Game client/server interactions with Amazon GameLift Servers
The components in your Amazon GameLift Servers hosting solution interact with each other in specific ways to run game sessions in response to player demand. This topic describes how components communicate with each other when your game server is hosted on Amazon GameLift Servers managed EC2 fleets, self-managed Amazon GameLift Servers Anywhere fleets, or a hybrid solution.
Hosting solution components include a game server, the Amazon GameLift Servers service, a client-side backend service, and a game client. The game server uses the Amazon GameLift Servers server SDK to interact with the Amazon GameLift Servers service. The backend service uses the Amazon GameLift Servers service API (part of the AWS SDK) to interact with the service on behalf of the game client. When joining a game session, the game client connects directly to a game session using the game session's unique IP address and port number.
Interactions diagram
The following diagram illustrates how your game hosting components interact so that the Amazon GameLift Servers service can track the status of game server availability and start game sessions in response to player demands.
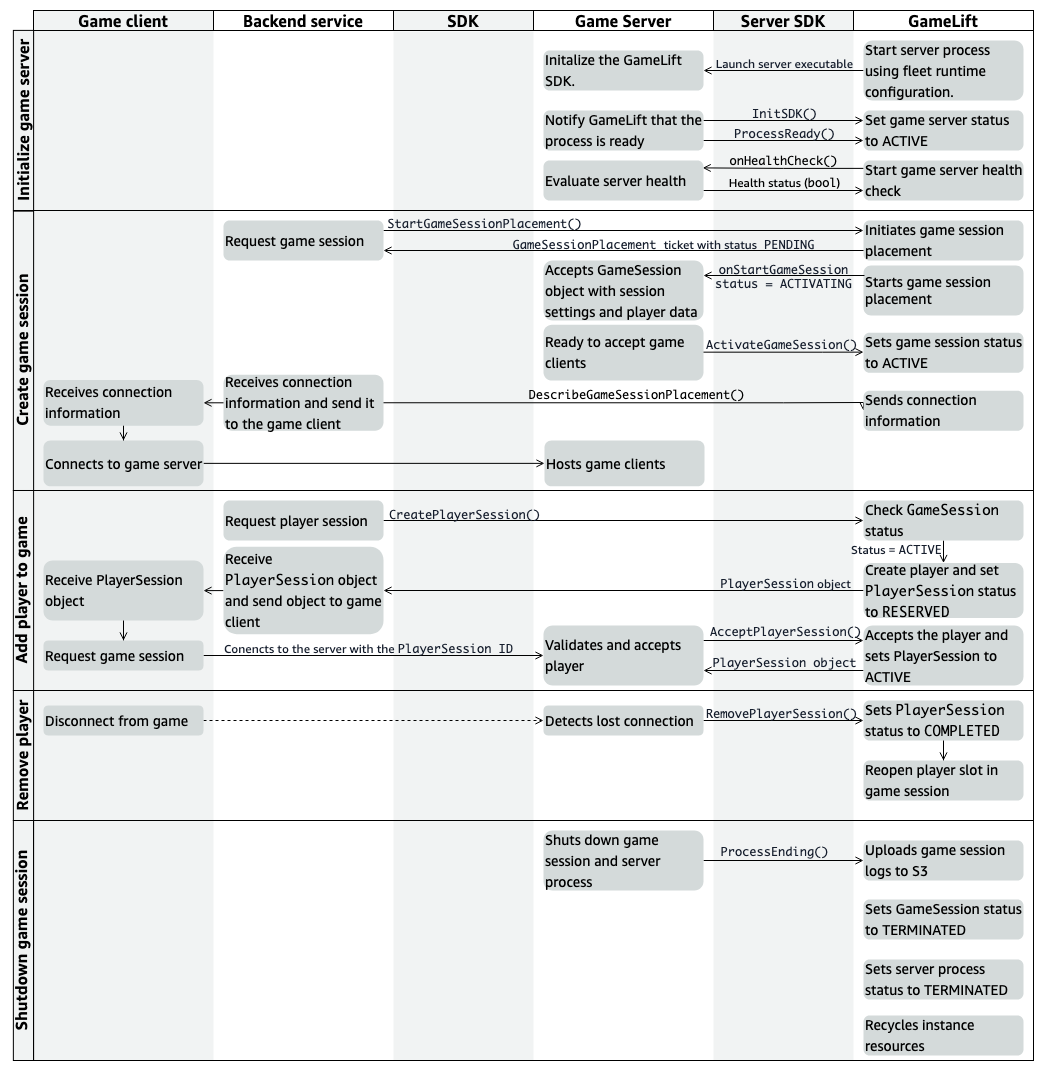
Interaction behaviors
The following sections describe the sequence of events in each of the key interactions.
Initializing a game server process
On startup, a game server process establishes communication with the Amazon GameLift Servers service and reports its status as ready to host a game session.
