Tutorial: Create a calculator REST API with two AWS service integrations and one Lambda non-proxy integration
The Tutorial: Create a REST API with a Lambda non-proxy
integration uses Lambda Function integration exclusively.
Lambda Function integration is a special case of the AWS
Service integration type that performs much of the integration setup for you,
such as automatically adding the required resource-based permissions for invoking the Lambda
function. Here, two of the three integrations use AWS Service integration. In
this integration type, you have more control, but you'll need to manually perform tasks like
creating and specifying an IAM role containing appropriate permissions.
In this tutorial, you'll create a Calc Lambda function that implements basic
arithmetic operations, accepting and returning JSON-formatted input and output. Then you'll
create a REST API and integrate it with the Lambda function in the following ways:
-
By exposing a
GETmethod on the/calcresource to invoke the Lambda function, supplying the input as query string parameters. (AWS Serviceintegration) -
By exposing a
POSTmethod on the/calcresource to invoke the Lambda function, supplying the input in the method request payload. (AWS Serviceintegration) -
By exposing a
GETon nested/calc/{operand1}/{operand2}/{operator}resources to invoke the Lambda function, supplying the input as path parameters. (Lambda Functionintegration)
In addition to trying out this tutorial, you may wish to study the OpenAPI definition
file for the Calc API, which you can import into API Gateway by following
the instructions in Develop REST APIs using
OpenAPI in API Gateway.
Topics
Integration 1: Create a GET method with query parameters to call the Lambda function
Integration 2: Create a POST method with a JSON payload to call the Lambda function
Integration 3: Create a GET method with path parameters to call the Lambda function
OpenAPI definitions of sample API integrated with a Lambda function
Create an assumable IAM role
In order for your API to invoke your Calc Lambda function, you'll need to
have an API Gateway assumable IAM role, which is an IAM role with the following trusted
relationship:
The role you create will need to have Lambda InvokeFunction permission. Otherwise, the API caller will receive a
500 Internal Server Error response. To give the role this permission,
you'll attach the following IAM policy to it:
Here's how to accomplish all this:
Create an API Gateway assumable IAM role
-
Log in to the IAM console.
-
Choose Roles.
-
Choose Create Role.
-
Under Select type of trusted entity, choose AWS Service.
-
Under Choose the service that will use this role, choose Lambda.
-
Choose Next: Permissions.
-
Choose Create Policy.
A new Create Policy console window will open up. In that window, do the following:
-
In the JSON tab, replace the existing policy with the following:
-
Choose Review policy.
-
Under Review Policy, do the following:
-
For Name, type a name such as
lambda_execute. -
Choose Create Policy.
-
-
-
In the original Create Role console window, do the following:
-
Under Attach permissions policies, choose your
lambda_executepolicy from the dropdown list.If you don't see your policy in the list, choose the refresh button at the top of the list. (Don't refresh the browser page!)
-
Choose Next:Tags.
-
Choose Next:Review.
-
For the Role name, type a name such as
lambda_invoke_function_assume_apigw_role. -
Choose Create role.
-
-
Choose your
lambda_invoke_function_assume_apigw_rolefrom the list of roles. -
Choose the Trust relationships tab.
-
Choose Edit trust relationship.
-
Replace the existing policy with the following:
-
Choose Update Trust Policy.
-
Make a note of the role ARN for the role you just created. You'll need it later.
Create a Calc
Lambda function
Next you'll create a Lambda function using the Lambda console.
-
In the Lambda console, choose Create function.
-
Choose Author from Scratch.
-
For Name, enter
Calc. -
For Runtime, choose either the latest supported Node.js or Python runtime.
For all other options, use the default setting.
-
Choose Create function.
-
Copy the following Lambda function in your preferred runtime and paste it into the code editor in the Lambda console.
-
Under Execution role, choose Choose an existing role.
-
Enter the role ARN for the
lambda_invoke_function_assume_apigw_rolerole you created earlier. -
Choose Deploy.
This function requires two operands (a and b) and an
operator (op) from the event input parameter. The input is a
JSON object of the following format:
{ "a": "Number" | "String", "b": "Number" | "String", "op": "String" }
This function returns the calculated result (c) and the input. For an
invalid input, the function returns either the null value or the "Invalid op" string as
the result. The output is of the following JSON format:
{ "a": "Number", "b": "Number", "op": "String", "c": "Number" | "String" }
You should test the function in the Lambda console before integrating it with the API in the next step.
