Creating DB instances for Amazon RDS on AWS Outposts
Creating an Amazon RDS on AWS Outposts DB instance is similar to creating an Amazon RDS DB instance in the AWS Cloud. However, make sure that you specify a DB subnet group that is associated with your Outpost.
A virtual private cloud (VPC) based on the Amazon VPC service can span all of the Availability Zones in an AWS Region. You can extend any VPC in the AWS Region to your Outpost by adding an Outpost subnet. To add an Outpost subnet to a VPC, specify the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the Outpost when you create the subnet.
Before you create an RDS on Outposts DB instance, you can create a DB subnet group that includes one subnet that is associated with your Outpost. When you create an RDS on Outposts DB instance, specify this DB subnet group. You can also choose to create a new DB subnet group when you create your DB instance.
For information about configuring AWS Outposts, see the AWS Outposts User Guide.
Creating a DB subnet group
Create a DB subnet group with one subnet that is associated with your Outpost.
You can also create a new DB subnet group for the Outpost when you create your DB instance. If you want to do so, then skip this procedure.
Note
To create a DB subnet group for the AWS Cloud, specify at least two subnets.
To create a DB subnet group for your Outpost
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/
. -
In the upper-right corner of the Amazon RDS console, choose the AWS Region where you want to create the DB subnet group.
-
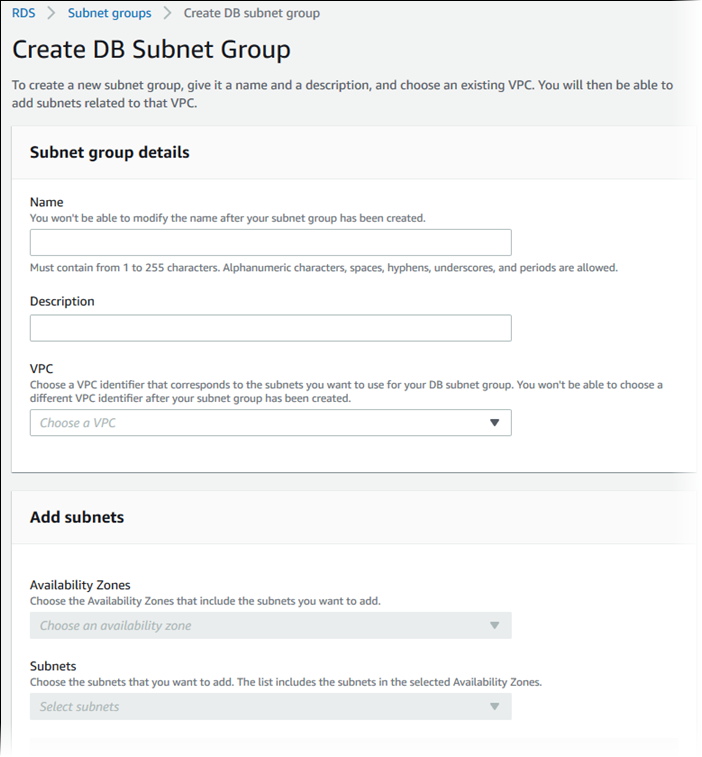
Choose Subnet groups, and then choose Create DB Subnet Group.
The Create DB subnet group page appears.
-
For Name, choose the name of the DB subnet group.
-
For Description, choose a description for the DB subnet group.
-
For VPC, choose the VPC that you're creating the DB subnet group for.
-
For Availability Zones, choose the Availability Zone for your Outpost.
-
For Subnets, choose the subnet for use by RDS on Outposts.
-
Choose Create to create the DB subnet group.
Creating the RDS on Outposts DB instance
Create the DB instance, and choose the Outpost for your DB instance.
To create an RDS on Outposts DB instance using the console
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/
. -
In the upper-right corner of the Amazon RDS console, choose the AWS Region where the Outpost on which you want to create the DB instance is attached.
-
In the navigation pane, choose Databases.
-
Choose Create database.
The AWS Management Console detects available Outposts that you have configured and presents the On-premises option in the Database location section.
