Architecture for certificate-based access controls in AWS
You can use AWS Identity and Access Management Roles Anywhere to obtain temporary security credentials in AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for workloads such as servers, containers, and applications that run outside of AWS. Your workloads can use the same IAM policies and IAM roles that you use to access AWS resources. IAM Roles Anywhere eliminates the need to manage long-term credentials for workloads that operate outside of the AWS Cloud.
To use IAM Roles Anywhere, your workloads must use X.509 certificates that are issued by your certificate authority (CA). You register the CA with IAM Roles Anywhere as a trust anchor to establish trust between your public-key infrastructure and IAM Roles Anywhere. In this guide, you use AWS Private Certificate Authority (AWS Private CA) as the CA and then establish trust with IAM Roles Anywhere. In the context of IAM Roles Anywhere, AWS Private CA serves as a trusted source for issuing certificates with specific attributes that can be used to control access to AWS resources through fine-grained policies.
This guide provides two different options for configuring certificate-based access to the AWS resources in the target AWS account and AWS Region. The following diagram shows the resources that are common between both options. AWS Private CA is set up in the same account and Region where IAM Roles Anywhere is deployed. A trust anchor exists between IAM Roles Anywhere and AWS Private CA. By default, all the certificates that AWS Private CA generates are allowed for use during the signing process and are stored within AWS Certificate Manager (ACM). For the purposes of this guide, the applications are accessing one or more Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) buckets in the AWS account.
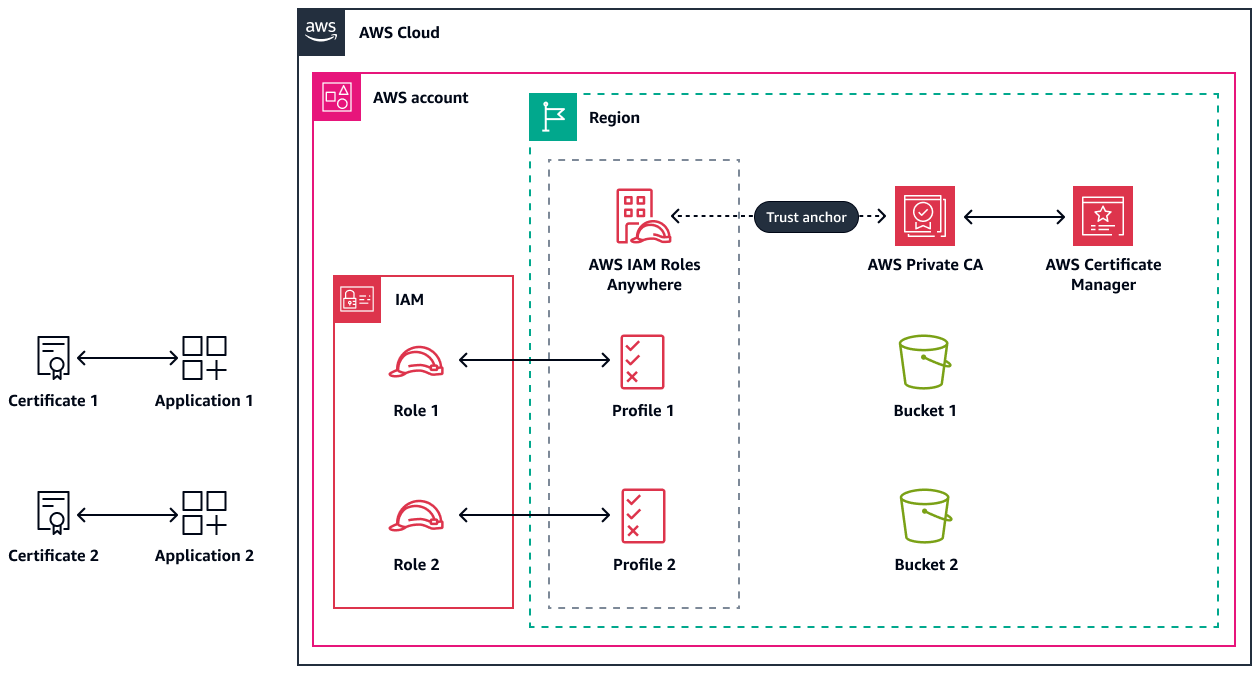
The architecture must have the following features:
-
Certificates – You can use ACM to generate certificates. Because ACM is a Regional service, it must be deployed in the same AWS Region as AWS Private CA. Due to cross-account limitations, we recommend that you deploy ACM in the same account as AWS Private CA. For more information, see Conditions for using AWS Private CA to sign ACM private certificates in the ACM documentation.
-
A certificate authority – You can use AWS Private CA or use an external CA. Because AWS Private CA is a Regional service, it must be deployed in the same AWS Region as ACM and the certificates.
-
IAM roles – Map IAM policies and permissions to IAM roles, based on your organization's business or use case requirements. For more information, see IAM role creation in the IAM documentation.
-
IAM Roles Anywhere profiles – Set up profiles to specify which roles IAM Roles Anywhere assumes and what your workloads can do with the temporary credentials. In the profile, define IAM session policies to limit the permissions created for a session. For more information, see Configure roles in the IAM Roles Anywhere documentation.
-
Credential Helper tool – Use the credential helper tool that IAM Roles Anywhere provides in order to obtain temporary security credentials. For more information, see Get temporary security credentials from IAM Roles Anywhere in the IAM Roles Anywhere documentation.
To delegate permission to access a resource through IAM Roles Anywhere, you create an IAM role that has a permission policy and a trust policy. A permissions policy grants the assuming entity the needed permissions to carry out the intended tasks on the resource. A trust policy specifies which trusted account members are allowed to assume the role. In this guide, the permissions policies define which Amazon S3 buckets the entity can access, and the trust policies define which application can assume the role.
This guide covers the following scenarios to illustrate the configuration options for the IAM role trust policies:
-
Option 1: Applications can assume any role linked to an IAM Roles Anywhere profile – One or more certificates have been provisioned in ACM from the AWS Private CA and shared with the applications that require access to AWS resources. These applications can assume any role that is linked to an IAM Roles Anywhere profile. This is because the trust policy doesn't limit which application can assume it.
-
Option 2: Applications can assume only the role that the trust policy allows – Two certificates have been provisioned in ACM from the AWS Private CA and shared with the applications that require access to AWS resources. Because of the certificate-based access controls in the trust policies, Application 1 can assume only Role 1, and Application 2 can assume only Role 2.
Prerequisites
To set up these options, you must complete the following:
-
An external application that requires access to resources in your AWS account and target AWS Region.
-
The certificate authority is set up in the same Region as IAM Roles Anywhere. For instructions on setting up AWS Private Certificate Authority, see Getting started with IAM Roles Anywhere.
-
You have issued a certificate for the application. For more information and instructions, see AWS Certificate Manager certificates.