Test the Calc
Lambda function
Here's how to test your Calc function in the Lambda console:
-
Choose the Test tab.
-
For the test event name, enter
calc2plus5. -
Replace the test event definition with the following:
{ "a": "2", "b": "5", "op": "+" } -
Choose Save.
-
Choose Test.
-
Expand Execution result: succeeded. You should see the following:
{ "a": 2, "b": 5, "op": "+", "c": 7 }
Create a Calc
API
The following procedure shows how to create an API for the Calc Lambda
function you just created. In subsequent sections, you'll add resources and methods to
it.
To create an API
Sign in to the API Gateway console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway
. -
If this is your first time using API Gateway, you see a page that introduces you to the features of the service. Under REST API, choose Build. When the Create Example API popup appears, choose OK.
If this is not your first time using API Gateway, choose Create API. Under REST API, choose Build.
For API name, enter
LambdaCalc.(Optional) For Description, enter a description.
Keep API endpoint type set to Regional.
For IP address type, select IPv4.
Choose Create API.
Integration 1: Create a GET method with query parameters to call the
Lambda function
By creating a GET method that passes query string parameters to the Lambda
function, you enable the API to be invoked from a browser. This approach can be useful,
especially for APIs that allow open access.
After you create an API, you create a resource. Typically, API resources are organized in a resource tree according to the application logic. For this step, you create a /calc resource.
To create a /calc resource
Choose Create resource.
Keep Proxy resource turned off.
Keep Resource path as
/.For Resource name, enter
calc.Keep CORS (Cross Origin Resource Sharing) turned off.
Choose Create resource.
By creating a GET method that passes query string parameters to the Lambda
function, you enable the API to be invoked from a browser. This approach can be useful,
especially for APIs that allow open access.
In this method, Lambda requires that the POST request be used to invoke any Lambda function. This example
shows that the HTTP method in a frontend method request can be different from the integration request in the
backend.
To create a GET method
Select the /calc resource, and then choose Create method.
For Method type, select GET.
For Integration type, select AWS service.
For AWS Region, select the AWS Region where you created your Lambda function.
For AWS service, select Lambda.
Keep AWS subdomain blank.
For HTTP method, select POST.
For Action type, select Use path override. This option allows us to specify the ARN of the Invoke action to execute our
Calcfunction.For Path override, enter
2015-03-31/functions/arn:aws:lambda:. Forus-east-2:account-id:function:Calc/invocationsaccount-idus-east-2For Execution role, enter the role ARN for
lambda_invoke_function_assume_apigw_role.Do not change the settings of Credential cache and Default timeout.
Choose Method request settings.
For Request validator, select Validate query string parameters and headers.
This setting will cause an error message to return if the client does not specify the required parameters.
Choose URL query string parameters.
Now you set up query string parameters for the GET method on the /calc resource so it can receive input on behalf of the backend Lambda function.
To create the query string parameters do the following:
Choose Add query string.
For Name, enter
operand1.Turn on Required.
Keep Caching turned off.
Repeat the same steps and create a query string named
operand2and a query string namedoperator.Choose Create method.
Now, you create a mapping template to translate the client-supplied query strings to the integration
request payload as required by the Calc function. This template maps the three query string
parameters declared in Method request into designated property values of the JSON object as the input to the
backend Lambda function. The transformed JSON object will be included as the integration request payload.
To map input parameters to the integration request
On the Integration request tab, under Integration request settings, choose Edit.
For Request body passthrough, select When there are no templates defined (recommended).
Choose Mapping templates.
Choose Add mapping template.
For Content type, enter
application/json.For Template body, enter the following code:
{ "a": "$input.params('operand1')", "b": "$input.params('operand2')", "op": "$input.params('operator')" }Choose Save.
You can now test your GET method to verify that it has been
properly set up to invoke the Lambda function.
