IVS Private Ingest
For workloads that require secure, live video ingestion, you can use an interface VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) endpoint to establish a secure private connection between your Amazon VPC and IVS. This keeps your IVS ingest traffic within the AWS network and off the public internet. Interface VPC endpoints are powered by AWS PrivateLink, an AWS technology that enables private communication between AWS services, using an elastic network interface with private IPs in your Amazon VPC. For more information, see Amazon Virtual Private Cloud and Access an AWS service using an interface VPC endpoint (AWS PrivateLink).
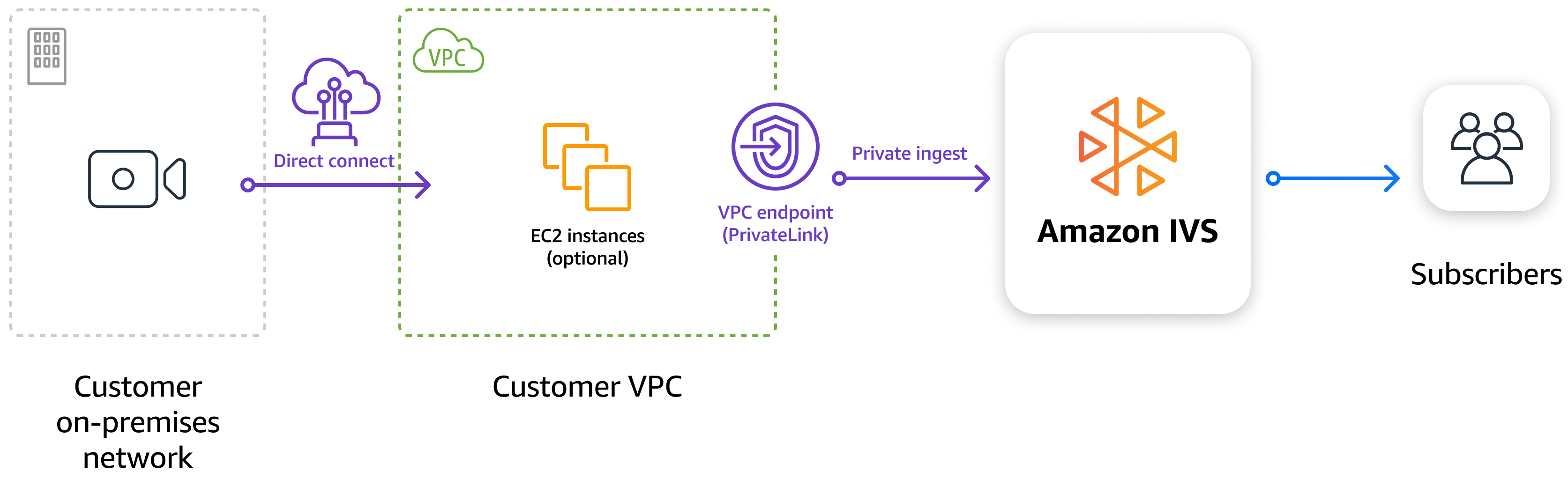
You can ingest RTMP(S) streams into IVS from your Amazon VPC or through AWS Direct
Connect, and send video privately to either IVS low-latency channels or IVS real-time
stages. You are billed for standard interface VPC endpoint hourly usage and data-processing
charges; for details, see Interface
endpoint pricing
Ensure that your Amazon VPC is in a supported region:
-
us-west-2
-
eu-central-1
-
eu-west-1
Note: While your Amazon VPC must be in one of these supported regions, IVS control-plane resources need not be in the same region or AWS account as the Amazon VPC. For more details, see Global Solution, Regional Control.