Note
If you haven't configured any Outposts, either the Database location section doesn't appear or the RDS on Outposts option isn't available in the Choose an on-premises creation method section.
-
For Database location, choose On-premises.
-
For On-premises creation method, choose RDS on Outposts.
-
Specify your settings for Outposts Connectivity. These settings are for the Outpost that uses the VPC that has the DB subnet group for your DB instance. Your VPC must be based on the Amazon VPC service.
-
For Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), choose the VPC that contains the DB subnet group for your DB instance.
-
For VPC security group, choose the Amazon VPC security group for your DB instance.
-
For DB subnet group, choose the DB subnet group for your DB instance.
You can choose an existing DB subnet group that's associated with the Outpost—for example, if you performed the procedure in Creating a DB subnet group.
You can also create a new DB subnet group for the Outpost.
-
-
For Multi-AZ deployment, choose Create a standby instance (recommended for production usage) to create a standby DB instance in another Outpost.
Note
This option isn't available for Microsoft SQL Server.
If you choose to create a Multi-AZ deployment, you can't store backups on your Outpost.
-
Under Backup, do the following:
-
For Backup target, choose one of the following:
-
AWS Cloud to store automated backups and manual snapshots in the parent AWS Region.
-
Outposts (on-premises) to create local backups.
Note
To store backups on your Outpost, your Outpost must have Amazon S3 capability. For more information, see Amazon S3 on Outposts
. Local backups aren't supported for Multi-AZ deployments or read replicas.
-
-
Choose Enable automated backups to create point-in-time snapshots of your DB instance.
If you turn on automated backups, then you can choose values for Backup retention period and Backup window, or leave the default values.
-
-
Specify other DB instance settings as needed.
For information about each setting when creating a DB instance, see Settings for DB instances.
-
Choose Create database.
The Databases page appears. A banner tells you that your DB instance is being created, and displays the View credential details button.
Viewing DB instance details
After you create your DB instance, you can view credentials and other details for it.
To view DB instance details
-
To view the master user name and password for the DB instance, choose View credential details on the Databases page.
You can connect to the DB instance as the master user by using these credentials.
Important
You can't view the master user password again. If you don't record it, you might have to change it. To change the master user password after the DB instance is available, modify the DB instance. For more information about modifying a DB instance, see Modifying an Amazon RDS DB instance.
-
Choose the name of the new DB instance on the Databases page.
On the RDS console, the details for the new DB instance appear. The DB instance has a status of Creating until the DB instance is created and ready for use. When the state changes to Available, you can connect to the DB instance. Depending on the DB instance class and storage allocated, it can take several minutes for the new DB instance to be available.
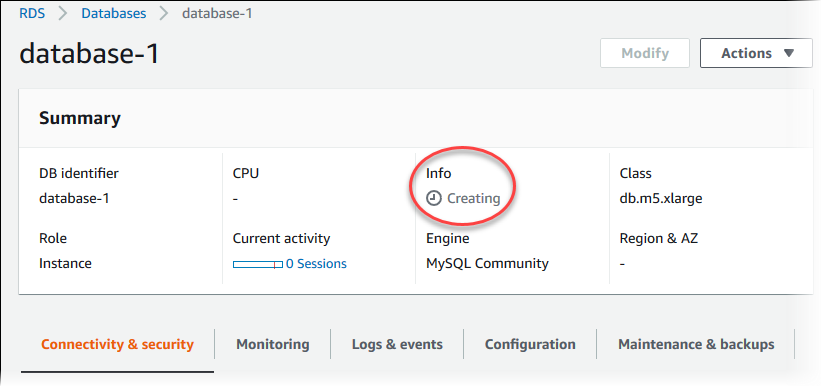
After the DB instance is available, you can manage it the same way that you manage RDS DB instances in the AWS Cloud.
Before you create a new DB instance in an Outpost with the AWS CLI, first create a DB subnet group for use by RDS on Outposts.
