Joining an Amazon FSx file system to a self-managed Microsoft Active Directory domain
When you create a new FSx for Windows File Server file system, you can configure Microsoft Active Directory integration so that it joins to your self-managed Microsoft Active Directory domain. To do this, provide the following information for your Microsoft Active Directory:
-
The fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of your on-premises Microsoft Active Directory directory.
Note
Amazon FSx currently does not support Single Label Domain (SLD) domains.
-
The IP addresses of the DNS servers for your domain.
-
Credentials for an Active Directory service account that Amazon FSx uses to join the file system to your domain. You can provide these as either:
-
Option 1: AWS Secrets Manager secret ARN - The secret containing the username and password for a service account on your Active Directory domain. For more information, see Storing Active Directory credentials using AWS Secrets Manager.
-
Option 2: Plaintext credentials
-
Service account username – The user name of the service account in your existing Microsoft Active Directory. Don't include a domain prefix or suffix. For example, for
EXAMPLE\ADMIN, use onlyADMIN. -
Service account password – The password for the service account.
-
-
Optionally, you can also specify the following:
-
A specific Organizational Unit (OU) within the domain that you want your Amazon FSx file system to join to.
-
The name of the domain group whose members are granted administrative privileges for the Amazon FSx file system. The domain group name you provide must be unique in your Active Directory.
After you specify this information, Amazon FSx joins your new file system to your self-managed Active Directory domain using the service account that you provided.
Important
Amazon FSx only registers DNS records for a file system if the Active Directory domain that you are joining it to is using Microsoft DNS as the default DNS. If you are using a third-party DNS, you will need to manually setup DNS entries for your Amazon FSx file systems after you create your file system. For more information on choosing the correct IP addresses to use for the file system, see Getting the correct file system IP addresses to use for manual DNS entries.
Before you begin
Make sure that you have completed the Prerequisites detailed in Using a self-managed Microsoft Active Directory.
-
Open the Amazon FSx console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/fsx/
. -
On the dashboard, choose Create file system to start the file system creation wizard.
Choose FSx for Windows File Server and then choose Next. The Create file system page appears.
-
Provide a name for your file system. You can use a maximum of 256 Unicode letters, white space, and numbers, plus the special characters + - = . _ : /
-
For Storage capacity, enter the storage capacity of your file system, in GiB. If you're using SSD storage, enter any whole number in the range of 32–65,536. If you're using HDD storage, enter any whole number in the range of 2,000–65,536. You can increase the amount of storage capacity as needed at any time after you create the file system. For more information, see Managing storage capacity.
-
Keep Throughput capacity at its default setting. Throughput capacity is the sustained speed at which the file server that hosts your file system can serve data. The Recommended throughput capacity setting is based on the amount of storage capacity you choose. If you need more than the recommended throughput capacity, choose Specify throughput capacity, and then choose a value. For more information, see FSx for Windows File Server performance.
You can modify the throughput capacity as needed at any time after you create the file system. For more information, see Managing throughput capacity.
-
Choose the VPC that you want to associate with your file system. For the purposes of this getting started exercise, choose the same VPC as for your Directory Service directory and Amazon EC2 instance.
-
Choose any value for Availability Zones and Subnet.
-
For VPC security groups, the default security group for your default Amazon VPC is already added to your file system in the console. Please ensure that the security group and the VPC Network ACLs for the subnet(s) where you're creating your FSx file system allow traffic on the ports and in the directions shown in the following diagram.