To ingest a stream through an interface VPC endpoint, use a private ingest URL composed of the VPC endpoint’s DNS name and the stream key for the IVS resource (channel or stage ingest configuration), in this format:
rtmps://<VPC_ENDPOINT_DNS_NAME>/app/<STREAM_KEY>
To stream to a channel, create a channel and retrieve its stream key as explained in set up streaming software. To stream to a stage using RTMP(S) or E-RTMP(S), create an RTMP ingest configuration and use its associated stream key.
Below is a quick walkthrough of streaming from an EC2 instance to an IVS channel or stage using an interface VPC endpoint:
Step 1: Create an Interface VPC Endpoint
Each VPC endpoint needs to be associated with a VPC in your account. If your account already has a default VPC, you can use that; otherwise, create a new VPC. If you want to use IPv6 or dualstack with your VPC endpoint, ensure that your VPC has subnets with IPv6 CIDRs assigned.
To create a VPC endpoint, see the instructions in Create a VPC endpoint (in the Amazon VPC documentation). Once you are on the Create endpoint page:
-
Select AWS services. Then in the Services section, search for IVS. You should see a service like com.amazonaws.<region>.ivs.contribute.
-
In the Network settings section, select the VPC where you want to create the endpoint. In the Subnets section, select which subnets and other network settings you want to configure for the endpoint.
-
In the Security groups section, select a security group that allows inbound traffic on TCP ports 443 and 1935 from wherever you will be streaming. You can edit this later, after creating the endpoint, so if you don’t know what security group you want to use yet, leave it unselected for now.
After you select Create endpoint, you will be taken back to the VPC Endpoints overview page, where you will see the VPC endpoint you just created:
-
The Status of the new endpoint is Pending for about 30 seconds, then it will be auto-accepted and its Status will change to a green Available.
-
On the right side of the VPC endpoint information panel, you will see several DNS names associated with your VPC endpoint. Copy and save the first one listed; you will need to specify it as your stream-ingestion server URL in a future step.
Step 2: Launch an EC2 Instance
There are many options that customers can use to broadcast a stream from AWS. The example here uses an Ubuntu EC2 instance with FFmpeg installed.
First, create an EC2 instance (a t2.micro is fine). Be sure to create the instance within the same VPC where you created your VPC endpoint.
The security group you assign to this instance will need egress to the VPC endpoint for TCP ports 443 and 1935. Also be sure to enable ingress on TCP port 22 if using SSH to access the instance, as well as egress on TCP port 80 for the package manager operations in step 3 below.
Launch the instance. Once it initializes, use SSH or AWS Session Manager to connect to the instance.
Step 3: Install FFmpeg on your Instance
Once connected to your instance, run the following commands on your machine (assuming you created the instance with Ubuntu) to install FFmpeg:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:savoury1/ffmpeg4 sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install ffmpeg
Step 4: Stream to an IVS Channel or Stage
The private ingest URL format is:
rtmps://<VPC_ENDPOINT_DNS_NAME>/app/<STREAM_KEY>
For example:
rtmps://vpce-0a8dfb0b7a4611439-xyzabc12.contribute.ivs.us-west-2.vpce.amazonaws.com/app/sk-usw2-abc123example456
Run the following example FFmpeg command, replacing
<VPC_ENDPOINT_DNS_NAME> with the DNS name from Step 1 and
<STREAM_KEY> with the appropriate stream key (for a channel or
ingest configuration):
ffmpeg -re -f lavfi -i "testsrc=duration=360:size=1024x768:rate=30" -f lavfi -i "sine=frequency=1000" -pix_fmt yuv420p -profile:v baseline -level 3.0 -r 30 -g 60 -shortest -vcodec libx264 -acodec aac -f flv "rtmps://<VPC_ENDPOINT_DNS_NAME>/app/<STREAM_KEY>"
If all the above was successful, your stream should be running. A stream ingested through a VPC endpoint should be processed and treated the same as a stream ingested through a public IVS endpoint; the only difference is the ingestion path.
When you are done using them, be sure to delete the created EC2 instance and VPC endpoint to avoid any unnecessary charges.