To create a DB subnet group for your Outpost
-
Use the create-db-subnet-group command. For
--subnet-ids, specify the subnet group in the Outpost for use by RDS on Outposts.For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds create-db-subnet-group \ --db-subnet-group-namemyoutpostdbsubnetgr\ --db-subnet-group-description"DB subnet group for RDS on Outposts"\ --subnet-idssubnet-abc123For Windows:
aws rds create-db-subnet-group ^ --db-subnet-group-namemyoutpostdbsubnetgr^ --db-subnet-group-description"DB subnet group for RDS on Outposts"^ --subnet-idssubnet-abc123
To create an RDS on Outposts DB instance using the AWS CLI
-
Use the create-db-instance command. Specify an Availability Zone for the Outpost, an Amazon VPC security group associated with the Outpost, and the DB subnet group you created for the Outpost. You can include the following options:
-
--db-instance-identifier -
--db-instance-class -
--engine– The database engine. Use one of the following values:-
MySQL – Specify
mysql. -
PostgreSQL – Specify
postgres. -
Microsoft SQL Server – Specify
sqlserver-ee,sqlserver-se, orsqlserver-web.
-
-
--availability-zone -
--vpc-security-group-ids -
--db-subnet-group-name -
--allocated-storage -
--max-allocated-storage -
--master-username -
--master-user-password -
--multi-az | --no-multi-az– (Optional) Whether to create a standby DB instance in a different Availability Zone. The default is--no-multi-az.The
--multi-azoption isn't available for SQL Server. -
--backup-retention-period -
--backup-target– (Optional) Where to store automated backups and manual snapshots. Use one of the following values:-
outposts– Store them locally on your Outpost. -
region– Store them in the parent AWS Region. This is the default value.
If you use the
--multi-azoption, you can't useoutpostsfor--backup-target. In addition, the DB instance can't have read replicas if you useoutpostsfor--backup-target. -
-
--storage-encrypted -
--kms-key-id
-
The following example creates a MySQL DB instance named myoutpostdbinstance with backups stored on
your Outpost.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds create-db-instance \ --db-instance-identifiermyoutpostdbinstance\ --engine-version8.0.17\ --db-instance-classdb.m5.large\ --enginemysql\ --availability-zoneus-east-1d\ --vpc-security-group-idsoutpost-sg\ --db-subnet-group-namemyoutpostdbsubnetgr\ --allocated-storage100\ --max-allocated-storage1000\ --master-usernamemasterawsuser\ --manage-master-user-password \ --backup-retention-period3\ --backup-targetoutposts\ --storage-encrypted \ --kms-key-idmykey
For Windows:
aws rds create-db-instance ^ --db-instance-identifiermyoutpostdbinstance^ --engine-version8.0.17^ --db-instance-classdb.m5.large^ --enginemysql^ --availability-zoneus-east-1d^ --vpc-security-group-idsoutpost-sg^ --db-subnet-group-namemyoutpostdbsubnetgr^ --allocated-storage100^ --max-allocated-storage1000^ --master-usernamemasterawsuser^ --manage-master-user-password ^ --backup-retention-period3^ --backup-targetoutposts^ --storage-encrypted ^ --kms-key-idmykey
For information about each setting when creating a DB instance, see Settings for DB instances.
To create a new DB instance in an Outpost with the RDS API, first create a DB
subnet group for use by RDS on Outposts by calling the
CreateDBSubnetGroup operation.
For SubnetIds, specify the subnet group in the Outpost for use by RDS on Outposts.
Next, call the CreateDBInstance operation with the following parameters. Specify an Availability Zone for the Outpost, an Amazon VPC security group associated with the Outpost, and the DB subnet group you created for the Outpost.
-
AllocatedStorage -
AvailabilityZone -
BackupRetentionPeriod -
BackupTargetIf you are creating a Multi-AZ DB instance deployment, you can't use
outpostsforBackupTarget. In addition, the DB instance can't have read replicas if you useoutpostsforBackupTarget. -
DBInstanceClass -
DBInstanceIdentifier -
VpcSecurityGroupIds -
DBSubnetGroupName -
Engine -
EngineVersion -
MasterUsername -
MasterUserPassword -
MaxAllocatedStorage(optional) -
MultiAZ(optional) -
StorageEncrypted -
KmsKeyID
For information about each setting when creating a DB instance, see Settings for DB instances.