기계 번역으로 제공되는 번역입니다. 제공된 번역과 원본 영어의 내용이 상충하는 경우에는 영어 버전이 우선합니다.
예제 2: Verified Permissions 및 Cedar가 포함된 기본 RBAC
이 예제에서는 Verified Permissions 및 Cedar를 사용하여 기본 RBAC를 보여줍니다. 앞서 언급한 것처럼 Cedar의 기본 구성은 개체입니다. 개발자는 자체 엔터티를 정의하고 선택적으로 엔터티 간에 관계를 생성할 수 있습니다. 다음 예제에는 Users, Roles및의 세 가지 유형의 엔터티가 포함됩니다Problems. Students 및는 유형의 엔터티로 간주될 Teachers 수 Role, 있으며 각각은 0 또는 임의의와 연결될 User 수 있습니다Roles.
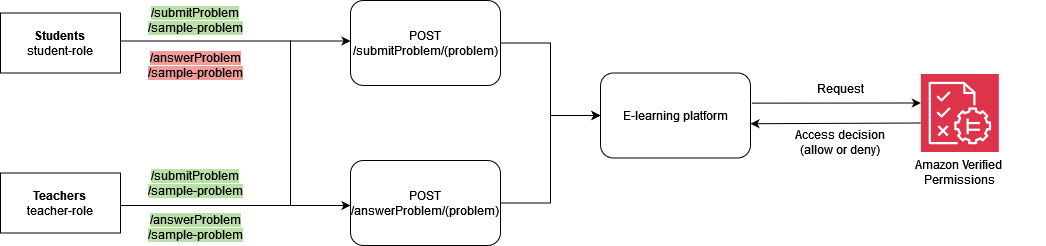
Cedar에서 이러한 관계는를 상위RoleStudentUserBob로에 연결하여 표현됩니다. 이 연결은 한 그룹의 모든 학생 사용자를 논리적으로 그룹화합니다. Cedar의 그룹화에 대한 자세한 내용은 Cedar 설명서를
다음 정책은 Students 유형의 논리적 그룹에 연결된 submitProblem, 모든 보안 주체에 ALLOW 대한 작업 결정에 따라 평가됩니다Role.
permit ( principal in ElearningApp::Role::"Students", action == ElearningApp::Action::"submitProblem", resource );
다음 정책은 유형의 논리적 그룹에 연결된 모든 보안 주체에 ALLOW 대해 작업 submitProblem 또는 Teachers에 answerProblem대한 결정에 따라 평가됩니다Role.
permit ( principal in ElearningApp::Role::"Teachers", action in [ ElearningApp::Action::"submitProblem", ElearningApp::Action::"answerProblem" ], resource );
이러한 정책을 사용하여 요청을 평가하려면 평가 엔진이 권한 부여 요청 내에서 참조되는 보안 주체가 적절한 그룹의 구성원인지 여부를 알아야 합니다. 따라서 애플리케이션은 권한 부여 요청의 일부로 평가 엔진에 관련 그룹 멤버십 정보를 전달해야 합니다. 이 작업은 entities 속성을 통해 수행되며, 이를 통해 권한 부여 호출과 관련된 보안 주체 및 리소스에 대한 속성 및 그룹 멤버십 데이터를 Cedar 평가 엔진에 제공할 수 있습니다. 다음 코드에서 그룹 멤버십은 라는 상위를 갖는 User::"Bob" 것으로 정의하여 표시됩니다Role::"Students".
{ "policyStoreId": "ELEARNING_POLICYSTOREID", "principal": { "entityType": "ElearningApp::User", "entityId": "Bob" }, "action": { "actionType": "ElearningApp::Action", "actionId": "answerProblem" }, "resource": { "entityType": "ElearningApp::Problem", "entityId": "SomeProblem" }, "entities": { "entityList": [ { "identifier": { "entityType": "ElearningApp::User", "entityId": "Bob" }, "attributes": {}, "parents": [ { "entityType": "ElearningApp::Role", "entityId": "Students" } ] }, { "identifier": { "entityType": "ElearningApp::Problem", "entityId": "SomeProblem" }, "attributes": {}, "parents": [] } ] } }
이 예제에서 Bob은 answerProblem 요청을 하는 로그인한 사용자입니다. 따라서 Bob은 보안 주체이고 개체는 유형입니다User. Bob이 수행하려고 하는 작업은 입니다answerProblem. Bob이 answerProblem 작업을 수행할 수 있는지 평가하려면 상위 개체를 로 나열하여 엔터티를 User의 값과 연결하고 그룹 멤버십을 Bob 할당하는 엔터티 구조를 제공해야 합니다Role::"Students". 사용자 그룹의 개체Role::"Students"는 작업 만 수행할 수 있으므로 submitProblem이 권한 부여 요청은 로 평가됩니다DENY.
반면, User 값이 Alice 이고 그룹의 일부인 유형이 answerProblem 작업을 수행Role::"Teachers"하려고 하면 정책에서 그룹의 보안 주체가 모든 리소스에 answerProblem 대해 작업을 수행할 수 있도록 지시ALLOW하므로 권한 부여 요청은 로 평가Role::"Teachers"됩니다. 다음 코드는가 로 평가하는 이러한 유형의 권한 부여 요청을 보여줍니다ALLOW.
{ "policyStoreId": "ELEARNING_POLICYSTOREID", "principal": { "entityType": "ElearningApp::User", "entityId": "Alice" }, "action": { "actionType": "ElearningApp::Action", "actionId": "answerProblem" }, "resource": { "entityType": "ElearningApp::Problem", "entityId": "SomeProblem" }, "entities": { "entityList": [ { "identifier": { "entityType": "ElearningApp::User", "entityId": "Alice" }, "attributes": {}, "parents": [ { "entityType": "ElearningApp::Role", "entityId": "Teachers" } ] }, { "identifier": { "entityType": "ElearningApp::Problem", "entityId": "SomeProblem" }, "attributes": {}, "parents": [] } ] } }