This whitepaper is for historical reference only. Some content might be outdated and some links might not be available.
Types of NoSQL databases
To support specific needs and use cases, NoSQL databases use a variety of data models for managing and accessing the data. The following section describes some of the common NoSQL database categories:
-
Key-value pair
-
Document-oriented
-
Column-oriented
-
Graph-based
-
Time series
These types of databases are optimized specifically for applications that need large data volumes, flexible data models, and low latency. To achieve these objectives, NoSQL databases employ various techniques, and it's important to note that not all database options prioritize the same set of factors that are mentioned here:
-
Consistency
-
Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability (ACID) transactions
-
Query language and data access richness (simplified Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD)-style operations
with known predictable cost) -
Sharding/partitioning
of data sets on primary identifier keys -
Shifting the burden of data and schema validation to the application (removing referential integrity enforcement by the database and so on)
Here’s a brief overview of most popular NoSQL data models.
-
Key-value — A key-value data store
is a type of database that stores data as a collection of key-value pairs. In this type of data store, each data item is identified by a unique key, and the value associated with that key can be anything, such as a string, number, object, or even another data structure. 
An example of data stored as key-value pairs.
AWS offers Amazon DynamoDB
as a key-value managed database service. -
Document — In a document database, the data is stored in documents. Each document is typically a nested structure of keys and values. The values can be atomic data types, or complex elements such as lists, arrays, nested objects, or child collections (for example, a collection in the document database is analogous to a table in a relational database, except there is no single schema enforced upon all documents).
Documents are retrieved by unique keys. It may also be possible to retrieve only parts of a document--for example, the cost of an item--to run queries such as aggregation, querying using examples based on a text string, or even full-text search. Most document databases also allow you to define secondary indexes.
You can transfer the application code object model directly into a document using several different formats. The most commonly used are JavaScript Object Notation (JSON), Binary JavaScript Object Notation (BSON
), and Extensible Markup Language (XML ). 
An example of a document data model
AWS offers a specialized document database service called Amazon DocumentDB (with MongoDB compatibility)
. -
Wide-column — A wide column data store
is a type of NoSQL database that stores data in columns rather than rows, making it highly scalable and flexible. In a wide column data store, data is organized into column families, which are groups of columns that share the same attributes. Each row in a wide column data store is identified by a unique row key, and the columns in that row are further divided into column names and values. Unlike traditional relational databases, which have a fixed number of columns and data types, wide column data stores allow for a variable number of columns and support multiple data types. The most significant benefit of having column-oriented databases is that you can store large amounts of data within a single column. This feature allows you to reduce disk resources and the time it takes to retrieve information from it.

An example of the kind of data you might store in a wide-column data store
AWS offers Amazon Keyspaces (for Apache Cassandra)
as a wide-column managed database service. -
Graph — Graph databases
are used to store and query highly connected data. Data can be modeled in the form of entities (also referred to as nodes, or vertices) and the relationships between those entities (also referred to as edges). The strength or nature of the relationships also carry significant meaning in graph databases. Users can then traverse the graph structure by starting at a defined set of nodes or edges and travel across the graph, along defined relationship types or strengths, until they reach some defined condition. Results can be returned in the form of literals, lists, maps, or graph traversal paths. Graph databases provide a set of query languages that contain syntax designed for traversing a graph structure, or matching a certain structural pattern.

An example of a social network graph. Given the people (nodes) and their relationships (edges), you can find out who the "friends of friends" of a particular person are—for example, the friends of Howard's friends.
AWS offers Amazon Neptune
as a managed graph database service. -
Time series — A time series database
is designed to store and retrieve data records that are sequenced by time, which are sets of data points that are associated with timestamps and stored in time sequence order. Time series databases make it easy to measure how measurements or events change over time; for example, temperature readings from weather sensors or intraday stock prices. 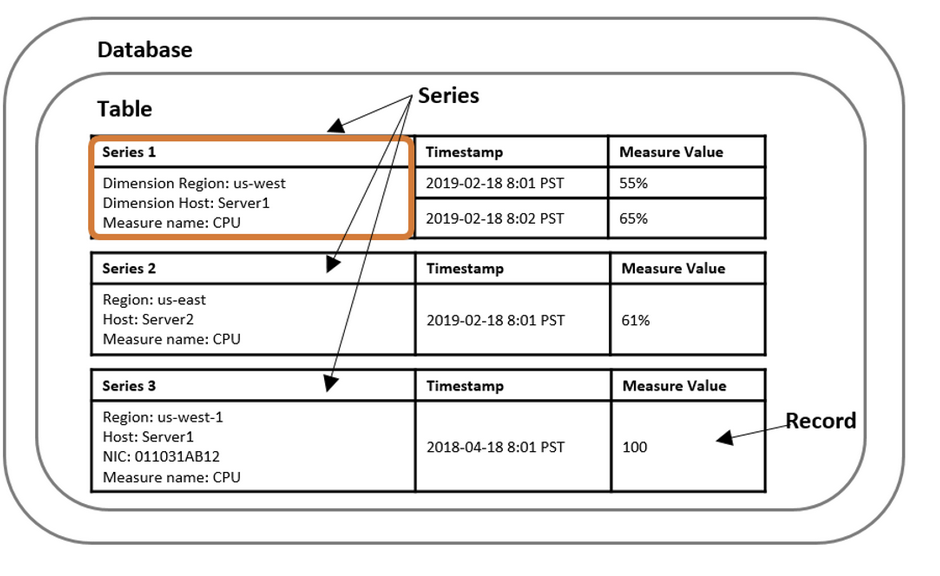
An example of a series data model
AWS offers Amazon Timestream
as a managed time series database service.