Amazon VPC across AWS Regions in AWS Device Farm
Device Farm services are located only in the US West (Oregon) (us-west-2) Region. You can use
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) to reach a service in your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud in another AWS Region using Device Farm. If Device Farm and your
service are in the same Region, see Using Amazon VPC endpoint services with Device Farm - Legacy
(not recommended).
There are two ways to access your private services located in a different Region. If you
have services located in one other Region that's not us-west-2, you can use VPC
Peering in order to peer that Region’s VPC to another VPC that is interfacing with Device
Farm in us-west-2. However, if you have services in multiple Regions, a Transit Gateway
will allow you to access those services with a simpler network configuration.
For more information, see VPC peering scenarios in the Amazon VPC Peering Guide.
VPC peering overview for VPCs in different Regions in AWS Device Farm
You can peer any two VPCs in different Regions as long as they have distinct, non-overlapping CIDR blocks.
This ensures that all of the private IP addresses are unique, and it allows all of the resources in the VPCs
to address each other without the need for any form of network address translation (NAT). For more
information about CIDR notation, see RFC
4632
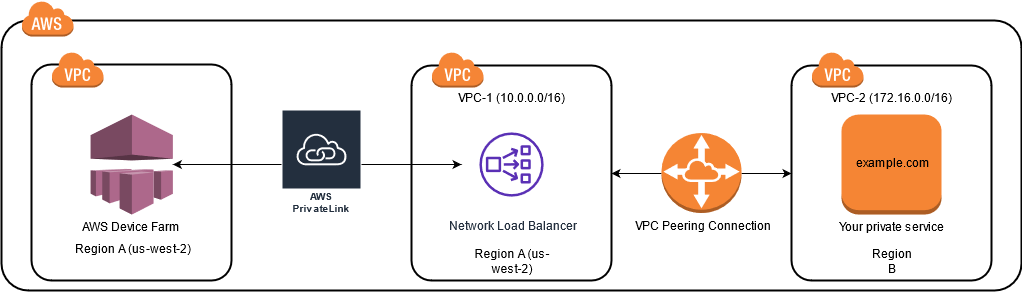
This topic includes a cross-Region example scenario in which Device Farm (referred to as
VPC-1) is located in the US West (Oregon)
(us-west-2) Region. The second VPC in this example (referred to as
VPC-2) is in another Region.
| VPC Component | VPC-1 | VPC-2 |
|---|---|---|
| CIDR | 10.0.0.0/16 | 172.16.0.0/16 |
Important
Establishing a peering connection between two VPCs can change the security posture
of the VPCs. In addition, adding new entries to their route tables can change the
security posture of the resources within the VPCs. It is your responsibility to
implement these configurations in a way that meets your organization's security
requirements. For more information, please see the Shared
responsibility model
The following diagram shows the components in the example and the interactions between these components.
Topics
Prerequisites for using Amazon VPC in AWS Device Farm
This example requires the following:
-
Two VPCs that are configured with subnets containing non-overlapping CIDR blocks.
-
VPC-1 must be in the
us-west-2Region and contain subnets for Availability Zonesus-west-2a,us-west-2b, andus-west-2c.
For more information on creating VPCs and configuring subnets, see Working with VPCs and subnets in the Amazon VPC Peering Guide.
Step 1: Setting up a peering connection between VPC-1 and VPC-2
Establish a peering connection between the two VPCs containing non-overlapping CIDR blocks. To do this, see Create and accept VPC peering connections in the Amazon VPC Peering Guide. Using this topic's cross-Region scenario and the Amazon VPC Peering Guide, the following example peering connection configuration is created:
- Name
-
Device-Farm-Peering-Connection-1 - VPC ID (Requester)
-
vpc-0987654321gfedcba (VPC-2) - Account
-
My account - Region
-
US West (Oregon) (us-west-2) - VPC ID (Accepter)
-
vpc-1234567890abcdefg (VPC-1)
Note
Ensure that you consult your VPC peering connection quotas when establishing any new peering connections. For more information, please see Amazon VPC quotas in the Amazon VPC Peering Guide.
Step 2: Updating the route tables in VPC-1 and VPC-2
After setting up a peering connection, you must establish a destination route between the two VPCs to transfer data between them. To establish this route, you can manually update the route table of VPC-1 to point to the subnet of VPC-2 and vice versa. To do this, see Update your route tables for a VPC peering connection in the Amazon VPC Peering Guide. Using this topic's cross-Region scenario and the Amazon VPC Peering Guide, the following example route table configuration is created:
| VPC component | VPC-1 | VPC-2 |
|---|---|---|
| Route table ID | rtb-1234567890abcdefg | rtb-0987654321gfedcba |
| Local address range | 10.0.0.0/16 | 172.16.0.0/16 |
| Destination address range | 172.16.0.0/16 | 10.0.0.0/16 |
Step 3: Creating a target group
After you set up your destination routes, you can configure a Network Load Balancer in VPC-1 to route requests to VPC-2.
