OIDC user pool IdP authentication flow
With OpenID Connect (OIDC) sign-in, your user pool automates an authorization-code
sign-in flow with your identity provider (IdP). After your user completes sign-in
with their IdP, Amazon Cognito collects their code at the oauth2/idpresponse
endpoint of the external provider. With the resulting access token, your user pool
queries the IdP userInfo endpoint to retrieve user attributes. Your
user pool then compares the received attributes to the attribute-mapping rules
you've set up and populates the user's profile and ID token accordingly.
The OAuth 2.0 scopes that you request in your OIDC provider configuration define
the user attributes that the IdP provides to Amazon Cognito. As a best security practice,
only request the scopes that correspond to attributes that you want to map to your
user pool. For example, if your user pool requests openid profile,
you'll get all possible attributes, but if you request openid email
phone_number you'll only get the user's email address and phone number.
You can configure the scopes that you request from OIDC IdPs
to differ from those you authorize and request in the app client and user pool
authentication request.
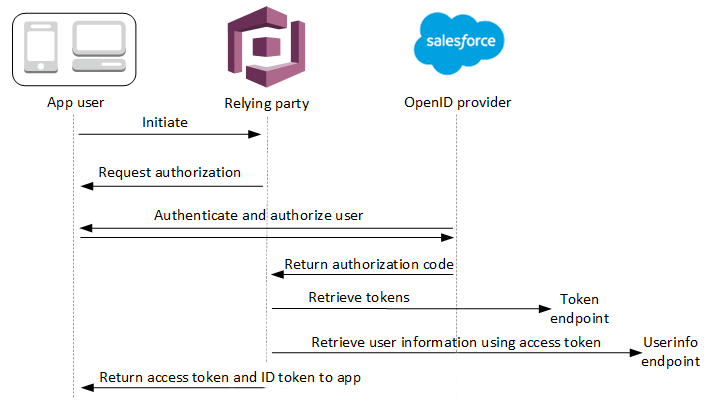
When your user signs in to your application using an OIDC IdP, your user pool conducts the following authentication flow.
-
A user accesses your managed login sign-in page, and chooses to sign in with their OIDC IdP.
-
Your application directs the user's browser to the authorization endpoint of your user pool.
-
Your user pool redirects the request to the authorization endpoint of the OIDC IdP.
-
Your IdP displays a login prompt.
-
In your application, your user's session displays a sign-in prompt for the OIDC IdP.
-
The user enters their credentials for the IdP or presents a cookie for an already-authenticated session.
-
After your user authenticates, the OIDC IdP redirects to Amazon Cognito with an authorization code.
-
Your user pool exchanges the authorization code for ID and access tokens. Amazon Cognito receives access tokens when you configure your IdP with the scopes
openid. The claims in the ID token and theuserInforesponse are determined by additional scopes from your IdP configuration, for exampleprofileandemail. -
Your IdP issues the requested tokens.
-
Your user pool determines the path to the IdP
jwks_uriendpoint from the issuer URLs in your IdP configuration and requests the token signing keys from the JSON web key set (JWKS) endpoint. -
The IdP returns signing keys from the JWKS endpoint.
-
Your user pool validates the IdP tokens from signature and expiration data in the tokens.
-
Your user pool authorizes a request to the IdP
userInfoendpoint with the access token. The IdP responds with user data based on the access token scopes. -
Your user pool compares the ID token and
userInforesponse from the IdP to the attribute-mapping rules in your user pool. It writes mapped IdP attributes to user pool profile attributes. -
Amazon Cognito issues your application bearer tokens, which might include identity, access, and refresh tokens.
-
Your application processes the user pool tokens and signs the user in.
Note
Amazon Cognito cancels authentication requests that do not complete within 5 minutes,
and redirects the user to managed login. The page displays a Something
went wrong error message.
OIDC is an identity layer on top of OAuth 2.0, which specifies JSON-formatted (JWT) identity tokens that are issued by IdPs to OIDC client apps (relying parties). See the documentation for your OIDC IdP for information about to add Amazon Cognito as an OIDC relying party.
When a user authenticates with an authorization code grant, the user pool returns
ID, access, and refresh tokens. The ID token is a standard OIDC
How a user pool processes claims from an OIDC provider
When your user completes sign-in with a third-party OIDC provider, managed
login retrieves an authorization code from the IdP. Your user pool exchanges the
authorization code for access and ID tokens with the token endpoint
of your IdP. Your user pool doesn't pass these tokens on to your user or your
app, but uses them to build a user profile with data that it presents in claims
in its own tokens.
Amazon Cognito doesn't independently validate the access token. Instead, it requests
user-attribute information from the provider userInfo endpoint and
expects the request to be denied if the token isn't valid.
Amazon Cognito validates the provider ID token with the following checks:
-
Check that the provider signed the token with an algorithm from the following set: RSA, HMAC, Elliptic Curve.
-
If the provider signed the token with an asymmetric signing algorithm, check that the signing key ID in the token
kidclaim is listed at the providerjwks_uriendpoint. Amazon Cognito refreshes the signing key from the JWKS endpoint in your IdP configuration for each IdP ID token that it processes. -
Compare the ID token signature to the signature that it expects based on provider metadata.
-
Compare the
issclaim to the OIDC issuer configured for the IdP. -
Compare the
audclaim matches the client ID configured on the IdP, or that it contains the configured client ID if there are multiple values in theaudclaim. -
Check that the timestamp in the
expclaim is not before the current time.
Your user pool validates the ID token, then attempts a request to the provider
userInfo endpoint with the provider access token. It retrieves
any user profile information that the scopes in the access token authorize it to
read. Your user pool then searches for the user attributes that you have set as
required in your user pool. You must create attribute mappings in your provider
configuration for required attributes. Your user pool checks the provider ID
token and the userInfo response. Your user pool writes all claims
that match mapping rules to user attributes on the user pool user profile. Your
user pool ignores attributes that match a mapping rule but aren't required and
aren't found in the provider's claims.