Create rules to process LoRaWAN device messages
AWS IoT rules send device messages to other services. AWS IoT rules can also process the binary messages received from a LoRaWAN device to convert the messages to other formats that can make them easier for other services to use.
AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN destinations associate a wireless device with the rule that processes the device's message data to send to other services. The rule acts on the device's data as soon as AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN receives it. AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN destinations can be shared by all devices whose messages have the same data format and that send their data to the same service.
How AWS IoT rules process device messages
How an AWS IoT rule processes a device's message data depends on the service that will receive the data, the format of the device's message data, and the data format that the service requires. Typically, the rule calls an AWS Lambda function to convert the device's message data to the format a service requires, and then sends the result to the service.
The following illustration shows how message data is secured and processed as it moves from the wireless device to an AWS service.
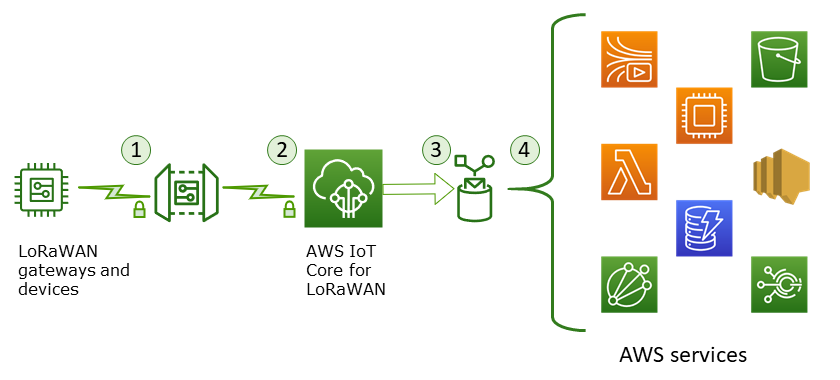
-
The LoRaWAN wireless device encrypts its binary messages using AES128 CTR mode before it transmits them.
-
AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN decrypts the binary message and encodes the decrypted binary message payload as a base64 string.
-
The resulting base64-encoded message is sent as a message payload, that is not formatted as a JSON document, to the AWS IoT rule described in the destination assigned to the device.
-
The AWS IoT rule directs the message data to the service described in the rule's configuration.
The encrypted binary payload received from the wireless device is not altered or interpreted by AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN. The decrypted binary message payload is encoded only as a base64 string. For services to access the data elements in the binary message payload, the data elements must be parsed out of the payload by a function called by the rule. The base64-encoded message payload is an ASCII string, so it could be stored as such to be parsed later.
Create rules for LoRaWAN devices
AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN uses AWS IoT rules to securely send device messages directly to other AWS services without the need to use the message broker. By removing the message broker from the ingestion path, it reduces costs and optimizes the data flow.
For an AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN rule to send device messages to other AWS services, it requires an AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN destination and an AWS IoT rule assigned to that destination. The AWS IoT rule must contain a SQL query statement and at least one rule action.
Typically, the AWS IoT rule query statement consists of:
-
A SQL SELECT clause that selects and formats the data from the message payload
-
A topic filter (the FROM object in the rule query statement) that identifies the messages to use
-
An optional conditional statement (a SQL WHERE clause) that specifies conditions on which to act
Here is an example of a rule query statement:
SELECT temperature FROM iot/topic' WHERE temperature > 50
When building AWS IoT rules to process payloads from LoRaWAN devices, you do not have to specify the FROM clause as part of the rule query object. The rule query statement must have the SQL SELECT clause and can optionally have the WHERE clause. If the query statement uses the FROM clause, it is ignored.
Here is an example of a rule query statement that can process payloads from LoRaWAN devices:
SELECT WirelessDeviceId, WirelessMetadata.LoRaWAN.FPort as FPort, WirelessMetadata.LoRaWAN.DevEui as DevEui, PayloadData
In this example, the PayloadData is a base64-encoded binary
payload sent by your LoRaWAN device.
Here is an example rule query statement that can perform a binary decoding of the incoming payload and transform it into a different format such as JSON:
SELECT WirelessDeviceId, WirelessMetadata.LoRaWAN.FPort as FPort, WirelessMetadata.LoRaWAN.DevEui as DevEui, aws_lambda("arn:aws:lambda:<region>:<account>:function:<name>", { ]"PayloadData":PayloadData, "Fport": WirelessMetadata.LoRaWAN.FPort } ) as decodingoutput
For more information on using the SELECT AND WHERE clauses, see AWS IoT SQL reference.
For information about AWS IoT rules and how to create and use them, see AWS IoT rules and AWS IoT rules tutorials.
For information about creating and using AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN destinations, see Add destinations to AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN.
For information about using binary message payloads in a rule, see Binary payloads.
For more information about the data security and encryption used to protect the message payload on its journey, see Data protection in AWS IoT Wireless.
For a reference architecture that shows a binary decoding and implementation
example for IoT rules, see AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN Solution Samples on GitHub