Attach a policy for cross-account access
When the CA administrator and the certificate issuer reside in different AWS accounts, the CA administrator must share CA access. This is accomplished by attaching a resource-based policy to the CA. The policy grants issuance permissions to a specific principal, which can be an AWS account owner, an IAM user, an AWS Organizations ID, or an organizational unit ID.
A CA administrator can attach and manage policies in the following ways:
-
In the management console, using AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM), which is a standard method for sharing AWS resources across accounts. When you share a CA resource in AWS RAM with a principal in another account, the required resource-based policy is attached to the CA automatically. For more information about RAM, see the AWS RAM User Guide.
Note
You can easily open the RAM console by choosing a CA and then choosing Actions, Manage resource shares.
-
Programmatically, using the PCA APIs PutPolicy, GetPolicy, and DeletePolicy.
-
Manually, using the PCA commands put-policy, get-policy, and delete-policy in the AWS CLI.
Only the console method requires RAM access.
Cross-account case 1: Issuing a managed certificate from the console
In this case, the CA administrator uses AWS Resource Access Manager (AWS RAM) to share CA access with another AWS account, which allows that account to issue managed ACM certificates. The diagram shows that AWS RAM can share the CA directly with the account, or indirectly through an AWS Organizations ID in which the account is a member.

After RAM shares a resource through AWS Organizations, the recipient principal must accept the resource for it to take effect. The recipient can configure AWS Organizations to accept offered shares automatically.
Note
The recipient account is responsible for configuring autorenewal in ACM. Typically, on the first occasion a shared CA is used, ACM installs a service-linked role that permits it to make unattended certificate calls on AWS Private CA. If this fails (usually due to a missing permission), certificates from the CA are not renewed automatically. Only the ACM user can resolve the problem, not the CA administrator. For more information, see Using a Service Linked Role (SLR) with ACM.
Cross-account case 2: Issuing managed and unmanaged certificates using the API or CLI
This second case demonstrates the sharing and issuance options that are possible using the AWS Certificate Manager and AWS Private CA API. All of these operations can also be carried out using the corresponding AWS CLI commands.
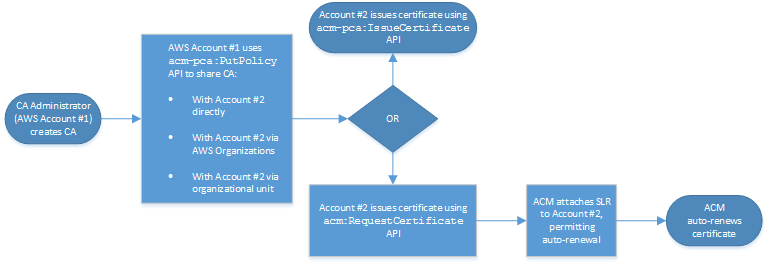
Because the API operations are being used directly in this example, the
certificate issuer has a choice of two API operations to issue a certificate. The
PCA API action IssueCertificate results in an unmanaged certificate
that will not be automatically renewed and must be exported and manually installed.
The ACM API action RequestCertificate results in a managed certificate that can be easily
installed on ACM integrated services and renews automatically.
Note
The recipient account is responsible for configuring auto-renewal in ACM. Typically, on the first occasion a shared CA is used, ACM installs a service-linked role that allows it to make unattended certificate calls on AWS Private CA. If this fails (usually due to a missing permission), certificates from the CA will not renew automatically, and only the ACM user can resolve the problem, not the CA administrator. For more information, see Using a Service Linked Role (SLR) with ACM.