Keyrings
Supported programming language implementations use keyrings to perform envelope encryption. Keyrings generate, encrypt, and decrypt data keys. Keyrings determine the source of the unique data keys that protect each message, and the wrapping keys that encrypt that data key. You specify a keyring when encrypting and the same or a different keyring when decrypting. You can use the keyrings that the SDK provides or write your own compatible custom keyrings.
You can use each keyring individually or combine keyrings into a multi-keyring. Although most keyrings can generate, encrypt, and decrypt data keys, you might create a keyring that performs only one particular operation, such as a keyring that only generates data keys, and use that keyring in combination with others.
We recommend that you use a keyring that protects your wrapping keys and performs
cryptographic operations within a secure boundary, such as the AWS KMS keyring, which uses
AWS KMS keys that never leave AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS)
unencrypted. You can also write a keyring that uses wrapping keys that are stored in your
hardware security modules (HSMs) or protected by other master key services. For details, see the
Keyring Interface
Keyrings play the role of the master keys and master key providers used in other programming language implementations. If you use different language implementations of the AWS Encryption SDK to encrypt and decrypt your data, be sure to use compatible keyrings and master key providers. For details, see Keyring compatibility.
This topic explains how to use the keyring feature of the AWS Encryption SDK and how to choose a keyring.
How keyrings work
When you encrypt data, the AWS Encryption SDK asks the keyring for encryption materials. The keyring returns a plaintext data key and a copy of the data key that's encrypted by each of the wrapping keys in the keyring. The AWS Encryption SDK uses the plaintext key to encrypt the data, and then destroys the plaintext data key. Then, the AWS Encryption SDK returns an encrypted message that includes the encrypted data keys and the encrypted data.
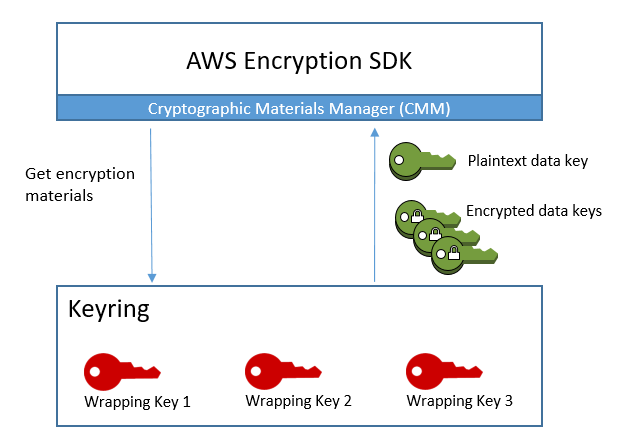
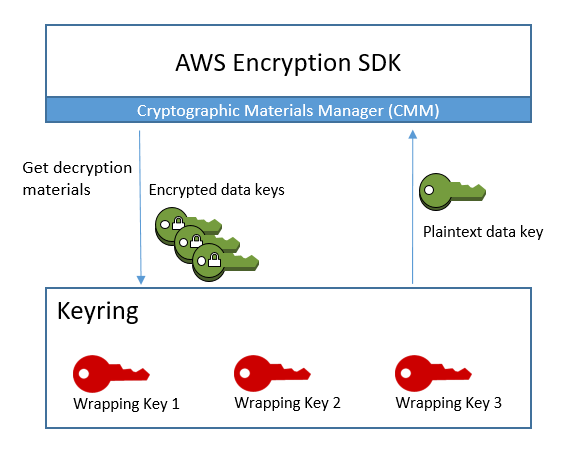
When you decrypt data, you can use the same keyring that you used to encrypt the data, or a different one. To decrypt the data, a decryption keyring must include (or have access to) at least one wrapping key in the encryption keyring.
The AWS Encryption SDK passes the encrypted data keys from the encrypted message to the keyring, and asks the keyring to decrypt any one of them. The keyring uses its wrapping keys to decrypt one of the encrypted data keys and returns a plaintext data key. The AWS Encryption SDK uses the plaintext data key to decrypt the data. If none of the wrapping keys in the keyring can decrypt any of the encrypted data keys, the decrypt operation fails.
You can use a single keyring or also combine keyrings of the same type or a different type into a multi-keyring. When you encrypt data, the multi-keyring returns a copy of the data key encrypted by all of the wrapping keys in all of the keyrings that comprise the multi-keyring. You can decrypt the data using a keyring with any one of the wrapping keys in the multi-keyring.
Keyring compatibility
Although the different language implementations of the AWS Encryption SDK have some architectural differences, they are fully compatible, subject to language constraints. You can encrypt your data using one language implementation and decrypt it with any other language implementation. However, you must use the same or corresponding wrapping keys to encrypt and decrypt your data keys. For information about language constraints, see the topic about each language implementation, such as Compatibility of the AWS Encryption SDK for JavaScript in the AWS Encryption SDK for JavaScript topic.
Keyrings are supported in the following programming languages:
-
AWS Encryption SDK for C
-
AWS Encryption SDK for JavaScript
-
AWS Encryption SDK for .NET
-
Version 3.x of the AWS Encryption SDK for Java
-
Version 4.x of the AWS Encryption SDK for Python, when used with the optional Cryptographic Material Providers Library
(MPL) dependency. -
AWS Encryption SDK for Rust
-
AWS Encryption SDK for Go
Varying requirements for encryption keyrings
In AWS Encryption SDK language implementations other than the AWS Encryption SDK for C, all wrapping keys in an encryption keyring (or multi-keyring) or master key provider must be able to encrypt the data key. If any wrapping key fails to encrypt, the encrypt method fails. As a result, the caller must have the required permissions for all keys in the keyring. If you use a discovery keyring to encrypt data, alone or in a multi-keyring, the encrypt operation fails.
The exception is the AWS Encryption SDK for C, where the encrypt operation ignores a standard discovery keyring, but fails if you specify a multi-Region discovery keyring, alone or in a multi-keyring.
Compatible Keyrings and Master Key Providers
The following table shows which master keys and master key providers are compatible with the keyrings that the AWS Encryption SDK supplies. Any minor incompatibility due to language constraints is explained in the topic about the language implementation.
| Keyring: | Master Key Provider: |
|---|---|
| AWS KMS keyring |
NoteThe AWS Encryption SDK for Python and AWS Encryption SDK for Java don't include a master key or master key provider that is equivalent to the AWS KMS regional discovery keyring. |
| AWS KMS Hierarchical keyring | Supported by the following programming languages and versions:
|
| AWS KMS ECDH keyring | Supported by the following programming languages and versions:
|
| Raw AES keyring | When they are used with symmetric encryption keys: JceMasterKeyRawMasterKey |
| Raw RSA keyring | When they are used with asymmetric encryption keys: JceMasterKeyRawMasterKey NoteThe Raw RSA keyring does not support asymmetric
KMS keys. If you want to use asymmetric RSA KMS keys,
version 4.x of the AWS Encryption SDK for .NET
supports AWS KMS keyrings that use symmetric encryption
( |
| Raw ECDH keyring | Supported by the following programming languages and versions:
|