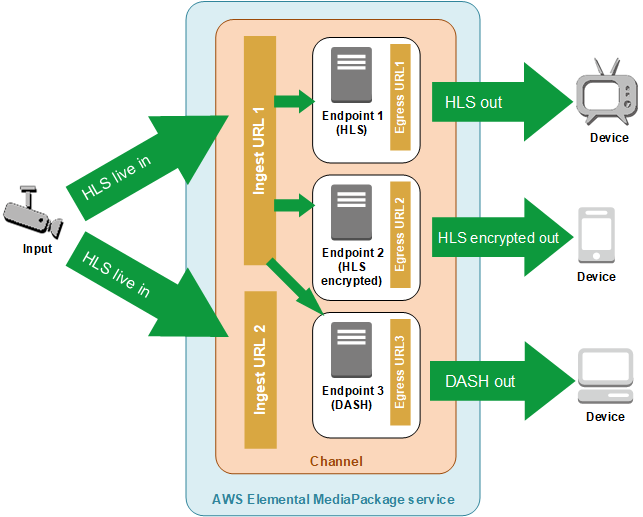
General MediaPackage live processing flow
The following outlines the general flow of live content in MediaPackage:
-
An upstream encoder (such as AWS Elemental MediaLive) sends an HLS live stream with digest authentication over WebDAV to the MediaPackage channel input URL, and includes the channel's access credentials (as supplied in MediaPackage). If you're using input redundancy, the encoder sends two identical HLS live streams to MediaPackage, one to each input URL on the channel. MediaPackage uses the stream from one input URL as the source content. If MediaPackage stops receiving content on the active input URL, it automatically switches to the other input URL for source content. Additionally, AWS scales resources up and down to handle the incoming traffic.
For more information, see Live input redundancy AWS Elemental MediaPackage processing flow.
Note
To allow support for features like time-shifted viewing, MediaPackage stores all received content for a limited time. This stored content is only available for playback if it falls within the startover window that's defined on the endpoint. Stored content isn't available for playback if it's outside the startover window, or if you haven't defined a window on the endpoint. For more information, see Time-shifted viewing reference in AWS Elemental MediaPackage.
-
A downstream device requests content from MediaPackage through the endpoint output URL. A downstream device is either a video player or a CDN. The output URL is associated with an endpoint for a specific streaming format (either Apple HLS, DASH-ISO, Microsoft Smooth Streaming, or CMAF).
-
When MediaPackage receives the playback request from the downstream device, it dynamically packages the stream according to the settings that you specified on the endpoint. Packaging can include adding encryption and configuring audio, video, and subtitles or captions track outputs.
Be sure to order your inputs so that your preferred audio rendition is listed first in the audio section of the parent manifest. Do the same for the subtitles or captions. When packaging audio and subtitles or captions tracks, MediaPackage designates the first audio and captions or subtitles track as
DEFAULT=YESandAUTO-SELECT=YES. This packaging overrides default and auto-select settings from the input. -
MediaPackage delivers the output stream over HTTPS to the requesting device. As with input, AWS scales resources up and down to handle changes in traffic.
-
MediaPackage logs activity through Amazon CloudWatch. You can view information such as the number of content requests and amount of content that MediaPackage has received or delivered. For information about viewing MediaPackage metrics in CloudWatch, see Monitoring AWS Elemental MediaPackage with Amazon CloudWatch metrics.
Throughout the content input and output processes, MediaPackage detects and mitigates potential infrastructure failures before they become a problem for viewers.
The following illustration shows the overall process.