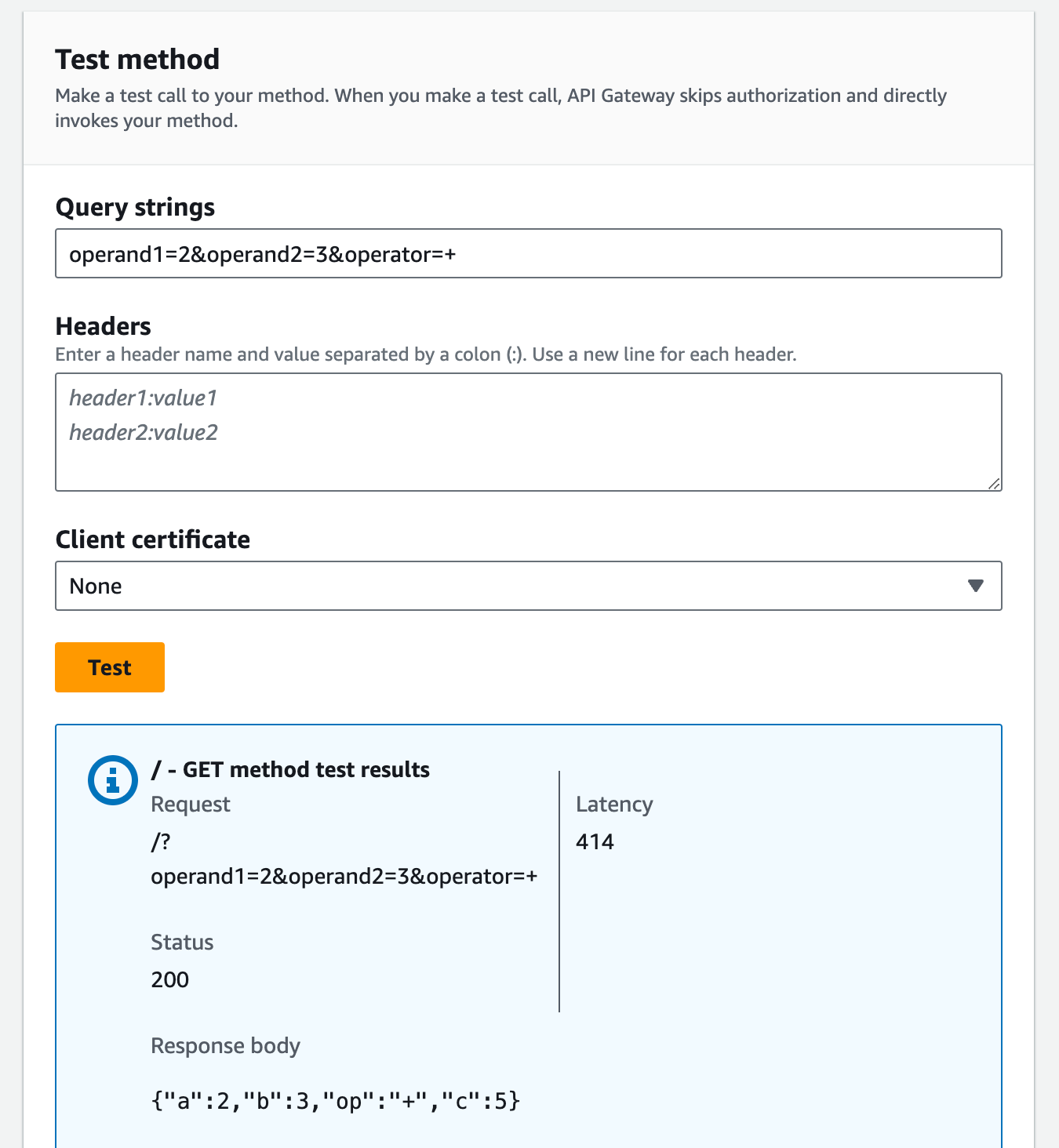
To test the GET method
-
Choose the Test tab. You might need to choose the right arrow button to show the tab.
For Query strings, enter
operand1=2&operand2=3&operator=+.-
Choose Test.
The results should look similar to this:
Integration 2: Create a POST method with a JSON payload to call the
Lambda function
By creating a POST method with a JSON payload to call the Lambda function,
you make it so that the client must provide the necessary input to the backend function
in the request body. To ensure that the client uploads the correct input data, you'll
enable request validation on the payload.
To create a POST method with a JSON payload
Select the /calc resource, and then choose Create method.
For Method type, select POST.
For Integration type, select AWS service.
For AWS Region, select the AWS Region where you created your Lambda function.
For AWS service, select Lambda.
Keep AWS subdomain blank.
For HTTP method, select POST.
For Action type, select Use path override. This option allows us to specify the ARN of the Invoke action to execute our
Calcfunction.For Path override, enter
2015-03-31/functions/arn:aws:lambda:. Forus-east-2:account-id:function:Calc/invocationsaccount-idus-east-2For Execution role, enter the role ARN for
lambda_invoke_function_assume_apigw_role.Do not change the settings of Credential cache and Default timeout.
