IPAM
Amazon VPC IP Address Manager (IPAM) is an AWS feature that helps you manage all your organization's public and private IP addresses. IPAM categorizes IP addresses in different business units and specific AWS Regions. IPAM tracks the IP addresses that are already in use and leftover IP addresses. It also helps avoid overlapping IP addresses and provides specific CIDR blocks to the VPC based on the selected netmask.
Delegate IPAM
By default, IPAM configuration for an organization is available in the AWS Control Tower management account. To manage IPAM from the network account, delegate IPAM administration from the AWS Control Tower management account to the network account:
-
In the AWS Control Tower management account, navigate to the Amazon VPC service.
-
Open the Amazon VPC IP Address Manager.
-
In the left pane, choose the organization setting.
-
Choose Edit, and then enter the network account number that you noted when you created the account.
-
Save the changes.
After you configure the delegation, you can see those details reflected in the IPAM organization settings of the network account.
Design IPAM hierarchy
Before you start to configure IPAM, analyze the structure that your organization needs based on following criteria:
-
The CIDR block that IPAM will use
-
The business units for which the network account should be configured through IPAM
-
The AWS Regions to be managed through this IPAM
Configure IPAM
To configure IPAM, do the following:
-
Open the AWS Management Console, and navigate to the Amazon VPC IP Address Manager console.
-
Create the IPAM. Enter a name, the operational AWS Regions, and a description.
When the IPAM is created, it will include two scopes:
-
Public, used for configuring and using public CIDR blocks
-
Private, used for configuring and using private CIDR blocks
-
-
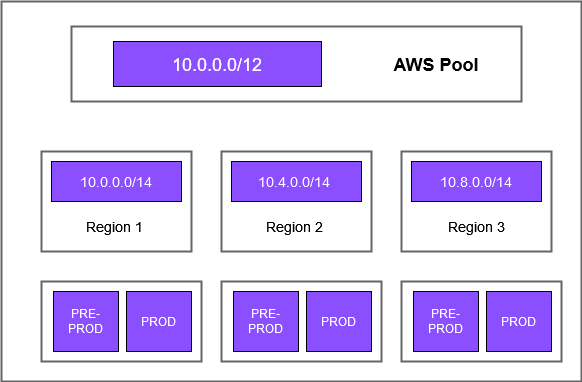
Create the top-level IPAM pool. In the following diagram, the top-level pool is AWS Pool.
-
Create the lower-level pools:
-
A pool for the Region
-
Pools for preproduction and production within the Region
Be sure to specify the appropriate scope for the pools. In general, we recommend using the private scope for most of the network unless you want to host services with a public IP address from your own public CIDR block.
-
-
Share the IPAM with other AWS Organizations organizational unit (OU) accounts by using AWS Resource Access Manager (AWS RAM). Share the IPAM with each account in which you want to create resources. The accounts should be in organization network range and part of the top-level IPAM pool.
We recommend using IPAM based VPC creation when you create all your VPCs. This helps in making sure that the CIDR blocks of new VPCs are not colliding with the existing VPC. New VPCs are created using the pool configurations that you set up earlier.