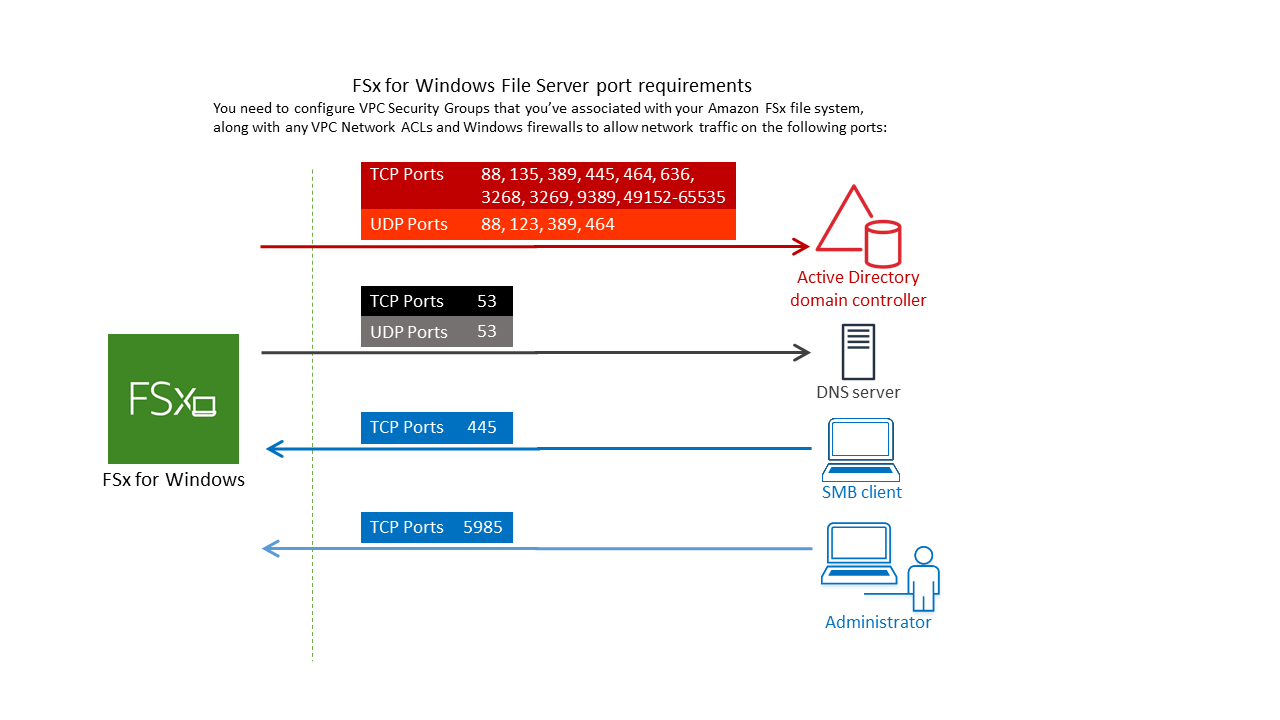
The following table identifies the role of each port.
Protocol
Ports
Role
TCP/UDP
53
Domain Name System (DNS)
TCP/UDP
88
Kerberos authentication
TCP/UDP
464
Change/Set password
TCP/UDP
389
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
UDP 123 Network Time Protocol (NTP)
TCP 135 Distributed Computing Environment / End Point Mapper (DCE / EPMAP)
TCP
445
Directory Services SMB file sharing
TCP
636
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol over TLS/SSL (LDAPS)
TCP
3268
Microsoft Global Catalog
TCP
3269
Microsoft Global Catalog over SSL
TCP
5985
WinRM 2.0 (Microsoft Windows Remote Management)
TCP
9389
Microsoft Active Directory DS Web Services, PowerShell
TCP
49152 - 65535
Ephemeral ports for RPC
Important
Allowing outbound traffic on TCP port 9389 is required for Single-AZ 2 and all Multi-AZ file system deployments.
Note
If you're using VPC network ACLs, you must also allow outbound traffic on dynamic ports (49152-65535) from your FSx file system.
-
Outbound rules to allow all traffic to the IP addresses associated with the DNS servers and domain controllers for your self-managed Microsoft Active Directory domain. For more information, see Microsoft's documentation on configuring your firewall for Active Directory communication
. -
Ensure that these traffic rules are also mirrored on the firewalls that apply to each of the Active Directory domain controllers, DNS servers, FSx clients and FSx administrators.