Choose Create method.
Now you create an input model to describe the input data structure and validate the incoming request body.
To create an input model
-
In the main navigation pane, choose Models.
-
Choose Create model.
-
For Name, enter
input. -
For Content type, enter
application/json.If no matching content type is found, request validation is not performed. To use the same model regardless of the content type, enter
$default. -
For Model schema, enter the following model:
{ "type":"object", "properties":{ "a":{"type":"number"}, "b":{"type":"number"}, "op":{"type":"string"} }, "title":"input" } Choose Create model.
You now create an output model. This model describes the data structure of the calculated output from the backend. It can be used to map the integration response data to a different model. This tutorial relies on the passthrough behavior and does not use this model.
To create an output model
-
Choose Create model.
-
For Name, enter
output. -
For Content type, enter
application/json.If no matching content type is found, request validation is not performed. To use the same model regardless of the content type, enter
$default. -
For Model schema, enter the following model:
{ "type":"object", "properties":{ "c":{"type":"number"} }, "title":"output" } Choose Create model.
You now create a result model. This model describes the data structure of the returned response data. It references both the input and output schemas defined in your API.
To create a result model
-
Choose Create model.
-
For Name, enter
result. -
For Content type, enter
application/json.If no matching content type is found, request validation is not performed. To use the same model regardless of the content type, enter
$default. -
For Model schema, enter the following model with your
restapi-id. Yourrestapi-idis listed in parenthesis at the top of the console in the following flow:API Gateway > APIs > LambdaCalc (abc123).{ "type":"object", "properties":{ "input":{ "$ref":"https://apigateway.amazonaws.com/restapis/restapi-id/models/input" }, "output":{ "$ref":"https://apigateway.amazonaws.com/restapis/restapi-id/models/output" } }, "title":"result" } Choose Create model.
You now configure the method request of your POST method to enable request validation on the incoming request body.
To enable request validation on the POST method
-
In the main navigation pane, choose Resources, and then select the
POSTmethod from the resource tree. -
On the Method request tab, under Method request settings, choose Edit.
For Request validator, select Validate body.
Choose Request body, and then choose Add model.
For Content type, enter
application/json.If no matching content type is found, request validation is not performed. To use the same model regardless of the content type, enter
$default.For Model, select input.
Choose Save.
You can now test your POST method to verify that it has been
properly set up to invoke the Lambda function.
To test the POST method
-
Choose the Test tab. You might need to choose the right arrow button to show the tab.
For Request body, enter the following JSON payload.
{ "a": 1, "b": 2, "op": "+" }-
Choose Test.
You should see the following output:
{ "a": 1, "b": 2, "op": "+", "c": 3 }
Integration 3: Create a GET method with path parameters to call the
Lambda function
Now you'll create a GET method on a resource specified by a sequence of
path parameters to call the backend Lambda function. The path parameter values specify
the input data to the Lambda function. You'll use a mapping template to map the incoming path
parameter values to the required integration request payload.
The resulting API resource structure will look like this:
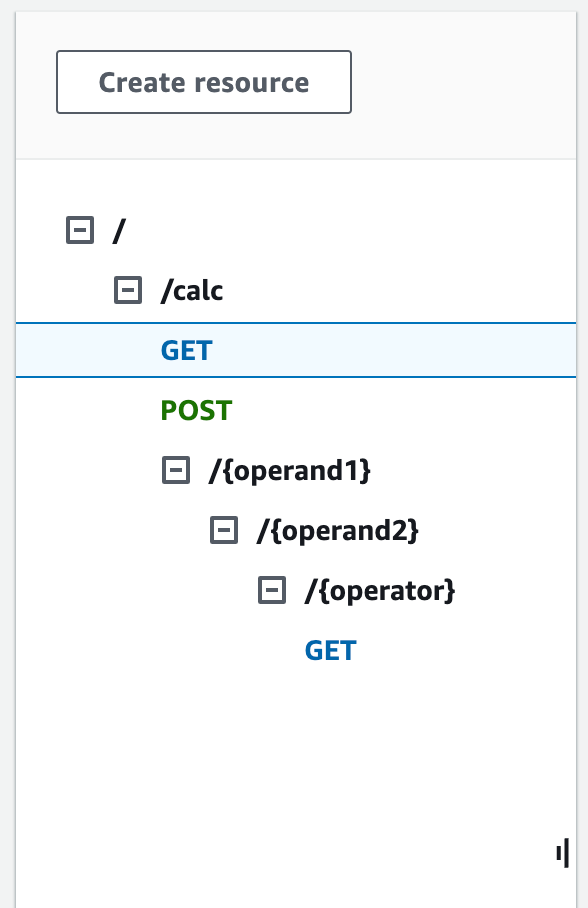
To create a /{operand1}/{operand2}/{operator} resource
Choose Create resource.
