Configuring reserved concurrency for a function
In Lambda, concurrency is the number of in-flight requests that your function is currently handling. There are two types of concurrency controls available:
-
Reserved concurrency – This sets both the maximum and minimum number of concurrent instances allocated to your function. When a function has reserved concurrency, no other function can use that concurrency. Reserved concurrency is useful for ensuring that your most critical functions always have enough concurrency to handle incoming requests. Additionally, reserved concurrency can be used for limiting concurrency to prevent overwhelming downstream resources, like database connections. Reserved concurrency acts as both a lower and upper bound - it reserves the specified capacity exclusively for your function while also preventing it from scaling beyond that limit. Configuring reserved concurrency for a function incurs no additional charges.
-
Provisioned concurrency – This is the number of pre-initialized execution environments allocated to your function. These execution environments are ready to respond immediately to incoming function requests. Provisioned concurrency is useful for reducing cold start latencies for functions and designed to make functions available with double-digit millisecond response times. Generally, interactive workloads benefit the most from the feature. Those are applications with users initiating requests, such as web and mobile applications, and are the most sensitive to latency. Asynchronous workloads, such as data processing pipelines, are often less latency sensitive and so do not usually need provisioned concurrency. Configuring provisioned concurrency incurs additional charges to your AWS account.
This topic details how to manage and configure reserved concurrency. For a conceptual overview of these two types of concurrency controls, see Reserved concurrency and provisioned concurrency. For information on configuring provisioned concurrency, see Configuring provisioned concurrency for a function.
Note
Lambda functions linked to an Amazon MQ event source mapping have a default maximum concurrency. For Apache Active MQ, the maximum number of concurrent instances is 5. For Rabbit MQ, the maximum number of concurrent instances is 1. Setting reserved or provisioned concurrency for your function doesn't change these limits. To request an increase in the default maximum concurrency when using Amazon MQ, contact Support.
Sections
Configuring reserved concurrency
You can configure reserved concurrency settings for a function using the Lambda console or the Lambda API.
To reserve concurrency for a function (console)
Open the Functions page
of the Lambda console. -
Choose the function you want to reserve concurrency for.
-
Choose Configuration and then choose Concurrency.
-
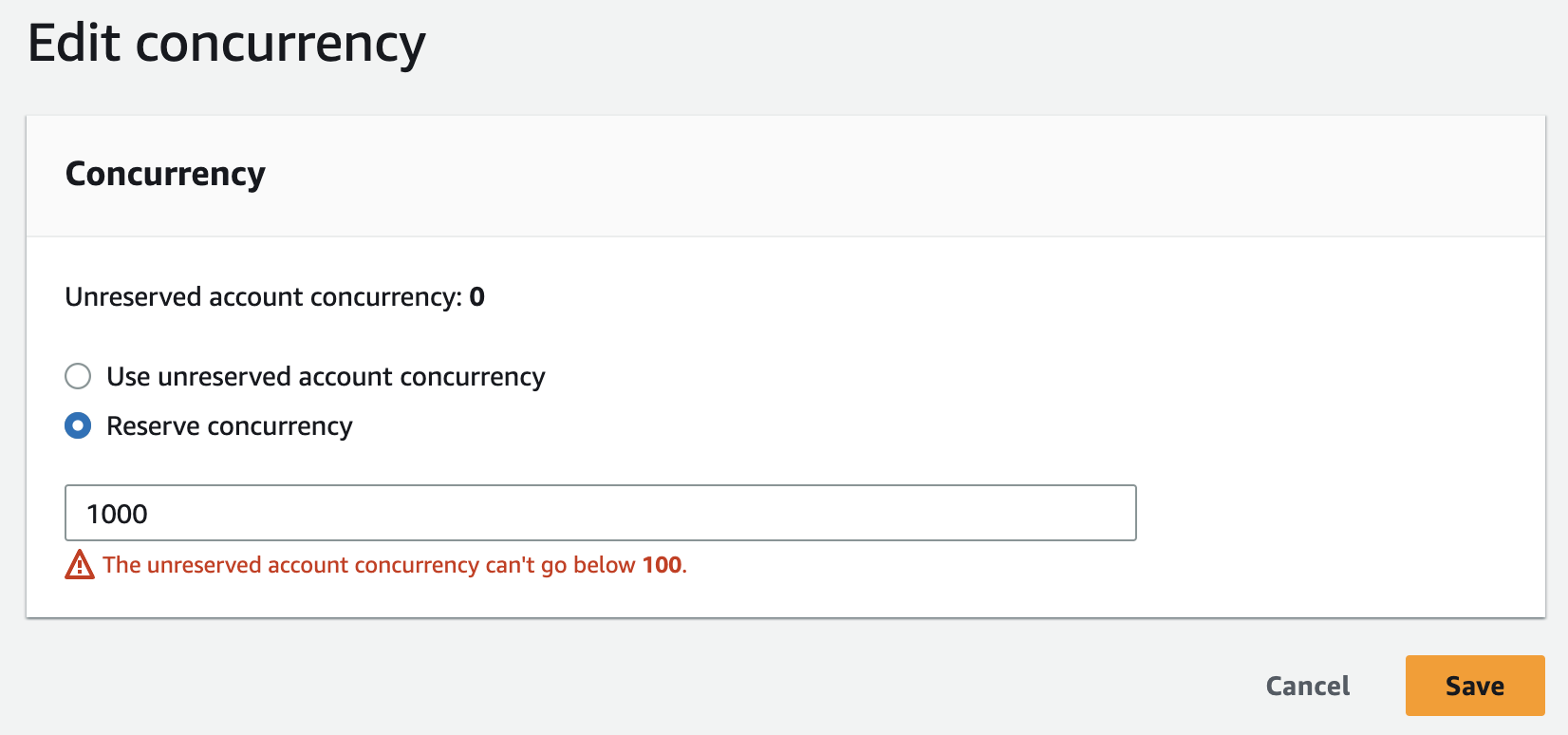
Under Concurrency, choose Edit.
-