Note
If you have Active Directory sites defined, you must ensure that the subnet(s) in the VPC associated with your Amazon FSx file system are defined in an Active Directory site, and that no conflicts exist between the subnet(s) in your VPC and the subnets in your other sites. You can view and change these settings using the Active Directory Sites and Services MMC snap-in.
Important
While Amazon VPC security groups require ports to be opened only in the direction that network traffic is initiated, most Windows firewalls and VPC network ACLs require ports to be open in both directions.
-
-
For Windows authentication, choose Self-managed Microsoft Active Directory.
-
Enter a value for Fully qualified domain name for the self-managed Microsoft Active Directory directory.
Note
Domain name must not be in the Single Label Domain (SLD) format. Amazon FSx currently does not support SLD domains.
Important
For Single-AZ 2 and all Multi-AZ file systems, the Active Directory domain name cannot exceed 47 characters.
-
Enter a value for Organizational Unit for the self-managed Microsoft Active Directory directory.
Note
Ensure that the service account you provided has permissions delegated to the OU that you specify here or to the default OU if you don’t specify one.
-
Enter at least one, and no more than two, values for DNS Server IP Addresses for the self-managed Microsoft Active Directory directory.
-
Service account credentials – Choose how to provide your service account credentials:
-
Option 1: AWS Secrets Manager secret ARN - The secret containing the username and password for a service account on your Active Directory domain. For more information, see Storing Active Directory credentials using AWS Secrets Manager.
-
Option 2: Plaintext credentials
-
Service account username – The user name of the service account in your existing Microsoft Active Directory. Don't include a domain prefix or suffix. For example, for
EXAMPLE\ADMIN, use onlyADMIN. -
Service account password – The password for the service account.
Confirm password – The password for the service account.
Important
DO NOT include a domain prefix (
corp.com\ServiceAcct) or domain suffix (ServiceAcct@corp.com) when entering the Service account username.DO NOT use the Distinguished Name (DN) when entering the Service account username (
CN=ServiceAcct,OU=example,DC=corp,DC=com). -
-
-
For Delegated file system administrators group, specify the
Domain Adminsgroup or a custom delegated file system administrators group (if you've created one). The group you specify should have the delegated authority to perform administrative tasks on your file system. If you don't provide a value, Amazon FSx uses the BuiltinDomain Adminsgroup. Note that Amazon FSx does not support having aDelegated file system administrators group(either theDomain Adminsgroup or a custom group you specify) that is located in the Builtin container.Important
If you do not provide a Delegated file system administrators group, by default Amazon FSx attempts to use the Builtin
Domain Adminsgroup in your Active Directory domain. If the name of this Builtin group has been changed or if you’re using a different group for domain administration, you must provide that name for the group here.Important
DO NOT include a domain prefix (corp.com\FSxAdmins) or domain suffix (FSxAdmins@corp.com) when providing the group name parameter.
DO NOT use the Distinguished Name (DN) for the group. An example of a distinguished name is CN=FSxAdmins,OU=example,DC=corp,DC=com.
The following example creates an FSx for Windows File Server file system with a
SelfManagedActiveDirectoryConfiguration in the us-east-2 Availability
Zone.
aws fsx --region us-east-2 \ create-file-system \ --file-system-type WINDOWS \ --storage-capacity 300 \ --security-group-idssecurity-group-id\ --subnet-idssubnet-id\ --windows-configuration SelfManagedActiveDirectoryConfiguration='{DomainName="corp.example.com", \ OrganizationalUnitDistinguishedName="OU=FileSystems,DC=corp,DC=example,DC=com",FileSystemAdministratorsGroup="FSxAdmins", \ UserName="FSxService",Password="password", \ DnsIps=["10.0.1.18"]}',ThroughputCapacity=8
Important
Do not move computer objects that Amazon FSx creates in the OU after your file system is created. Doing so will cause your file system to become misconfigured.