Strengthening security in IAM Roles Anywhere by using certificate-based access controls
Alberto Sagrado Amador, Amazon Web Services
July 2025 (document history)
As organizations expand their cloud footprints and embrace automation, it's increasingly
critical to manage secure access for non-human identities, such as applications, servers,
and containers. Traditional approaches use long-term credentials or hard-coded secrets, but
these approaches can create security risks and operational overhead. AWS Identity and Access Management Roles Anywhere addresses these challenges by allowing workloads outside of the
AWS Cloud to access AWS resources securely through X.509 certificates
Organizations commonly struggle with the proliferation of access keys, complex credential rotation, and limited ability to enforce fine-grained access controls. Modern security frameworks emphasize Zero Trust principles, just-in-time access, and the principle of least privilege—all of which can be achieved through proper implementation of certificate-based authentication.
This guide demonstrates how to enhance security in IAM Roles Anywhere by effectively managing certificate attributes and AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role trust relationships. It uses a practical architectural example to demonstrate how to implement fine-grained access controls and enforce the principle of least privilege in IAM Roles Anywhere sessions.
The architecture uses IAM Roles Anywhere and AWS Private Certificate Authority (AWS Private CA). AWS Private CA acts as a trust anchor, and AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) manages the certificates. This foundation reflects real-world security configurations and their implications.
Without proper policy configurations for IAM roles, any certificate issued by AWS Private CA could potentially be used to assume roles. This can create significant security vulnerabilities, including unauthorized role assumption, data breaches, and credential compromise. This guide shows how to help mitigate these risks through proper configuration of policies and management of certificate attributes.
The following diagram shows the workflow of how an application can request access through IAM Roles Anywhere and then perform the permitted actions in the target AWS account.
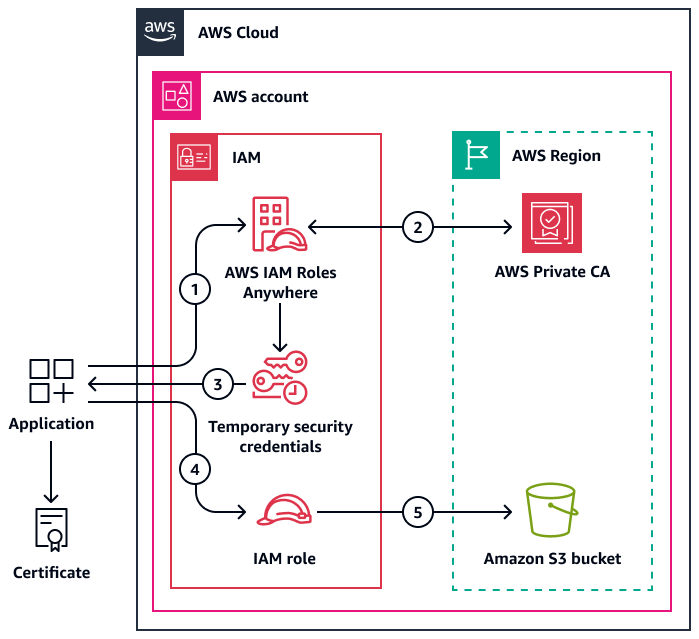
The diagram shows the following workflow:
-
The application requests temporary security credentials from IAM Roles Anywhere and provides its certificate for authentication.
-
IAM Roles Anywhere uses a trust relationship to authenticate the application with AWS Private CA.
-
IAM Roles Anywhere generates a JSON file that contains the temporary security credentials and returns it to the application.
-
Using the temporary security credentials, the application assumes an IAM role in the AWS account.
The application performs the actions allowed by the policies attached to the IAM role and in the account. For example, it might access an Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket.
Intended audience
This guide is intended for cloud architects, security engineers, and DevOps engineers who are implementing access controls for hybrid cloud environments or automating permissions management for non-human identities. This guide can also help you comply with regulations or meet security best practices. To understand the concepts and recommendations in this guide, you should be familiar with the following:
-
IAM fundamentals
-
Public key infrastructure (PKI) and X.509 certificate management
-
Principles of Zero Trust security and least-privilege access
-
AWS services for certificate-based authentication, such as IAM Roles Anywhere and AWS Private CA
Objectives
Using IAM Roles Anywhere and X.509 certificates for authentication can deliver the following key business outcomes:
-
Enhanced security – Eliminates risks associated with use of long-term credentials
-
Reduced operational overhead – Automates credential management and rotation
-
Improved compliance – Provides detailed audit trails and enforces least-privilege access
-
Scalable management – Centralizes access control across hybrid environments
-
Cost efficiency – Reduces costs associated with security incident response efforts and management complexity