clean Rooms
What is AWS Glue? in the AWS Glue Developer Guide
-
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3)
Collaboration members can store data that they bring into AWS Clean Rooms in Amazon S3.
For more information, see the following topics:
Preparing data tables for queries in AWS Clean Rooms
Creating a configured table – Amazon S3 data source
What is Amazon S3? in the Amazon Simple Storage Service User Guide
-
AWS Secrets Manager
Collaboration members can create secrets to access and read data stored in Snowflake.
For more information, see the following topics:
Create a service role to read data from Snowflake
Preparing data tables for queries in AWS Clean Rooms
What is AWS Secrets Manager? in the AWS Secrets Manager User Guide
Third-party services
The following third-party service is related to AWS Clean Rooms:
-
Snowflake
Collaboration members can store data that they bring into AWS Clean Rooms in a Snowflake warehouse.
For more information, see the following topics:
Accessing AWS Clean Rooms
You can access AWS Clean Rooms through the following options:
-
Directly through the AWS Clean Rooms console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/cleanrooms/
. -
Programmatically through the AWS Clean Rooms API. For more information, see the AWS Clean Rooms API Reference.
Pricing for AWS Clean Rooms
For pricing information, see AWS Clean Rooms Pricing
Note
For collaboration members who associated data that is stored in Snowflake, you will be charged by their respective data warehouse provider or cloud provider for both data egress and compute each time a query is run that uses data stored in those locations.
Billing for AWS Clean Rooms
AWS Clean Rooms gives the collaboration creator the ability to designate which member is paying for query or job compute costs in the collaboration.
In most cases, the member who can query and the member paying for query compute costs are the same. However, if the member who can query and the member paying for query compute costs are different, then, when the member who can query runs queries against their own membership resource, the membership resource of the member paying for query compute costs is billed.
The member paying for query compute costs doesn't see any event for queries being run in their CloudTrail Event history because the payer is neither the one running the queries nor the owner of the resource against which the queries are run. However, the payer does see charges generated on their membership resource for all queries run by the member who can run queries in the collaboration.
For more information about how to create a collaboration and configure the member paying for query compute costs, see Creating a collaboration.