Access AWS services through AWS PrivateLink
You access an AWS service using an endpoint. The default service endpoints are public interfaces, so you must add an internet gateway to your VPC so that traffic can get from the VPC to the AWS service. If this configuration doesn't work with your network security requirements, you can use AWS PrivateLink to connect your VPC to AWS services as if they were in your VPC, without the use of an internet gateway.
You can privately access the AWS services that integrate with AWS PrivateLink using VPC endpoints. You can build and manage all layers of your application stack without using an internet gateway.
Pricing
You are billed for each hour that your interface VPC endpoint is provisioned in each
Availability Zone. You are also billed per GB of data processed. For more information, see
AWS PrivateLink Pricing
Contents
Overview
You can access AWS services through their public service endpoints or connect to supported AWS services using AWS PrivateLink. This overview compares these methods.
Access through public service endpoints
The following diagram shows how instances access AWS services through the public service endpoints. Traffic to an AWS service from an instance in a public subnet is routed to the internet gateway for the VPC and then to the AWS service. Traffic to an AWS service from an instance in a private subnet is routed to a NAT gateway, then to the internet gateway for the VPC, and then to the AWS service. While this traffic traverses the internet gateway, it does not leave the AWS network.

Connect through AWS PrivateLink
The following diagram shows how instances access AWS services through AWS PrivateLink. First, you create an interface VPC endpoint, which establishes connections between the subnets in your VPC and an AWS service using network interfaces. Traffic destined for the AWS service is resolved to the private IP addresses of the endpoint network interfaces using DNS, and then sent to the AWS service using the connection between the VPC endpoint and the AWS service.
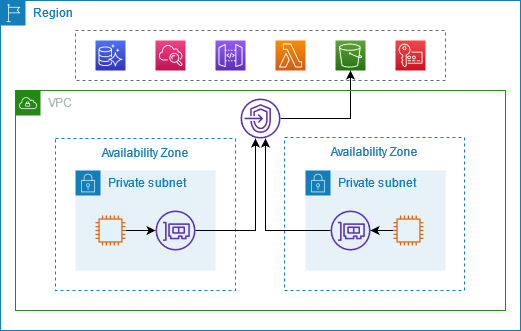
AWS services accept connection requests automatically. The service can't initiate requests to resources through the VPC endpoint.
DNS hostnames
Most AWS services offer public Regional endpoints, which have the following syntax.
protocol://service_code.region_code.amazonaws.comFor example, the public endpoint for Amazon CloudWatch in us-east-2 is as follows.
https://monitoring.us-east-2.amazonaws.comWith AWS PrivateLink, you send traffic to the service using private endpoints. When you create an interface VPC endpoint, we create Regional and zonal DNS names that you can use to communicate with the AWS service from your VPC.
The Regional DNS name for your interface VPC endpoint has the following syntax:
endpoint_id.service_id.region.vpce.amazonaws.comThe zonal DNS names have the following syntax:
endpoint_id-az_name.service_id.region.vpce.amazonaws.comWhen you create an interface VPC endpoint for an AWS service, you can enable private DNS. With private DNS, you can continue to make requests to a service using the DNS name for its public endpoint, while leveraging private connectivity through the interface VPC endpoint. For more information, see DNS resolution.
The following describe-vpc-endpoints command displays the DNS entries for an interface endpoint.
aws ec2 describe-vpc-endpoints --vpc-endpoint-idvpce-099deb00b40f00e22--query VpcEndpoints[*].DnsEntries
The following is example output for an interface endpoint for Amazon CloudWatch with private DNS names enabled. The first entry is the private Regional endpoint. The next three entries are the private zonal endpoints. The final entry is from the hidden private hosted zone, which resolves requests to the public endpoint to the private IP addresses of the endpoint network interfaces.
[ [ { "DnsName": "vpce-099deb00b40f00e22-lj2wisx3.monitoring.us-east-2.vpce.amazonaws.com", "HostedZoneId": "ZC8PG0KIFKBRI" }, { "DnsName": "vpce-099deb00b40f00e22-lj2wisx3-us-east-2c.monitoring.us-east-2.vpce.amazonaws.com", "HostedZoneId": "ZC8PG0KIFKBRI" }, { "DnsName": "vpce-099deb00b40f00e22-lj2wisx3-us-east-2a.monitoring.us-east-2.vpce.amazonaws.com", "HostedZoneId": "ZC8PG0KIFKBRI" }, { "DnsName": "vpce-099deb00b40f00e22-lj2wisx3-us-east-2b.monitoring.us-east-2.vpce.amazonaws.com", "HostedZoneId": "ZC8PG0KIFKBRI" }, { "DnsName": "monitoring.us-east-2.amazonaws.com", "HostedZoneId": "Z06320943MMOWYG6MAVL9" } ] ]
DNS resolution
The DNS records that we create for your interface VPC endpoint are public. Therefore, these DNS names are publicly resolvable. However, DNS requests from outside the VPC still return the private IP addresses of the endpoint network interfaces, so these IP addresses can't be used to access the endpoint service unless you have access to the VPC.
Private DNS
If you enable private DNS for your interface VPC endpoint, and your VPC has both DNS hostnames and DNS resolution enabled, we create a hidden, AWS-managed private hosted zone for you. The hosted zone contains a record set for the default DNS name for the service that resolves it to the private IP addresses of the endpoint network interfaces in your VPC. Therefore, if you have existing applications that send requests to the AWS service using a public Regional endpoint, those requests now go through the endpoint network interfaces, without requiring that you make any changes to those applications.
We recommend that you enable private DNS names for your VPC endpoints for AWS services. This ensures that requests that use the public service endpoints, such as requests made through an AWS SDK, resolve to your VPC endpoint.
Amazon provides a DNS server for your VPC, called the Route 53 Resolver. The Route 53 Resolver automatically
resolves local VPC domain names and record in private hosted zones. However, you can't use the
Route 53 Resolver from outside your VPC. If you'd like to access your VPC endpoint from your on-premises
network, you can use Route 53 Resolver endpoints and Resolver rules. For more information, see
Integrating AWS Transit Gateway with AWS PrivateLink and Amazon Route 53 Resolver
Subnets and Availability Zones
You can configure your VPC endpoint with one subnet per Availability Zone. We create an endpoint network interface for the VPC endpoint in your subnet. We assign IP addresses to each endpoint network interface from its subnet, based on the IP address type of the VPC endpoint. The IP addresses of an endpoint network interface will not change during the lifetime of its VPC endpoint.
In a production environment, for high availability and resiliency, we recommend the following:
-
Configure at least two Availability Zones per VPC endpoint and deploy your AWS resources that must access the AWS service in these Availability Zones.
-
Configure private DNS names for the VPC endpoint.
-
Access the AWS service by using its Regional DNS name, also known as the public endpoint.
The following diagram shows a VPC endpoint for Amazon CloudWatch with an endpoint network interface in a single Availability Zone. When any resource in any subnet in the VPC accesses Amazon CloudWatch using its public endpoint, we resolve the traffic to the IP address of the endpoint network interface. This includes traffic from subnets in other Availability Zones. However, if Availability Zone 1 is impaired, the resources in Availability Zone 2 lose access to Amazon CloudWatch.

