Creating a custom language model
Before you can create your custom language model, you must:
-
Prepare your data. Data must be saved in plain text format and can't contain any special characters.
-
Upload your data into an Amazon S3 bucket. Creating separate folders for training and tuning data is recommended.
-
Make sure Amazon Transcribe has access to your Amazon S3 bucket. You must specify an IAM role that has access permissions to use your data.
Preparing your data
You can compile all your data in one file or save it as multiple files. Note that if you choose to include tuning data, it must be saved in a separate file from your training data.
It doesn't matter how many text files you use for your training or tuning data. Uploading one file with 100,000 words produces the same result as uploading 10 files with 10,000 words. Prepare your text data in a way that's most convenient for you.
Make sure all your data files meet the following criteria:
-
They are all in the same language as the model you want to create. For example, if you want to create a custom language model that transcribes audio in US English (
en-US), all your text data must be in US English. -
They are in plain text format with UTF-8 encoding.
-
They don't contain any special characters or formatting, such as HTML tags.
-
They amount to a maximum combined total of 2 GB in size for training data and 200 MB for tuning data.
If any of these criteria are not met, your model fails.
Uploading your data
Before uploading your data, create a new folder for your training data. If using tuning data, create another separate folder.
The URIs for your buckets might look like:
-
s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/my-model-training-data/ -
s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/my-model-tuning-data/
Upload your training and tuning data into the appropriate buckets.
You can add more data to these buckets at a later date. However, if you do, you need to recreate your model with the new data. Existing models can't be updated with new data.
Allowing access to your data
To create a custom language model, you must specify an IAM role that has permissions to access your Amazon S3 bucket. If you don't already have a role with access to the Amazon S3 bucket where you placed your training data, you must create one. After you create a role, you can attach a policy to grant that role permissions. Do not attach a policy to a user.
For example policies, see Amazon Transcribe identity-based policy examples.
To learn how to create a new IAM identity, see IAM Identities (users, user groups, and roles).
To learn more about policies, see:
Creating your custom language model
When creating your custom language model, you must choose a base model. There are two base model options:
-
NarrowBand: Use this option for audio with a sample rate of less than 16,000 Hz. This model type is typically used for telephone conversations recorded at 8,000 Hz. -
WideBand: Use this option for audio with a sample rate greater than or equal to 16,000 Hz.
You can create custom language models using the AWS Management Console, AWS CLI, or AWS SDKs.; see the following examples:
-
Sign in to the AWS Management Console
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Custom language model. This opens the Custom language models page where you can view existing custom language models or train a new custom language model.
