IVS Real-Time Streaming Optimizations
To ensure that your users have the best experience when streaming and viewing video using IVS real-time streaming, there are several ways you can improve or optimize for parts of the experience, using features that we offer today.
Introduction
When optimizing for a user's quality of experience, it’s important to consider their desired experience, which can change depending on the content they are watching and network conditions.
Throughout this guide we focus on users who are either publishers of streams or subscribers of streams, and we consider the desired actions and experiences of those users.
The IVS SDKs allow you to configure the maximum bitrate, framerate, and resolution of the stream. When network congestion occurs for publishers, the SDK automatically adapts and lowers the video quality by lowering the bitrate, framerate, and resolution. On Android and iOS, it’s possible to select the degradation preference when congestion is encountered. The same behavior is true whether you enable layered encoding with simulcast or keep the default configuration.
Adaptive Streaming: Layered Encoding with Simulcast
This feature is supported only in the following client versions:
-
iOS and Android 1.18.0+
-
Web 1.12.0+
When using IVS real-time broadcast SDKs, publishers can encode multiple layers of video and subscribers automatically adapt or change to the quality best suited for their network. We call this layered encoding with simulcast.
Layered encoding with simulcast is supported on Android and iOS, and on the Chrome and Edge desktop browsers (for Windows and macOS). We do not support layered encoding on other browsers.
In the diagram below, the host is sending three video qualities (high, medium, and low). IVS forwards the highest quality video to each viewer based on available bandwidth; this provides an optimal experience for each viewer. If Viewer 1's network connection changes from good to bad, IVS automatically starts sending Viewer 1 lower quality video, so Viewer 1 can keep watching the stream uninterrupted (with the best quality possible).
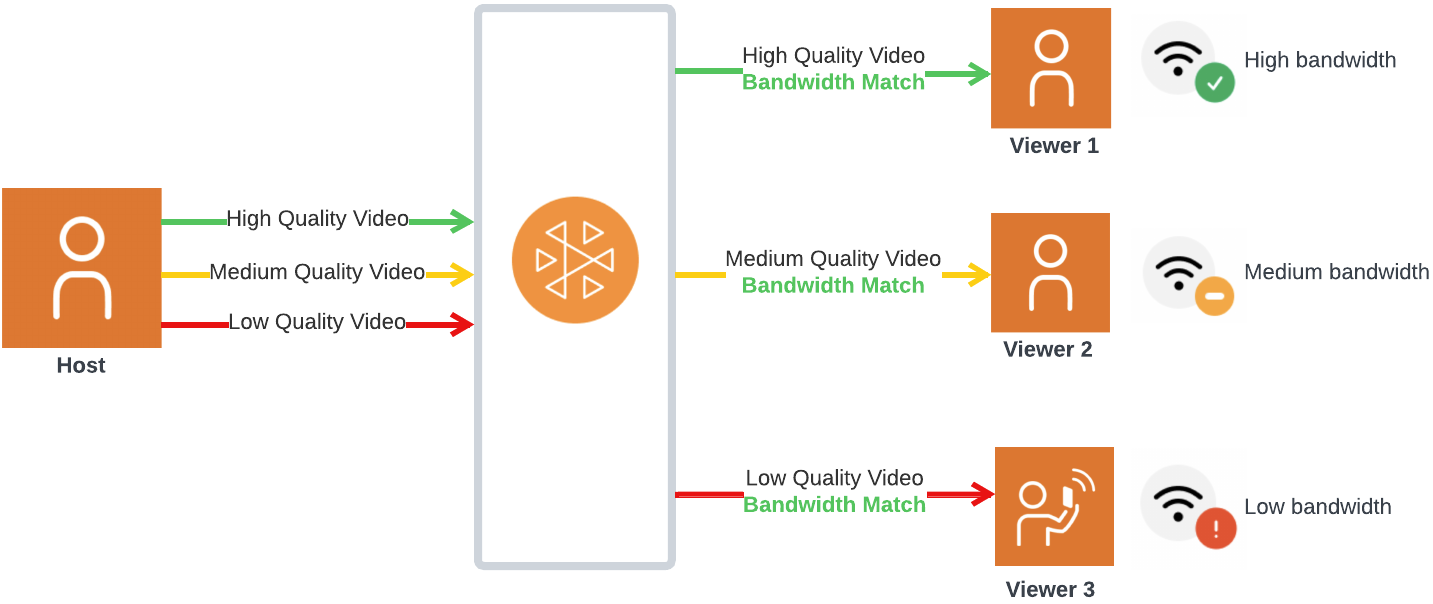
Default Layers, Qualities, and Framerates
The default qualities and layers provided for mobile and web users are as follows:
| Mobile (Android, iOS) | Web (Chrome) |
|---|---|
High layer (or custom):
|
High layer (or custom):
|
Mid layer: none (not needed, because the difference between the high- and low-layer bitrates on mobile is narrow) |
Mid layer:
|
Low layer:
|
Low layer:
|
Resolution of Layers
The resolutions of the mid and low layers are automatically scaled down from the high layer, to maintain the same aspect ratio.