The following diagram shows a VPC endpoint for Amazon CloudWatch with endpoint network interfaces in two Availability Zones. When any resource in any subnet in the VPC accesses Amazon CloudWatch by using its public endpoint, we select a healthy endpoint network interface, using the round robin algorithm to alternate between them. We then resolve the traffic to the IP address of the selected endpoint network interface.

If it's better for your use case, you can send traffic from your resources to the AWS service by using the endpoint network interface in the same Availability Zone. To do so, use the private zonal endpoint or IP address of the endpoint network interface.

IP address types
AWS services can support IPv6 through their private endpoints even if they do not support IPv6 through their public endpoints. Endpoints that support IPv6 can respond to DNS queries with AAAA records.
Requirements to enable IPv6 for an interface endpoint
-
The AWS service must make its service endpoints available over IPv6. For more information, see View IPv6 support.
-
The IP address type of an interface endpoint must be compatible with the subnets for the interface endpoint, as described here:
-
IPv4 – Assign IPv4 addresses to your endpoint network interfaces. This option is supported only if all selected subnets have IPv4 address ranges.
-
IPv6 – Assign IPv6 addresses to your endpoint network interfaces. This option is supported only if all selected subnets are IPv6 only subnets.
-
Dualstack – Assign both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses to your endpoint network interfaces. This option is supported only if all selected subnets have both IPv4 and IPv6 address ranges.
-
If an interface VPC endpoint supports IPv4, the endpoint network interfaces have IPv4
addresses. If an interface VPC endpoint supports IPv6, the endpoint network interfaces have
IPv6 addresses. The IPv6 address for an endpoint network interface is unreachable from the
internet. If you describe an endpoint network interface with an IPv6 address, notice that
denyAllIgwTraffic is enabled.
DNS record IP type
Depending on your IP address type, when you call a VPC endpoint, the AWS service can return A records, AAAA records, or both A and AAAA records. You can customize which record types your AWS service returns by modifying the DNS record IP type. The following table shows the supported DNS record IP types and the returned record types:
| DNS record IP type | Returned record types |
|---|---|
| IPv4 | A |
| IPv6 | AAAA |
| Dualstack | A and AAAA |
By default, the DNS record type is the same as the IP address type. You can choose a different DNS record IP type, but you must use a compatible IP address type for the endpoint service. The following table shows the supported DNS record IP type for each IP address types for interface endpoints:
| IP address type | Supported DNS record IP types |
|---|---|
| IPv4 | IPv4 |
| IPv6 | IPv6 |
| Dualstack | Dualstack*, IPv4, IPv6, service-defined |
* Represents the default DNS record IP type.
A service-defined DNS record IP type returns DNS records based on the service endpoint you call. If you use a service-defined DNS record IP type, make sure your service can handle variable calls from service endpoints. To see the DNS records supported by your interface endpoint, see the DNS names for your VPC endpoint in the AWS Management Console, or use DescribeVpcEndpoints.
The DNS record IP type behavior is different for gateway endpoints. For more information, see DNS record IP type for gateway endpoints.