Resource-based policy examples for Amazon Lex V2
A resource-based policy is attached to a resource, such as a bot or a bot alias. With a resource-based policy you can specify who has access to the resource and the actions that they can perform on it. For example, you can add resource-based policies that enable a user to modify a specific bot, or to allow a user to use runtime operations on a specific bot alias.
When you use a resource-based policy you can allow other AWS services to access resources in your account. For example, you can allow Amazon Connect to access an bot.
To learn how to create a bot or bot alias, see Working with Amazon Lex V2 bots.
Topics
Use the console to specify a resource-based policy
You can use the console to manage the resource-based policies for your bots and bot aliases. You enter the JSON structure of a policy and the console associates it with the resource. If there is a policy already associated with a resource, you can use the console to view and modify the policy.
When you save a policy with the policy editor, the console checks the syntax of the policy. If the policy contains errors, such as a non-existent user or an action that is not supported by the resource, it returns an error and doesn't save the policy.
The following shows the resource-based policy editor for a bot in the console. The policy editor for a bot alias is similar.
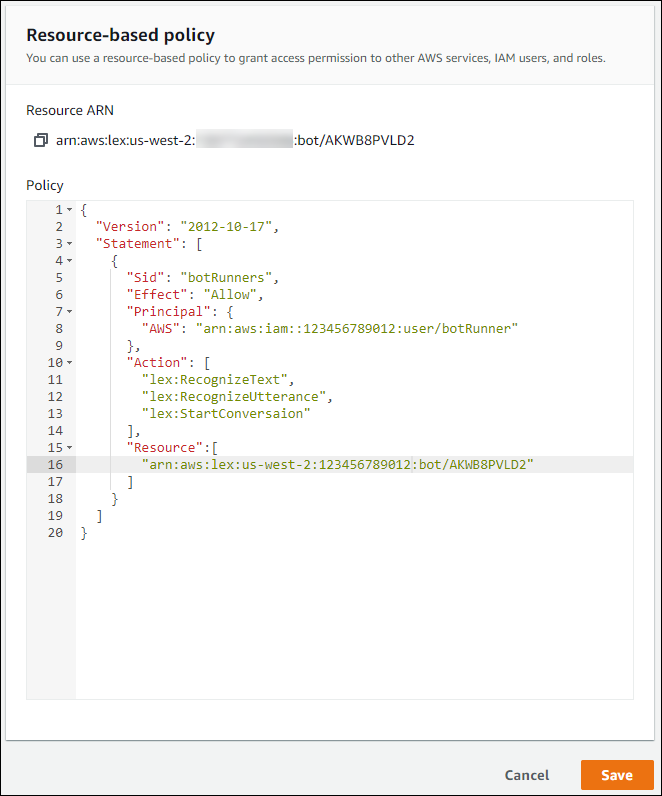
To open the policy editor for a bot
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon Lex console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/lex/
. -
From the Bots list, choose the bot whose policy you want to edit.
-
In the Resource-based policy section, choose Edit.
To open the policy editor for a bot alias
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon Lex console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/lex/
. -
From the Bots list, choose the bot that contains the alias that you want to edit.
-
From the left menu, choose Aliases, then choose the alias to edit.
-
In the Resource-based policy section, choose Edit.
Use the API to specify a resource-based policy
You can use API operations to manage the resource-based policies for your bots and bot aliases. There are operations to create, update and delete policies.
- CreateResourcePolicy
-
Adds a new resource policy with the specified policy statements to a bot or bot alias.
- CreateResourcePolicyStatement
-
Adds a new resource policy statement to a bot or bot alias.
- DeleteResourcePolicy
-
Removes a resource policy from a bot or bot alias.
- DeleteResourcePolicyStatement
-
Removes a resource policy statement from a bot or bot alias.
- DescribeResourcePolicy
-
Gets a resource policy and the policy revision.
- UpdateResourcePolicy
-
Replaces the existing resource policy for a bot or bot alias with a new one.
Allow an IAM role to update a bot and list bot aliases
The following example grants permissions for a specific IAM role to call Amazon Lex V2 model building API operations to modify an existing bot. The user can list aliases for a bot and update the bot, but can't delete the bot or bot aliases.
Allow a user to have a conversation with a bot
The following example grants permission for a specific user to call Amazon Lex V2 runtime API operations on a single alias of a bot.
The user is specifically denied permission to update or delete the bot alias.
Allow an AWS service to use a specific Amazon Lex V2 bot
The following example grants permission for AWS Lambda and Amazon Connect to call Amazon Lex V2 runtime API operations.
The condition block is required for service principals, and must
use the global context keys AWS:SourceAccount and
AWS:SourceArn.
The AWS:SourceAccount is the account ID that is
calling the Amazon Lex V2 bot.
The AWS:SourceArn is the resource ARN of the Amazon Connect
service instance or Lambda function that the call to the Amazon Lex V2 bot
alias originates from.