Mid and low layers are excluded if their resolutions are too close to the layer above. For example, if the configured resolution is 320x180, the SDK won't also send lower-resolution layers.
The table below shows the resolutions of layers generated for different configured resolutions. The listed values are in landscape orientation but can be applied in reverse for portrait content.
| Input Resolution | Output Layer Resolutions: Mobile | Output Layer Resolutions: Web |
|---|---|---|
|
720p (1280x720) |
Hi (1280x720) Low (320x180) |
Hi (1280x720) Mid (640x360) Low (320x180) |
|
540p (960x540) |
Hi (960x540) Low (320x180) |
Hi (960x540) Low (320x180) |
|
360p (640x360) |
Hi (640x360) Low (360x180) |
Hi (640x360) Low (360x180) |
|
270p (480x270) |
Hi (480x270) |
Hi (480x270) |
|
180p (320x180) |
Hi (320x180) |
Hi (320x180) |
For custom input resolutions not mapped above, you can calculate them using the following tool
Configuring Layered Encoding with Simulcast (Publisher)
To use layered encoding with simulcast, you must have enabled the feature on the client. If you enable it, you will see an increase in upload bandwidth usage by the publisher, potentially with less video freezing for viewers.
Android
// Enable Simulcast StageVideoConfiguration config = new StageVideoConfiguration(); config.simulcast.setEnabled(true); ImageLocalStageStream cameraStream = new ImageLocalStageStream(frontCamera, config); // Other Stage implementation code
iOS
// Enable Simulcast let config = IVSLocalStageStreamVideoConfiguration() config.simulcast.enabled = true let cameraStream = IVSLocalStageStream(device: camera, configuration: config) // Other Stage implementation code
Web
// Enable Simulcast let cameraStream = new LocalStageStream(cameraDevice, { simulcast: { enabled: true } }) // Other Stage implementation code
For detailed information on configurating individual layers, see "Configuring Layered Encoding (Publisher)" in each broadcast SDK guide: Android, iOS, and Web.
Configuring Layered Encoding with Simulcast (Subscriber)
To configure what layers are received by subscribers, see the "Layered Encoding with Simulcast" sections in the real-time streaming SDK guides:
With subscriber configuration, it’s possible to define the InitialLayerPreference. This dictates what quality of video is delivered initially, as well as the preferredLayerForStream, which in turn determines what layer is selected during video playback. There are events and stream methods for notifying when layers change, adaption changes, or a layer selection is made.
Streaming Configurations
This section explores other configurations you can make to your video and audio streams.
Changing Video Stream Bitrate
To change the bitrate of your video stream, use the following configuration samples.
Android
StageVideoConfiguration config = new StageVideoConfiguration(); // Update Max Bitrate to 1.5mbps config.setMaxBitrate(1500000); ImageLocalStageStream cameraStream = new ImageLocalStageStream(frontCamera, config); // Other Stage implementation code
iOS
let config = IVSLocalStageStreamVideoConfiguration(); // Update Max Bitrate to 1.5mbps try! config.setMaxBitrate(1500000); let cameraStream = IVSLocalStageStream(device: camera, configuration: config); // Other Stage implementation code
Web
let cameraStream = new LocalStageStream(camera.getVideoTracks()[0], { // Update Max Bitrate to 1.5mbps or 1500kbps maxBitrate: 1500 }) // Other Stage implementation code
Changing Video Stream Framerate
To change the framerate of your video stream, use the following configuration samples.
