Serverless In-Game Screenshot Processor Pipeline for Game Studios
Publication date: December 23, 2021 (Diagram history)
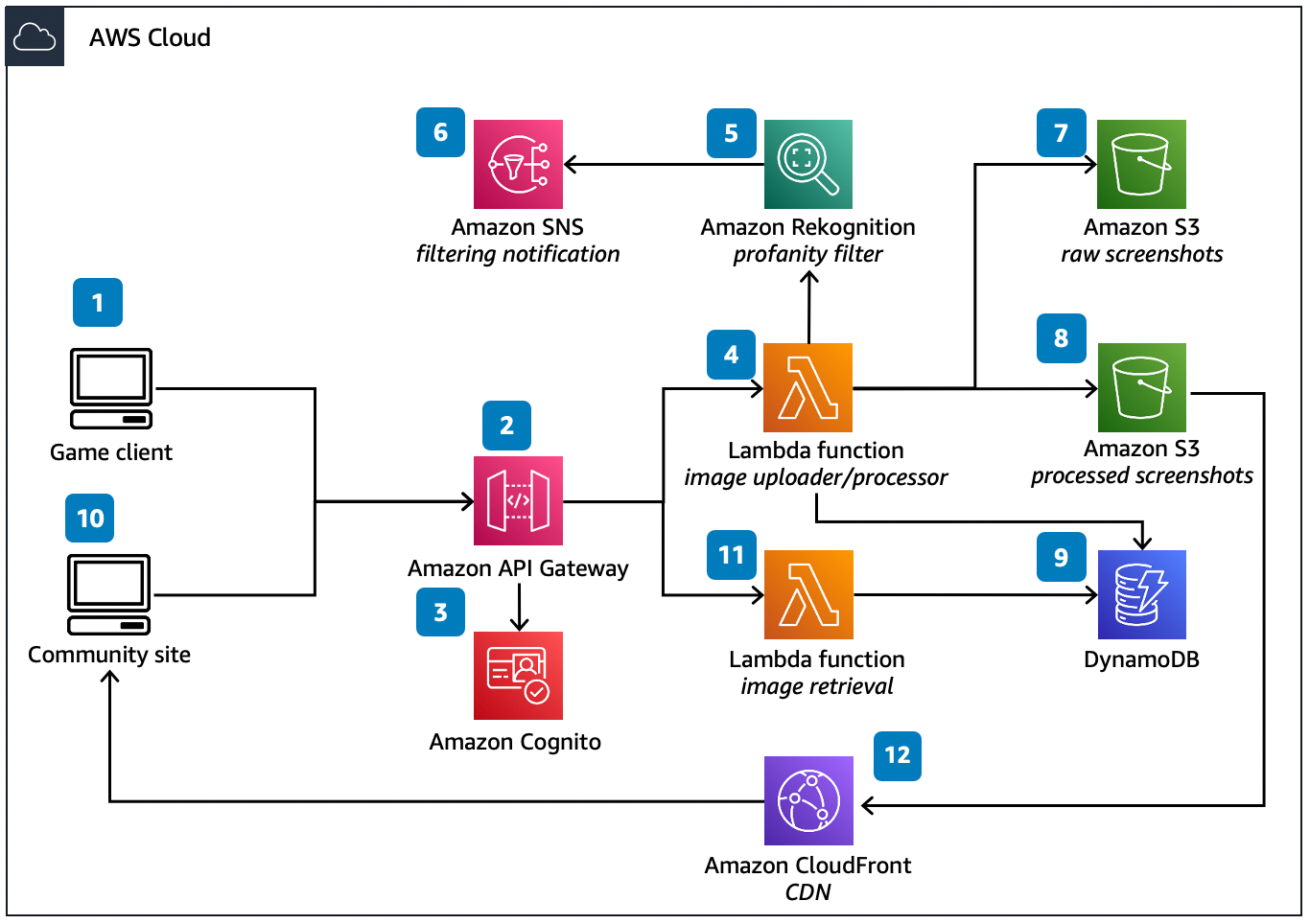
This architecture helps you build a serverless image processing pipeline for your games that receives players’ in-game screenshots, checks them for profanity, performs transformation, and stores them in the cloud. The processed images can be retrieved for the players’ gallery by the game client and the community site.
Serverless In-Game Screenshot Processor Pipeline for Game Studios
-
Players take screenshots in-game, which invokes an API to upload those screenshots. The game client needs to send player metadata to the application program interface (API).
-
An Amazon API Gateway instance hosts the REST API for the image uploader and processor function.
-
It is recommended to use an authentication method such as Amazon Cognito to authenticate all requests processed by API Gateway.
API Gateway also supports custom authorization using an AWS Lambda function to perform the authentication with an external identity provider.
-
An AWS Lambda function is invoked by the API Gateway to receive the image and pre-process it.
-
As part of pre-processing, the image is sent to the Amazon Rekognition
DetectModerationLabelsAPI. -
You can send a notification for the result of the filtering process to your user through Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS).
-
Optionally, the raw image can be stored in an Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket.
-
The image processor Lambda function can perform transformations/resizing of the image and add watermarks. The processed image is uploaded to an S3 bucket meant for processed screenshots.
-
The image processor Lambda function extracts the associated in-game metadata (such as player ID, timestamp, and in-game location) in the request object. The metadata is then stored in Amazon DynamoDB. The image’s associated S3 key is also included in the same DynamoDB item. This step completes the image processing portion of this pipeline.
-
The community site and game client might want to retrieve the stored screenshots to present the gallery of images to players by retrieving the URLs stored in DynamoDB. To retrieve the image, the client or community site initiates a request using API Gateway.
-
The retrieval request invokes the image retrieval Lambda function, which gets the associated item from DynamoDB, which contains the S3 key for the image. Optionally, you can use DynamoDB Accelerator to cache your read requests.
-
The game client and community site requests the image from CloudFront content delivery network (CDN) fronting the S3 bucket to serve the screenshots.
Download editable diagram
To customize this reference architecture diagram based on your business needs, download the ZIP file which contains an editable PowerPoint.
Create a free AWS account
Sign up for an AWS account. New accounts include 12 months of AWS Free Tier
Further reading
For additional information, refer to
Diagram history
To be notified about updates to this reference architecture diagram, subscribe to the RSS feed.
| Change | Description | Date |
|---|---|---|
Initial publication | Reference architecture diagram first published. | December 23, 2021 |
Note
To subscribe to RSS updates, you must have an RSS plugin enabled for the browser you are using.
