Decomposing uncertainty
Bayesian neural networks (BNNs) yield a predictive distribution
 , which provides a set of different predictions from which you can estimate
variance
, which provides a set of different predictions from which you can estimate
variance
 ; that is, total predictive uncertainty
; that is, total predictive uncertainty
 . The total predictive uncertainty can be split into these two components of
uncertainty by using the law of total variance:
. The total predictive uncertainty can be split into these two components of
uncertainty by using the law of total variance:

The expected value
 of a target variable
of a target variable
 , given input
, given input
 and random parameters
and random parameters
 that specify a BNN,
that specify a BNN,
 , is estimated by a BNN with a single forward propagation and denoted as
, is estimated by a BNN with a single forward propagation and denoted as
 . The variance of the target, given input and random parameters,
. The variance of the target, given input and random parameters,
 , is output by the BNN, too, and denoted as
, is output by the BNN, too, and denoted as
 . Thus, the total predictive uncertainty is the sum of these two numbers:
. Thus, the total predictive uncertainty is the sum of these two numbers:
-
The variance about the BNN’s predicted means
 — the epistemic uncertainty
— the epistemic uncertainty -
The average of the BNN’s predicted variance
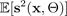 — the aleatoric uncertainty
— the aleatoric uncertainty
The following formula demonstrates how to calculate total uncertainty in accordance with
(Kendall and Gal 2017). BNNs input
 , generate a random parameter configuration
, generate a random parameter configuration
 , and make a single forward propagation through the neural network to output
a mean
, and make a single forward propagation through the neural network to output
a mean
 and variance
and variance
 . We denote a random generation, or simulation, by ~. With fixed
. We denote a random generation, or simulation, by ~. With fixed
 , you can reiterate this process
, you can reiterate this process
 many times to yield a set:
many times to yield a set:

These
 many samples
many samples
 provide the necessary statistics to ascertain uncertainties. You can do this
by estimating epistemic uncertainty and aleatoric uncertainty separately, and then take their
sum, as shown previously in the first equation in this section.
provide the necessary statistics to ascertain uncertainties. You can do this
by estimating epistemic uncertainty and aleatoric uncertainty separately, and then take their
sum, as shown previously in the first equation in this section.