Android
StageVideoConfiguration config = new StageVideoConfiguration(); // Update target framerate to 10fps config.targetFramerate(10); ImageLocalStageStream cameraStream = new ImageLocalStageStream(frontCamera, config); // Other Stage implementation code
iOS
let config = IVSLocalStageStreamVideoConfiguration(); // Update target framerate to 10fps try! config.targetFramerate(10); let cameraStream = IVSLocalStageStream(device: camera, configuration: config); // Other Stage implementation code
Web
// Note: On web it is also recommended to configure the framerate of your device from userMedia const camera = await navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia({ video: { frameRate: { ideal: 10, max: 10, }, }, }); let cameraStream = new LocalStageStream(camera.getVideoTracks()[0], { // Update Max Framerate to 10fps maxFramerate: 10 }) // Other Stage implementation code
Optimizing Audio Bitrate and Stereo Support
To change the bitrate and stereo settings of your audio stream, use the following configuration samples.
Web
// Note: Disable autoGainControl, echoCancellation, and noiseSuppression when enabling stereo. const camera = await navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia({ audio: { autoGainControl: false, echoCancellation: false, noiseSuppression: false }, }); let audioStream = new LocalStageStream(camera.getAudioTracks()[0], { // Optional: Update Max Audio Bitrate to 96Kbps. Default is 64Kbps maxAudioBitrateKbps: 96, // Signal stereo support. Note requires dual channel input source. stereo: true }) // Other Stage implementation code
Android
StageAudioConfiguration config = new StageAudioConfiguration(); // Update Max Bitrate to 96Kbps. Default is 64Kbps. config.setMaxBitrate(96000); AudioLocalStageStream microphoneStream = new AudioLocalStageStream(microphone, config); // Other Stage implementation code
iOS
let config = IVSLocalStageStreamConfiguration(); // Update Max Bitrate to 96Kbps. Default is 64Kbps. try! config.audio.setMaxBitrate(96000); let microphoneStream = IVSLocalStageStream(device: microphone, config: config); // Other Stage implementation code
Changing Subscriber Jitter Buffer MinDelay
To change the jitter buffer minimum delay for a participant who is being
subscribed to, a custom subscribeConfiguration can be used. The jitter
buffer determines how many packets are stored before playback begins. The minimum
delay represents the target for the minimum amount of data that should be stored.
Changing the minimum delay can help playback be more resilient when facing packet
loss/connection issues.
The tradeoff when increasing the size of the jitter buffer is that it also will increase the delay before playback begins. Increasing the minimum delay provides more resilience, at the cost of impacting time to video. Note that increasing the minimum delay during playback has a similar effect: playback will pause briefly to allow the jitter buffer to fill.
If more resiliency is needed, we recommend starting with a
minimum-delay preset of MEDIUM and setting the subscribe configuration
before playback begins.
Note that the minimum delay is applied only if a participant is subscribe-only. If a participant is publishing themselves, the minimum delay is not applied. This is done to ensure that multiple publishers can speak to each other without additional delay.
The examples below use a minimum delay preset of
MEDIUM. See the SDK reference documentation for all possible
values.
Web
const strategy = { subscribeConfiguration: (participant) => { return { jitterBuffer: { minDelay: JitterBufferMinDelay.MEDIUM } } // ... other strategy functions }
Android
@Override public SubscribeConfiguration subscribeConfigrationForParticipant(@NonNull Stage stage, @NonNull ParticipantInfo participantInfo) { SubscribeConfiguration config = new SubscribeConfiguration(); config.jitterBuffer.setMinDelay(JitterBufferConfiguration.JitterBufferDelay.MEDIUM()); return config; }
iOS
func stage(_ stage: IVSStage, subscribeConfigurationForParticipant participant: IVSParticipantInfo) -> IVSSubscribeConfiguration { let config = IVSSubscribeConfiguration() try! config.jitterBuffer.setMinDelay(.medium()) return config }
Suggested Optimizations
| Scenario | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Streams with text, or slow moving content, like presentations or slides | Use layered encoding with simulcast or configure streams with lower framerate. |
| Streams with action or a lot of movement | Use layered encoding with simulcast. |
| Streams with conversation or little movement | Use layered encoding with simulcast or choose audio-only (see "Subscribing to Participants" in the Real-Time Streaming Broadcast SDK Guides: Web, Android, and iOS). |
| Users streaming with limited data | Use layered encoding with simulcast or, if you want lower data usage for everyone, configure a lower framerate and lower the bitrate manually. |