Choose Reserve concurrency. Enter the amount of concurrency to reserve for the function.
-
Choose Save.
You can reserve up to the Unreserved account concurrency value minus 100. The remaining 100 units of concurrency are for functions that aren't using reserved concurrency. For example, if your account has a concurrency limit of 1,000, you cannot reserve all 1,000 units of concurrency to a single function.
Reserving concurrency for a function impacts the concurrency pool that's
available to other functions. For example, if you reserve 100 units of concurrency
for function-a, other functions in your account must share the
remaining 900 units of concurrency, even if function-a doesn't use
all 100 reserved concurrency units.
To intentionally throttle a function, set its reserved concurrency to 0. This stops your function from processing any events until you remove the limit.
To configure reserved concurrency with the Lambda API, use the following API operations.
For example, to configure reserved concurrency with the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI), use
the put-function-concurrency command. The following command reserves
100 concurrency units for a function named my-function:
aws lambda put-function-concurrency --function-name my-function \ --reserved-concurrent-executions 100
You should see output that looks like the following:
{ "ReservedConcurrentExecutions": 100 }
Accurately estimating required reserved concurrency for a function
If your function is currently serving traffic, you can easily view its concurrency
metrics using CloudWatch metrics.
Specifically, the ConcurrentExecutions metric shows you the number of
concurrent invocations for each function in your account.

The previous graph suggests that this function serves an average of 5 to 10 concurrent requests at any given time, and peaks at 20 requests on a typical day. Suppose that there are many other functions in your account. If this function is critical to your application and you don't want to drop any requests, use a number greater than or equal to 20 as your reserved concurrency setting.
Alternatively, recall that you can also calculate concurrency using the following formula:
Concurrency = (average requests per second) * (average request duration in seconds)
Multiplying average requests per second with the average request duration in
seconds gives you a rough estimate of how much concurrency you need to reserve.
You can estimate average requests per second using the Invocation
metric, and the average request duration in seconds using the Duration
metric. See Using CloudWatch metrics with Lambda
for more details.
You should also be familiar with your upstream and downstream throughput constraints. While Lambda functions scale seamlessly with load, upstream and downstream dependencies may not have the same throughput capabilities. If you need to limit how high your function can scale, configure reserved concurrency on your function.