-
To train a new model, select Train model.

This takes you to the Train model page. Add a name, specify the language, and choose the base model you want for your model. Then, add the path to your training and, optionally, your tuning data. You must include an IAM role that has permissions to access your data.
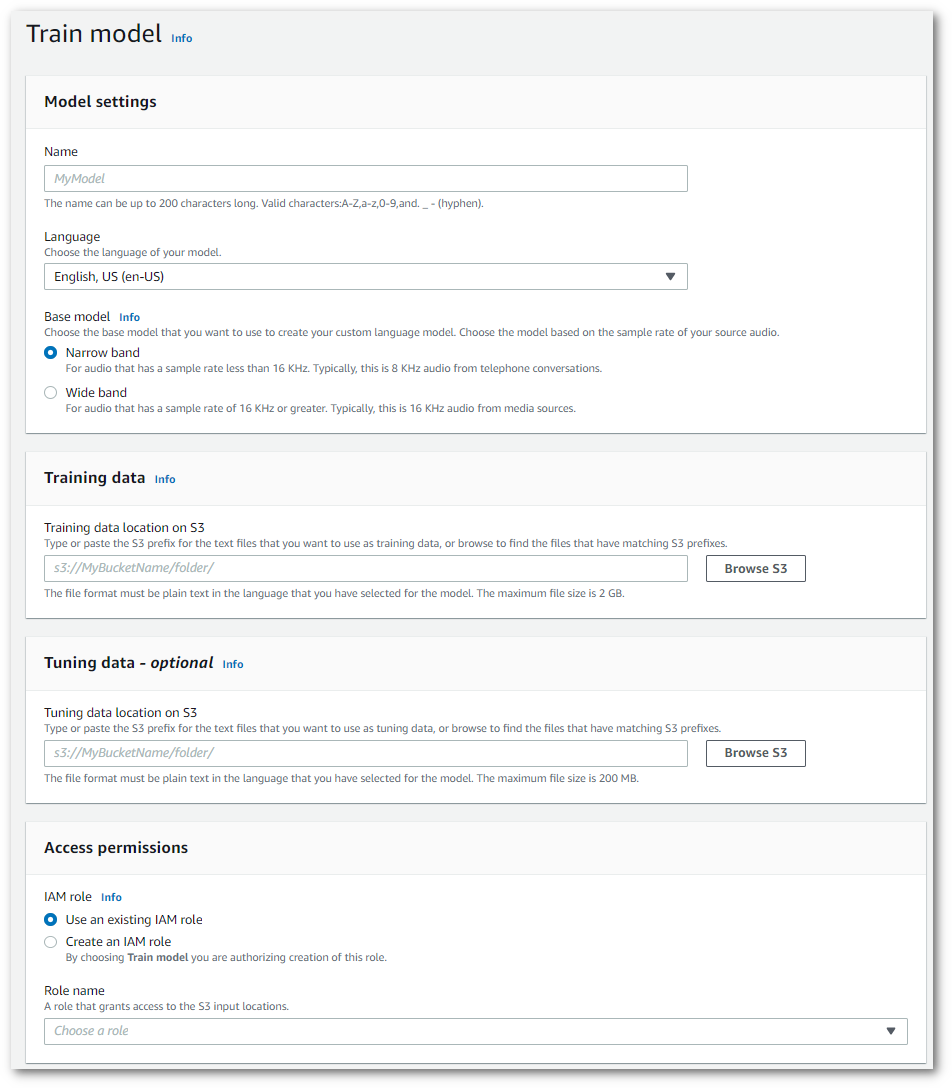
-
Once you have all fields completed, select Train model at the bottom of the page.
This example uses the create-language-modelCreateLanguageModel and
LanguageModel.
aws transcribe create-language-model \ --base-model-nameNarrowBand\ --model-namemy-first-language-model\ --input-data-config S3Uri=s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/my-clm-training-data/,TuningDataS3Uri=s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/my-clm-tuning-data/,DataAccessRoleArn=arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/ExampleRole\ --language-codeen-US
Here's another example using the create-language-model
aws transcribe create-language-model \ --cli-input-json file://filepath/my-first-language-model.json
The file my-first-language-model.json contains the following request body.
{ "BaseModelName": "NarrowBand", "ModelName": "my-first-language-model", "InputDataConfig": { "S3Uri": "s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/my-clm-training-data/", "TuningDataS3Uri"="s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/my-clm-tuning-data/", "DataAccessRoleArn": "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/ExampleRole" }, "LanguageCode": "en-US" }
This example uses the AWS SDK for Python (Boto3) to create a CLM using the
create_language_modelCreateLanguageModel and
LanguageModel.
For additional examples using the AWS SDKs, including feature-specific, scenario, and cross-service examples, refer to the Code examples for Amazon Transcribe using AWS SDKs chapter.
from __future__ import print_function import time import boto3 transcribe = boto3.client('transcribe', 'us-west-2') model_name = 'my-first-language-model', transcribe.create_language_model( LanguageCode = 'en-US', BaseModelName = 'NarrowBand', ModelName = model_name, InputDataConfig = { 'S3Uri':'s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/my-clm-training-data/', 'TuningDataS3Uri':'s3://amzn-s3-demo-bucket/my-clm-tuning-data/', 'DataAccessRoleArn':'arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/ExampleRole' } ) while True: status = transcribe.get_language_model(ModelName = model_name) if status['LanguageModel']['ModelStatus'] in ['COMPLETED', 'FAILED']: break print("Not ready yet...") time.sleep(5) print(status)
Updating your custom language model
Amazon Transcribe continually updates the base models available for custom language models. To benefit from these updates, we recommend training new custom language models every 6 to 12 months.
To see if your custom language model is using the latest base model, run a
DescribeLanguageModel
request using the AWS CLI or an AWS SDK, then find the
UpgradeAvailability field in your response.
If UpgradeAvailability is true, your model is not running
the latest version of the base model. To use the latest base model in a custom language model, you must
create a new custom language model. Custom language models cannot be upgraded.