For Resource path, select
/calc.For Resource name, enter
{operand1}.Keep CORS (Cross Origin Resource Sharing) turned off.
Choose Create resource.
For Resource path, select
/calc/{operand1}/.For Resource name, enter
{operand2}.Keep CORS (Cross Origin Resource Sharing) turned off.
Choose Create resource.
For Resource path, select
/calc/{operand1}/{operand2}/.For Resource name, enter
{operator}.Keep CORS (Cross Origin Resource Sharing) turned off.
Choose Create resource.
This time you'll use the built-in Lambda integration in the API Gateway console to set up the method integration.
To set up a method integration
Select the /{operand1}/{operand2}/{operator} resource, and then choose Create method.
For Method type, select GET.
For Integration type, select Lambda.
Keep Lambda proxy integration turned off.
For Lambda function, select the AWS Region where you created your Lambda function and enter
Calc.Keep Default timeout turned on.
Choose Create method.
You now create a mapping template to map the three URL path parameters, declared when the
/calc/{operand1}/{operand2}/{operator} resource
was created, into designated property values in the JSON object. Because
URL paths must be URL-encoded, the division operator must be specified
as %2F instead of /. This template translates
the %2F into '/' before passing it to the
Lambda function.
To create a mapping template
On the Integration request tab, under Integration request settings, choose Edit.
For Request body passthrough, select When there are no templates defined (recommended).
Choose Mapping templates.
For Content type, enter
application/json.For Template body, enter the following code:
{ "a": "$input.params('operand1')", "b": "$input.params('operand2')", "op": #if($input.params('operator')=='%2F')"/"#{else}"$input.params('operator')"#end }Choose Save.
You can now test your GET method to verify that it has been
properly set up to invoke the Lambda function and pass the original output through the integration response without mapping.
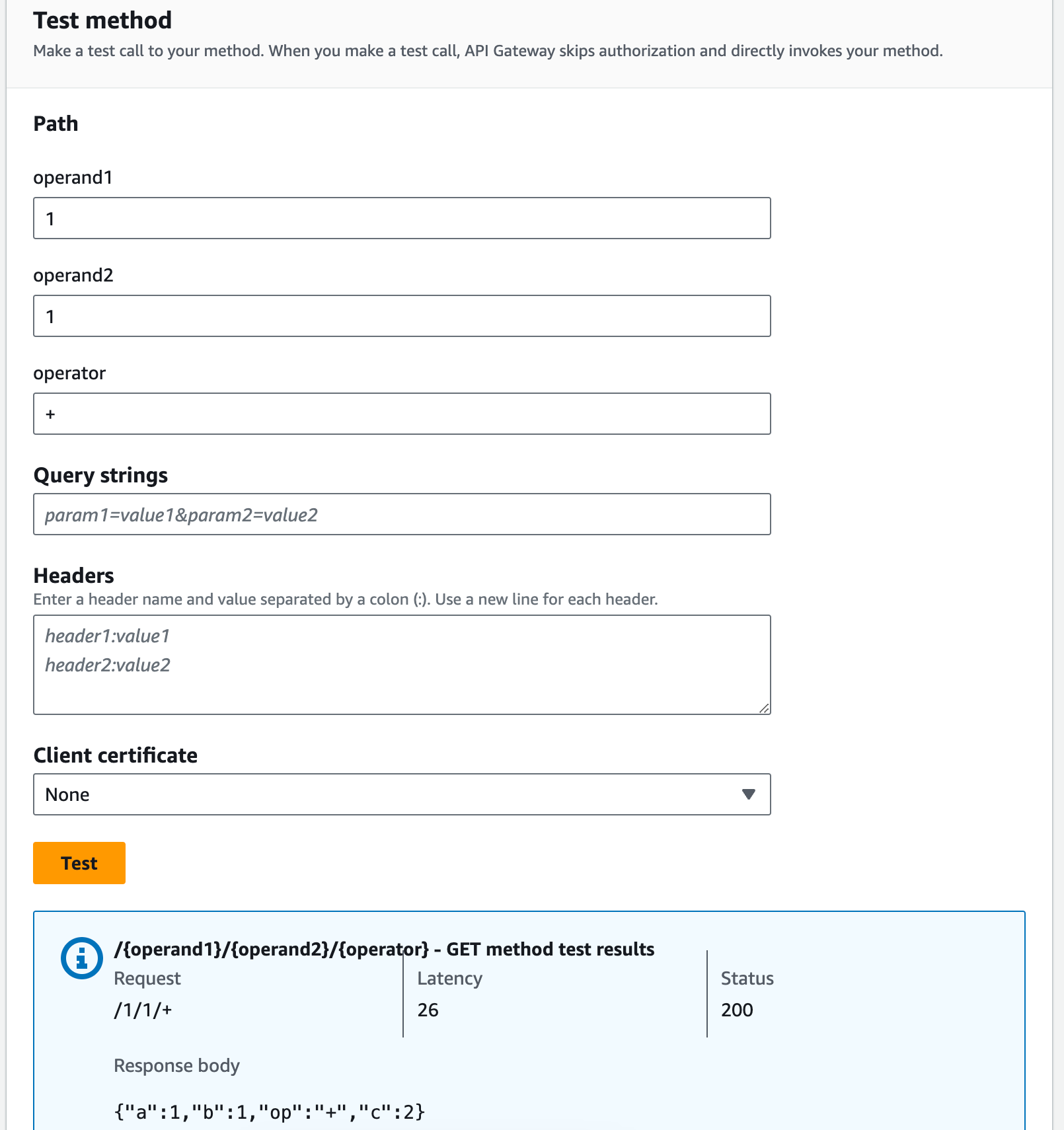
To test the GET method
-
Choose the Test tab. You might need to choose the right arrow button to show the tab.
-
For the Path, do the following:
For operand1, enter
1.For operand2, enter
1.For operator, enter
+.
-
Choose Test.
-
The result should look like this:
Next, you model the data structure of the method response
payload after the result schema.
