What is FreeRTOS?
Important
This is an archived version of the FreeRTOS User Guide for use with FreeRTOS release 202012.00. For the latest version of this document, see the FreeRTOS User Guide.
Developed in partnership with the world's leading chip companies over a 15-year period, and now downloaded every 175 seconds, FreeRTOS is a market-leading real-time operating system (RTOS) for microcontrollers and small microprocessors. Distributed freely under the MIT open source license, FreeRTOS includes a kernel and a growing set of libraries suitable for use across all industry sectors. FreeRTOS is built with an emphasis on reliability and ease of use.
FreeRTOS includes libraries for connectivity, security, and over-the-air (OTA) updates. FreeRTOS also
includes demo applications that show FreeRTOS features on qualified boards
FreeRTOS is an open-source project. You can download the source code, contribute changes or
enhancements, or report issues on the GitHub site at
https://github.com/aws/amazon-freertos
We also welcome contributions to the FreeRTOS documentation (FreeRTOS User
Guide, FreeRTOS Porting Guide, and FreeRTOS Qualification
Guide). The markdown source for the documentation is available at https://github.com/awsdocs/aws-freertos-docs
Downloading FreeRTOS source code
You can clone or download FreeRTOS from GitHub
FreeRTOS versioning
The FreeRTOS kernel and components are released individually and use semantic versioning. Integrated FreeRTOS releases are made periodically. All releases use date-based versioning with the format YYYYMM.NN, where:
-
Y represents the year.
-
M represents the month.
-
N represents the release order within the designated month (00 being the first release).
For example, a second release in July 2021 would be 202107.01.
Previously, FreeRTOS releases used semantic versioning for major releases. Although it has moved to date-based versioning (FreeRTOS 1.4.8 updated to FreeRTOS AWS Reference Integrations 201906.00), the FreeRTOS kernel and each individual FreeRTOS library still retain semantic versioning. In semantic versioning, the version number itself (X.Y.Z) indicates whether the release is a major, minor, or point release. You can use the semantic version of a library to assess the scope and impact of a new release on your application.
LTS releases are maintained differently than other release types. Major and minor releases are frequently updated with new features in addition to defect resolutions. LTS releases are only updated with changes to address critical defects and security vulnerabilities. No new features are introduced in a given LTS release after launch. They are maintained for at least three calendar years after release, and provide device manufacturers the option to use a stable baseline as opposed to a more dynamic baseline represented by major and minor releases.
FreeRTOS architecture
FreeRTOS is typically flashed to devices as a single compiled image with all of the components required for device applications. This image combines functionality for the applications written by the embedded developer, the software libraries provided by Amazon, the FreeRTOS kernel, and drivers and board support packages (BSPs) for the hardware platform. Independent of the individual microcontroller being used, embedded application developers can expect the same standardized interfaces to the FreeRTOS kernel and all FreeRTOS software libraries.
FreeRTOS-qualified hardware platforms
The following hardware platforms are qualified for FreeRTOS:
-
Microsoft Windows 7 or later, with at least a dual core and a hard-wired Ethernet connection
Qualified devices are also listed on the
AWS Partner Device Catalog
For information about qualifying a new device, see the FreeRTOS Qualification Guide.
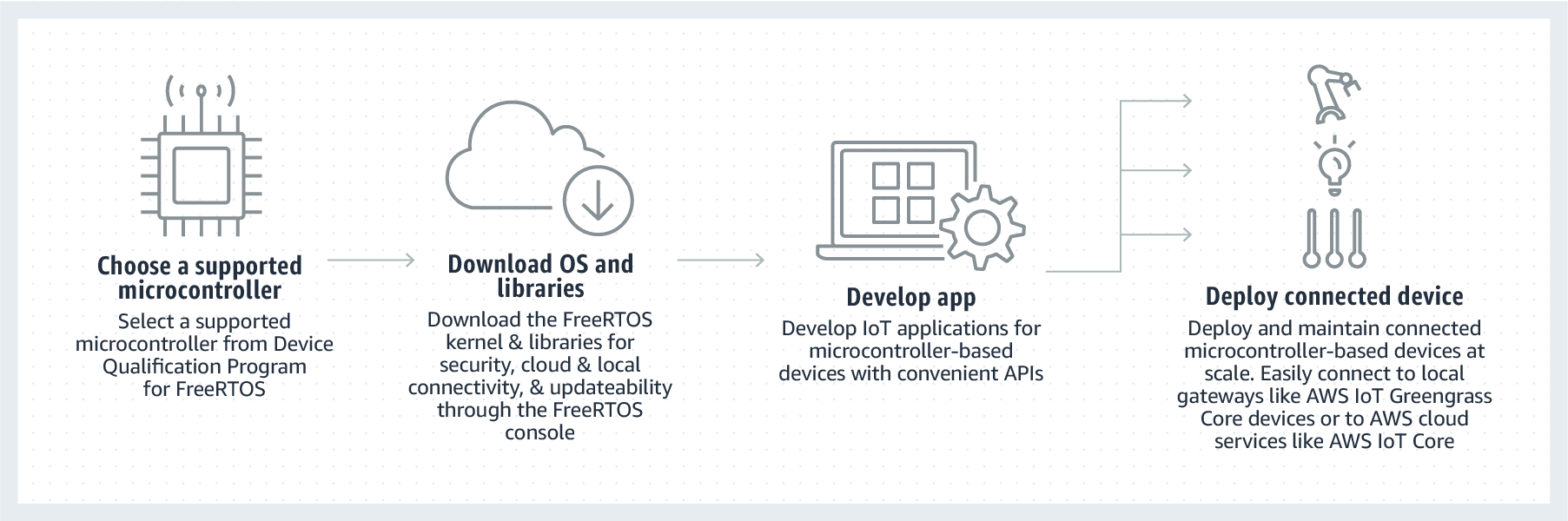
Development workflow
You start development by downloading FreeRTOS. You unzip the package and import it into your IDE. You can then develop an application on your selected hardware platform and manufacture and deploy these devices using the development process appropriate for your device. Deployed devices can connect to the AWS IoT service or AWS IoT Greengrass as part of a complete IoT solution.
Additional resources
These resources might be helpful to you.
-
Additional FreeRTOS Documentation
is available on freertos.org including the FreeRTOS v10.0.0 Reference Manual . -
For questions about FreeRTOS for the FreeRTOS engineering team, you can open an issue on the FreeRTOS GitHub page
. -
For technical questions about FreeRTOS visit the FreeRTOS Community Forums
. -
For more information about connecting devices to AWS IoT, see the AWS IoT Core Developer Guide and the chapter on Device Provisioning in that guide.
-
For technical support for AWS, visit the AWS Support Center
. -
For questions about AWS billing, account services, events, abuse, or other issues with AWS, visit the Contact Us
page.