Environment types
In AWS Elastic Beanstalk, you can create a load-balanced, scalable environment or a single-instance environment. The type of environment that you require depends on the application that you deploy. For example, you can develop and test an application in a single-instance environment to save costs and then upgrade that environment to a load-balanced, scalable environment when the application is ready for production.
Note
A worker environment tier for a web application that processes background tasks doesn't include a load balancer. However, a worker environment does effectively scale out by adding instances to the Auto Scaling group to process data from the Amazon SQS queue when the load necessitates it.
Load-balanced, scalable environment
A load-balanced and scalable environment uses the Elastic Load Balancing and Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling services to provision the Amazon EC2 instances that are required for your deployed application. Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling automatically starts additional instances to accommodate increasing load on your application. If the load on your application decreases, Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling stops instances but always leaves your specified minimum number of instances running. If your application requires scalability with the option of running in multiple Availability Zones, use a load-balanced, scalable environment. If you're not sure which environment type to select, you can pick one and, if required, switch the environment type later.
Single-instance environment
A single-instance environment contains one Amazon EC2 instance with an Elastic IP address. A single-instance environment doesn't have a load balancer, which can help you reduce costs compared to a load-balanced, scalable environment. Although a single-instance environment does use the Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling service, settings for the minimum number of instances, maximum number of instances, and desired capacity are all set to 1. Consequently, new instances are not started to accommodate increasing load on your application.
Use a single-instance environment if you expect your production application to have low traffic or if you are doing remote development. If you're not sure which environment type to select, you can pick one and, if required, you can switch the environment type later. For more information, see Changing environment type.
Changing environment type
You can change your environment type to a single-instance or load-balanced, scalable environment by editing your environment's configuration. In some cases, you might want to change your environment type from one type to another. For example, let's say that you developed and tested an application in a single-instance environment to save costs. When your application is ready for production, you can change the environment type to a load-balanced, scalable environment so that it can scale to meet the demands of your customers.
To change an environment's type
Open the Elastic Beanstalk console
, and in the Regions list, select your AWS Region. -
In the navigation pane, choose Environments, and then choose the name of your environment from the list.
In the navigation pane, choose Configuration.
-
In the Capacity category, choose Edit.
-
From the Environment Type list, select the type of environment that you want.
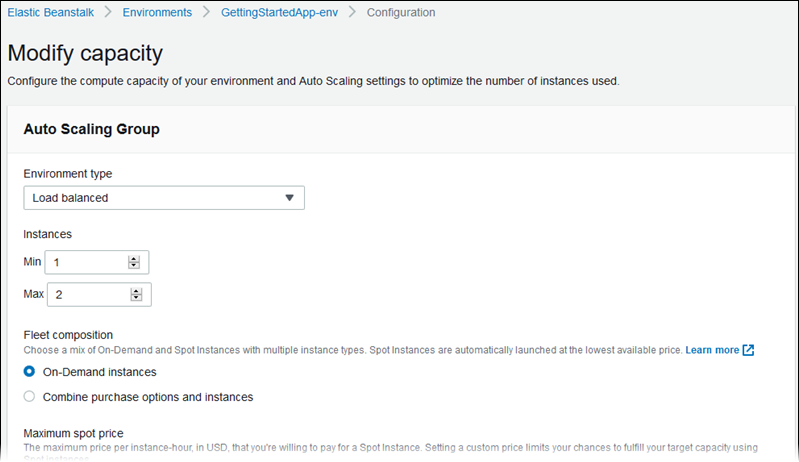
-
Choose Save.
It can take several minutes for the environment to update while Elastic Beanstalk provisions AWS resources.
If your environment is in a VPC, select subnets to place Elastic Load Balancing and Amazon EC2 instances in. Each Availability Zone that your application runs in must have both. See Using Elastic Beanstalk with Amazon VPC for details.