By default, the method response body is assigned an empty model. This will cause the integration response body to be passed through without mapping. However, when you generate an SDK for one of the strongly-type languages, such as Java or Objective-C, your SDK users will receive an empty object as the result. To ensure that both the REST client and SDK clients receive the desired result, you must model the response data using a predefined schema. Here you'll define a model for the method response body and to construct a mapping template to translate the integration response body into the method response body.
To create a method response
-
On the Method response tab, under Response 200, choose Edit.
-
Under Response body, choose Add model.
-
For Content type, enter
application/json. -
For Model, select result.
-
Choose Save.
Setting the model for the method response body ensures that the response data
will be cast into the result object of a given SDK. To make sure
that the integration response data is mapped accordingly, you'll need a mapping
template.
To create a mapping template
On the Integration response tab, under Default - Response, choose Edit.
Choose Mapping templates.
For Content type, enter
application/json.For Template body, enter the following code:
#set($inputRoot = $input.path('$')) { "input" : { "a" : $inputRoot.a, "b" : $inputRoot.b, "op" : "$inputRoot.op" }, "output" : { "c" : $inputRoot.c } }Choose Save.
To test the mapping template
-
Choose the Test tab. You might need to choose the right arrow button to show the tab.
-
For the Path, do the following:
For operand1, enter
1.For operand2, enter
2.For operator, enter
+.
-
Choose Test.
-
The result will look like the following:
{ "input": { "a": 1, "b": 2, "op": "+" }, "output": { "c": 3 } }
At this point, you can only call the API using the Test feature in the API Gateway console. To make it available to clients, you'll need to deploy your API. Always be sure to redeploy your API whenever you add, modify, or delete a resource or method, update a data mapping, or update stage settings. Otherwise, new features or updates will not be available to clients of your API. as follows:
To deploy the API
Choose Deploy API.
For Stage, select New stage.
For Stage name, enter
Prod.(Optional) For Description, enter a description.
Choose Deploy.
-
(Optional) Under Stage details, for Invoke URL, you can choose the copy icon to copy your API's invoke URL. You can use this with tools such as Postman
and cURL to test your API.
Note
Always redeploy your API whenever you add, modify, or delete a resource or method, update a data mapping, or update stage settings. Otherwise, new features or updates will not be available to clients of your API.