Working with Oracle replicas for RDS Custom for Oracle
You can create Oracle replicas for RDS Custom for Oracle DB instances that run Oracle Enterprise Edition. Both container databases (CDBs) and non-CDBs are supported. Standard Edition 2 doesn't support Oracle Data Guard.
Creating an RDS Custom for Oracle replica is similar to creating an RDS for Oracle replica, but with important differences. For general information about creating and managing Oracle replicas, see Working with DB instance read replicas and Working with read replicas for Amazon RDS for Oracle.
Topics
Overview of RDS Custom for Oracle replication
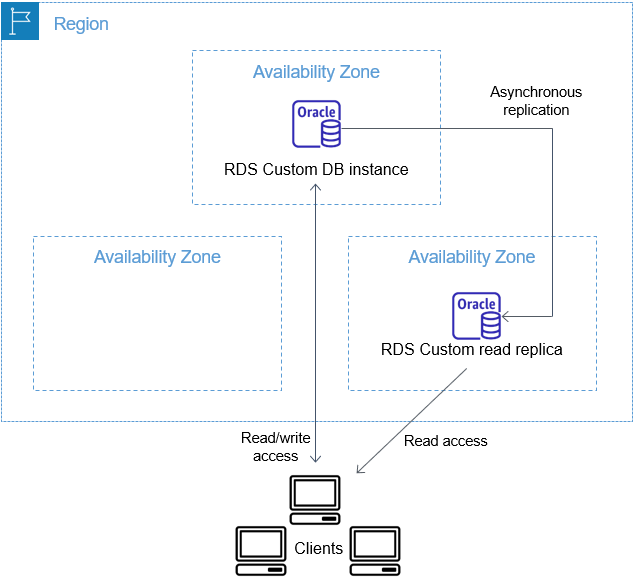
The architecture of RDS Custom for Oracle replication is analogous to RDS for Oracle replication. A primary DB instance replicates asynchronously to one or more Oracle replicas.
Maximum number of replicas
As with RDS for Oracle, you can create up to five managed Oracle replicas of your RDS Custom for Oracle primary DB instance. You can also create your own manually configured (external) Oracle replicas. External replicas don't count toward your DB instance limit. They also lie outside the RDS Custom support perimeter. For more information about the support perimeter, see RDS Custom support perimeter.
Replica naming convention
Oracle replica names are based on the database unique name. The format is
DB_UNIQUE_NAME_XORCL, the first two replicas are named ORCL_A and
ORCL_B. The first six letters, A–F, are reserved for RDS Custom.
RDS Custom copies database parameters from your primary DB instance to the replicas. For more
information, see DB_UNIQUE_NAME
Replica backup retention
By default, RDS Custom Oracle replicas use the same backup retention period as your primary DB instance. You can modify the backup retention period to 1–35 days. RDS Custom supports backing up, restoring, and point-in-time recovery (PITR). For more information about backing up and restoring RDS Custom DB instances, see Backing up and restoring an Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle DB instance.
Note
While creating a Oracle replica, RDS Custom temporarily pauses the cleanup of redo log files. In this way, RDS Custom ensures that it can apply these logs to the new Oracle replica after it becomes available.
Replica promotion
You can promote managed Oracle replicas in RDS Custom for Oracle using the console,
promote-read-replica AWS CLI command, or
PromoteReadReplica API. If you delete your primary DB instance, and all
replicas are healthy, RDS Custom for Oracle promotes your managed replicas to standalone
instances automatically. If a replica has paused automation or is outside the
support perimeter, you must fix the replica before RDS Custom can promote it
automatically. You can only promote external Oracle replicas manually.