-
A new process of the game server executable starts running on a hosting resource.
-
The game server process calls the following server SDK operations in sequence:
-
InitSDK()to initialize the server SDK, authenticate the server process, and establish communication with the Amazon GameLift Servers service. -
ProcessReady()to communicate readiness to host a game session. This call also reports the process's connection information, which game clients use to connect to the game session, and other information.
The server process then waits for prompts from the Amazon GameLift Servers service.
-
-
Amazon GameLift Servers updates the status of the server process to
ACTIVEand available to host a new game session. -
Amazon GameLift Servers begins periodically calling the
onHealthCheckcallback to request a health status from the server processes. These calls continue while the server process remains in active status. The server process must respond healthy or not healthy within one minute. If the server process responds not healthy or doesn't respond, at some point the Amazon GameLift Servers service changes the server process's active status and stops sending requests to start game session.
Creating a game session
The Amazon GameLift Servers service starts a new game session in response to a request from a player to play the game.
-
A player using the game client asks to join a game session. Depending on how your game handles the player join process, the game client sends a request to the backend service.
-
If the player join process requires starting a new game session, the backend service sends a request for a new game session to the Amazon GameLift Servers service. This request calls the service API operation
StartGameSessionPlacement(). (As an alternative, the backend service might callStartMatchmaking(), orCreateGameSession().) -
The Amazon GameLift Servers service responds by creating a new
GameSessionPlacementticket with statusPENDING. It returns ticket information to the backend service, so that it can track the placement ticket status and determine when the game session is ready for players. For more information, see Set up event notification for game session placement. -
The Amazon GameLift Servers service starts the game session placement process. It identifies which fleets to look at and searches those fleets for an active server process that's not hosting a game session. On locating an available server process, the Amazon GameLift Servers service does the following:
-
Creates a
GameSessionobject with the game session settings and player data from the placement request, and sets the status toACTIVATING. -
Prompts the server process to start a game session. The service invokes the server process's
onStartGameSessioncallback and passes theGameSessionobject. -
Changes the server process's number of game sessions to
1.
-
-
The server process runs its
onStartGameSessioncallback function. When the server process is ready to accept player connections, it calls the server SDK operationActivateGameSession()and waits for player connections. -
The Amazon GameLift Servers service updates the
GameSessionobject with connection information for the server process (as reported in the call toProcessReady()) and sets the game session status toACTIVE. It also updates theGameSessionPlacementticket status toFULFILLED. -
The backend service calls
DescribeGameSessionPlacement()to check ticket status and get game session information. When the game session is active, the backend service notifies the game client and passes the game session connection information. -
The game client uses the connection information to connect directly to the game server process and join the game session.
Adding a player to a game
A game can optionally use player sessions to track player connections to game sessions. Player sessions can be created individually or as part of a game session placement request.
-
The backend service calls the service API operation
CreatePlayerSession()with a game session ID. -
The Amazon GameLift Servers service checks the game session status (must be
ACTIVE), and looks for an open player slot in the game session. If a slot is available, then the service does the following:-
Creates a new
PlayerSessionobject and sets the status toRESERVED. -
Responds to the backend service request with player session information.
-
-
The backend service passes player session information to the game client along with game session connection information.
-
The game client uses the connection information and player session ID to connect directly to the game server process and ask to join the game session.
-
In response to a game client join attempt, the game server process calls the service API operation
AcceptPlayerSession()to validate the player session ID. The server process either accepts or rejects the connection. -
The Amazon GameLift Servers service does one of the following:
-
If the connection is accepted, then Amazon GameLift Servers sets the
PlayerSessionstatus toACTIVEand passes thePlayerSessionto the game server process. -
If the game server process doesn't call
AcceptPlayerSession()for the player session ID within a certain time period after the originalCreatePlayerSession()request, the Amazon GameLift Servers service changes thePlayerSessionstatus toTIMEDOUTand reopens the player slot in the game session.
-
Removing a player
For games that use player sessions, the game server process notifies the Amazon GameLift Servers service when a player disconnects. The service uses this information to track the status of player slots in a game session and can allow new players to use open slots.
-
A player disconnects from the game session.
-
The game server process detects the lost connection and calls the server SDK operation
RemovePlayerSession(). -
The Amazon GameLift Servers service changes the player session status to
COMPLETEDand reopens the player slot in the game session.
Shutting down the game session
At the end of a game session, or when shutting down the game session, the server process notifies the Amazon GameLift Servers service of game session status.
-
The game server process ends the game session and initiates process shut down by calling the server SDK operation
ProcessEnding(). -
The Amazon GameLift Servers service does the following:
-
Uploads game session logs to Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3).
-
Changes the game session status to
TERMINATED. -
Changes the server process status to
TERMINATED. -
Depending on how the hosting solution is designed, the newly available hosting resources are allocated to run a new game server process.
-