Overview
The purpose of this guide is to provide best practices for applications categorized as “retire” in a migration plan for the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cloud.
A critical first step in creating a migration strategy is collecting application portfolio data, such as extracts from a configuration management database. This data must be evaluated against the seven common migration strategies (7 Rs) for moving applications to the AWS Cloud. These strategies are refactor, replatform, repurchase, rehost, relocate, retain, and retire. For more information, see the 7 Rs in the glossary.
After you complete this initial portfolio analysis, you should have an initial plan for how each application will be migrated. This plan should be regularly optimized for future migration waves and teams, based on lessons learned and new data that becomes available during the migration process. The following diagram illustrates the strategy planning process.
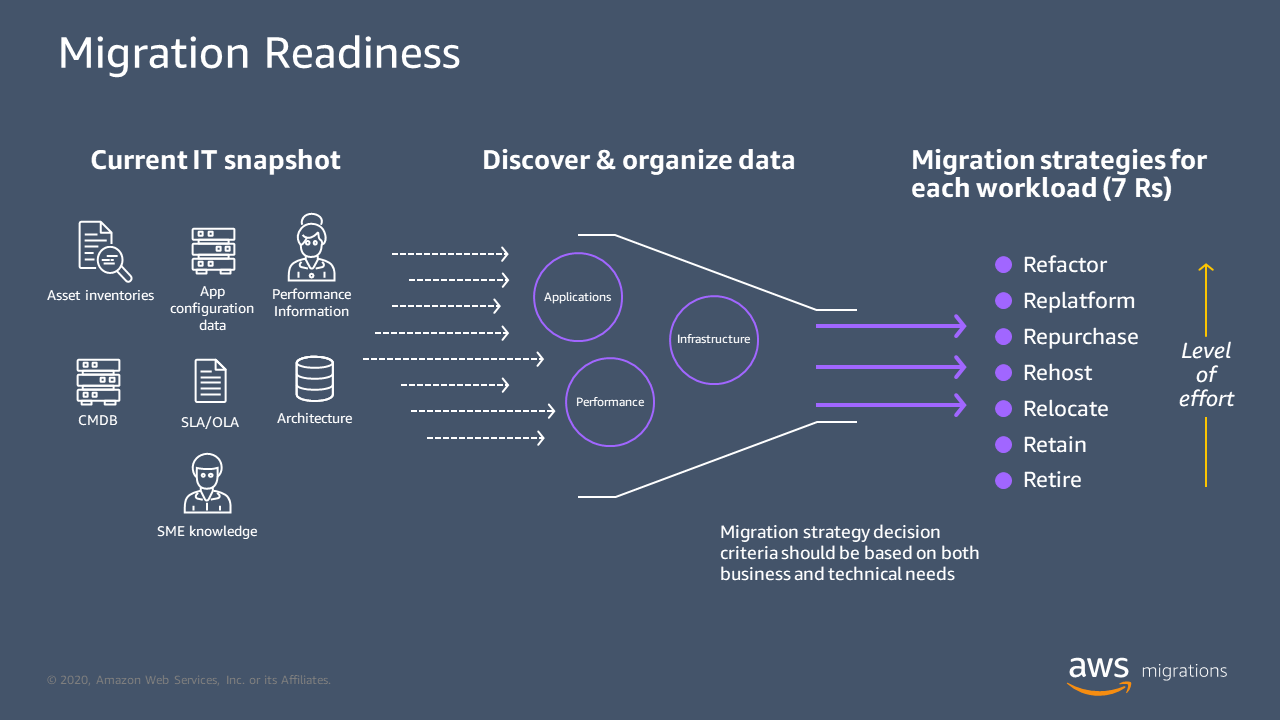
Deciding if applications should be retired can often become complex and involves a level of risk. This can result in action being postponed, especially if subject matter experts (SMEs) have left an organization. Also, documentation about legacy systems can be sparse.
However, identifying and retiring applications that are no longer useful helps boost your business case and directs your team’s attention toward maintaining resources that are more widely used. This guide outlines six best practices to use when assessing applications to be retired in your migration strategy.