The Network Load Balancer must first contain a target group that contains the IP addresses to which requests are sent.
To create a target group
-
Identify the IP addresses of the service that you want to target in VPC-2.
-
These IP addresses must be members of the subnet used in the peering connection.
-
The targeted IP addresses must be static and immutable. If your service has dynamic IP addresses, consider targeting a static resource (such as a Network Load Balancer) and having that static resource route requests to your true target.
Note
-
If you're targeting one or more stand-alone Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances, open the Amazon EC2 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/
, then choose Instances. -
If you're targeting an Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling group of Amazon EC2 instances, you must associate the Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling group to a Network Load Balancer. For more information, see Attaching a load balancer to your Auto Scaling group in the Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling User Guide.
Then, you can open the Amazon EC2 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/
, and then choose Network Interfaces. From there you can view the IP addresses for each of the Network Load Balancer's network interfaces in each Availability Zone.
-
-
-
Create a target group in VPC-1. To do this, see Create a target group for your Network Load Balancer in the User Guide for Network Load Balancers.
Target groups for services in a different VPC require the following configuration:
-
For Choose a target type, choose IP addresses.
-
For VPC, choose the VPC that will host the load balancer. For the topic example, this will be VPC-1.
-
On the Register targets page, register a target for each IP address in VPC-2.
For Network, choose Other private IP address.
For Availability Zone, choose your desired zones in VPC-1.
For IPv4 address, choose the VPC-2 IP address.
For Ports, choose your ports.
-
Choose Include as pending below. When you're finished specifying addresses, choose Register pending targets.
-
Using this topic's cross-Region scenario and the User Guide for Network Load Balancers, the following values are used in the target group configuration:
- Target type
-
IP addresses - Target group name
-
my-target-group - Protocol/Port
-
TCP : 80 - VPC
-
vpc-1234567890abcdefg (VPC-1) - Network
-
Other private IP address - Availability Zone
-
all - IPv4 address
-
172.16.100.60 - Ports
-
80
Step 4: Creating a Network Load Balancer
Create a Network Load Balancer using the target group described in step 3. To do this, see Creating a Network Load Balancer.
Using this topic's cross-Region scenario, the following values are used in an example Network Load Balancer configuration:
- Load balancer name
-
my-nlb - Scheme
-
Internal - VPC
-
vpc-1234567890abcdefg (VPC-1) - Mapping
-
us-west-2a-subnet-4i23iuufkdiufsloius-west-2b-subnet-7x989pkjj78nmn23jus-west-2c-subnet-0231ndmas12bnnsds - Protocol/Port
-
TCP : 80 - Target Group
-
my-target-group
Step 5: Creating a VPC endpoint service to connect your VPC to Device Farm
You can use the Network Load Balancer to create a VPC endpoint service. Through this VPC endpoint service, Device Farm can connect to your service in VPC-2 without any additional infrastructure, such as an internet gateway, NAT instance, or VPN connection.
To do this, see Creating an Amazon VPC endpoint service.
Step 6: Create a VPC endpoint configuration between your VPC and Device Farm
Now you can establish a private connection between your VPC and Device Farm. You can use Device Farm to test private services without exposing them through the public internet. To do this, see Creating a VPC endpoint configuration in Device Farm.
Using this topic's cross-Region scenario, the following values are used in an example VPC endpoint configuration:
- Name
-
My VPCE Configuration - VPCE service name
-
com.amazonaws.vpce.us-west-2.vpce-svc-1234567890abcdefg - Service DNS name
-
devicefarm.com
Step 7: Creating a test run to use the VPC endpoint configuration
You can create test runs that use the VPC endpoint configuration described in step 6. For more information, see Creating a test run in Device Farm or Creating a session.
Creating a scalable network with Transit Gateway
To create a scalable network using more than two VPCs, you can use Transit Gateway to act as a network transit hub to interconnect your VPCs and on-premises networks. To configure a VPC in the same region as Device Farm to use a Transit Gateway, you can follow the Amazon VPC endpoint services with Device Farm guide to target resources in another region based on their private IP addresses.
For more information about Transit Gateway, see What is a transit gateway? in the Amazon VPC Transit Gateways Guide.