Overview of Service Catalog
As you get started with Service Catalog, you'll benefit from understanding its components and the initial workflows for administrators and end users.
Users
Service Catalog supports the following types of users:
-
Catalog administrators (administrators) – Manage a catalog of products (applications and services), organizing them into portfolios and granting access to end users. Catalog administrators prepare AWS CloudFormation templates, configure constraints, and manage IAM roles for products to provide for advanced resource management.
-
End users – Receive AWS credentials from their IT department or manager and use the AWS Management Console to launch products to which they have been granted access. Sometimes referred to as simply users, end users may be granted different permissions depending on your operational requirements. For example, a user may have the maximum permission level (to launch and manage all of the resources required by the products they use) or only permission to use particular service features.
Products
A product is an IT service that you want to make available for deployment on AWS. A product consists of one or more AWS resources, such as EC2 instances, storage volumes, databases, monitoring configurations, and networking components, or packaged AWS Marketplace products. A product can be a single compute instance running AWS Linux, a fully configured multi-tier web application running in its own environment, or anything in between.
You create a product by importing an AWS CloudFormation template. AWS CloudFormation templates define the AWS resources required for the product, the relationships between resources, and the parameters that end users can plug in when they launch the product to configure security groups, create key pairs, and perform other customizations.
HashiCorp Terraform Open Source and Terraform Cloud support
AWS Service Catalog enables quick, self-service provisioning with governance for your HashiCorp Terraform Open Source and Terraform Cloud configurations within AWS. You can use Service Catalog as a single tool to organize, govern, and distribute your Terraform configurations at scale within AWS. You can access Service Catalog key features, including cataloging of standardized and pre-approved Terraform templates, access control, least-privilege provisioning, versioning, tagging, and sharing to thousands of AWS accounts. Your end users see a simple list of products and versions they have access to, and can then deploy those products in a single action.
To learn more and to complete a Terraform product tutorial, review Getting started with a Terraform product.
Provisioned Products
AWS CloudFormation stacks make it easier to manage the life cycle of your product by enabling you to provision, tag, update, and terminate your product instance as a single unit. An AWS CloudFormation stack includes an AWS CloudFormation template, written in either JSON or YAML format, and its associated collection of resources. A provisioned product is a stack. When an end user launches a product, the instance of the product that is provisioned by Service Catalog is a stack with the resources necessary to run the product. For more information, see AWS CloudFormation User Guide.
Portfolios
A portfolio is a collection of products that contains configuration information. Portfolios help manage who can use specific products and how they can use them. With Service Catalog, you can create a customized portfolio for each type of user in your organization and selectively grant access to the appropriate portfolio. When you add a new version of a product to a portfolio, that version is automatically available to all current users.
You also can share your portfolios with other AWS accounts and allow the administrator of those accounts to distribute your portfolios with additional constraints, such as limiting which EC2 instances a user can create. Through the use of portfolios, permissions, sharing, and constraints, you can ensure that users are launching products that are configured properly for the organization’s needs and standards.
Versioning
Service Catalog allows you to manage multiple versions of the products in your catalog. This approach allows you to add new versions of templates and associated resources based on software updates or configuration changes.
When you create a new version of a product, the update is automatically distributed to all users who have access to the product, allowing the user to select which version of the product to use. Users can update running instances of the product to the new version quickly and easily.
Permissions
Granting a user access to a portfolio enables that user to browse the portfolio and launch the products in it. You apply AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) permissions to control who can view and modify your catalog. IAM permissions can be assigned to IAM users, groups, and roles.
When a user launches a product that has an IAM role assigned to it, Service Catalog uses the role to launch the product's cloud resources using AWS CloudFormation. By assigning an IAM role to each product, you can avoid giving users permissions to perform unapproved operations and enable them to provision resources using the catalog.
Constraints
Constraints control the ways that you can deploy specific AWS resources for a product. You can use them to apply limits to products for governance or cost control. There are different types of AWS Service Catalog constraints: launch constraints, notification constraints, and template constraints.
With launch constraints, you specify a role for a product in a portfolio. Use this role to provision the resources at launch, so you can restrict user permissions without impacting users' ability to provision products from the catalog.
Notification constraints enable you to get notifications about stack events using an Amazon SNS topic.
Template constraints restrict the configuration parameters that are available for the user when launching the product (for example, EC2 instance types or IP address ranges). With template constraints, you reuse generic AWS CloudFormation templates for products and apply restrictions to the templates on a per-product or per-portfolio basis.
Initial Administrator Workflow
This diagram shows the initial workflow for an administrator to create a catalog.

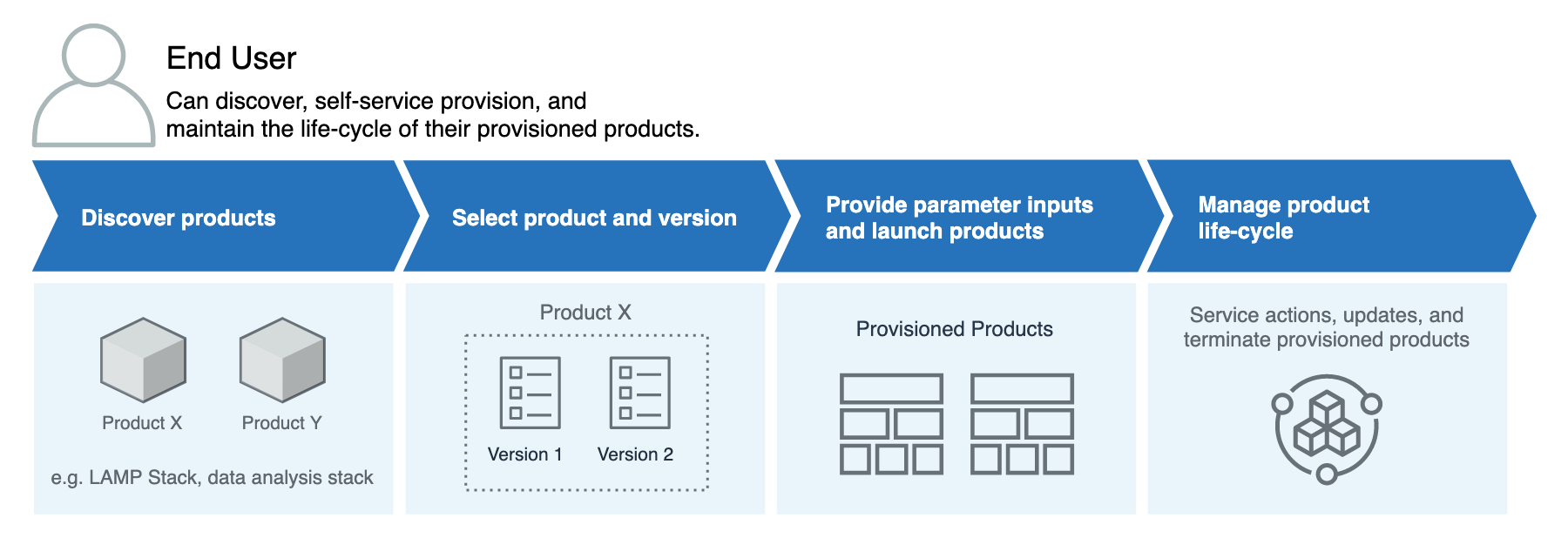
Initial End User Workflow
This diagram shows the initial workflow for an end user.