Orchestration
In this approach, a single orchestrator is responsible for calling each microservice, determining whether to issue calls in sequence or in parallel, manipulating individual service responses along the way, and compiling the end result. An orchestrator can mix synchronous and asynchronous invocations.
AWS Step Functions
Orchestration is a good choice when there are logical branches in your process and you need a single place to encapsulate that logic. It is also useful when you want to implement the asynchronous claim check pattern. For example, standard workflows in Step Functions can pause a workflow and wait for a callback from another service. Using an orchestrator also improves monitoring and observability of a process.
Example: Step Functions
You can use Step Functions to coordinate multiple Lambda functions and other AWS services, to build complex workflows for microservice integration. This option is particularly useful for long-running, multi-step processes that involve several microservices.
You should consider using Step Functions if:
-
Your microservice integration involves complex, multi-step processes.
-
You need to maintain state across long-running operations.
-
You want to implement error handling and retry logic at the workflow level.
-
You need to coordinate both synchronous and asynchronous operations.
Step Functions offers a visual editor for designing complex workflows, which simplifies the process of creating and managing state machines. It provides built-in error handling mechanisms, including retry logic and error state management, which enhance the reliability and robustness of your applications. Standard workflows support long-running processes for up to one year, which is suitable for workflows that span extended periods. This option separates orchestration logic from application code, so it significantly reduces code complexity. This means that developers can focus on core business logic while Step Functions handles the flow control and coordination of distributed components.
For example, consider a loan approval process in a financial services application, which is illustrated in the following diagram. The process starts when a loan application is submitted.
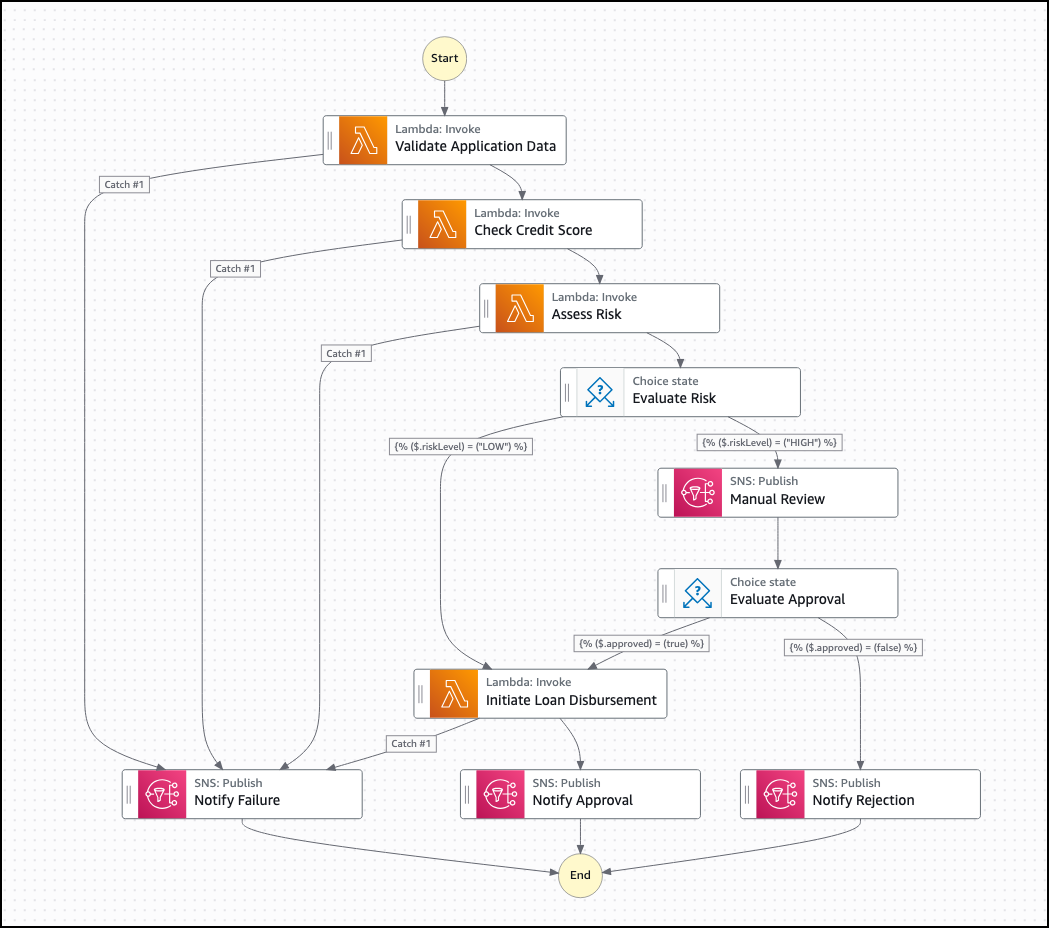
In the state machine that's illustrated in the previous diagram, Step Functions orchestrates the following steps:
-
Validate application data (Lambda function)
-
Check credit score (Lambda function that calls an external API)
-
Assess risk (Lambda function)
-
If high risk, route to manual review (human approval task)
-
If approved, initiate loan disbursement (Lambda function)
-
Send notification to applicant (Amazon SNS)
You can use this approach to manage a complex, potentially long-running process reliably, with built-in error handling and the ability to include both automated and manual steps.
Considerations:
-
Design your state machine carefully to handle all possible scenarios.
-
Perform steps in parallel where possible.
-
Use the built-in error handling and retry mechanisms in Step Functions for both permanent and temporary failures.
-
Consider using standard or express workflows based on your use case. Express workflows might be preferable for short-duration or high-volume workflows.
-
Monitor execution metrics to optimize your workflow.
-
Use nested workflows to encapsulate and reuse functionality across multiple state machines.
-
For complex workflows, consider using Amazon Bedrock Agents as an alternative to Step Functions.
For more information, see the Step Functions documentation.
Example: Amazon MWAA
If your organization already uses Apache Airflow, Amazon MWAA is a natural choice as a workflow orchestrator. In Apache Airflow, you build your workflows as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) by using Python. The DAG representation of the state machine that's illustrated in the Step Functions section might look like this:
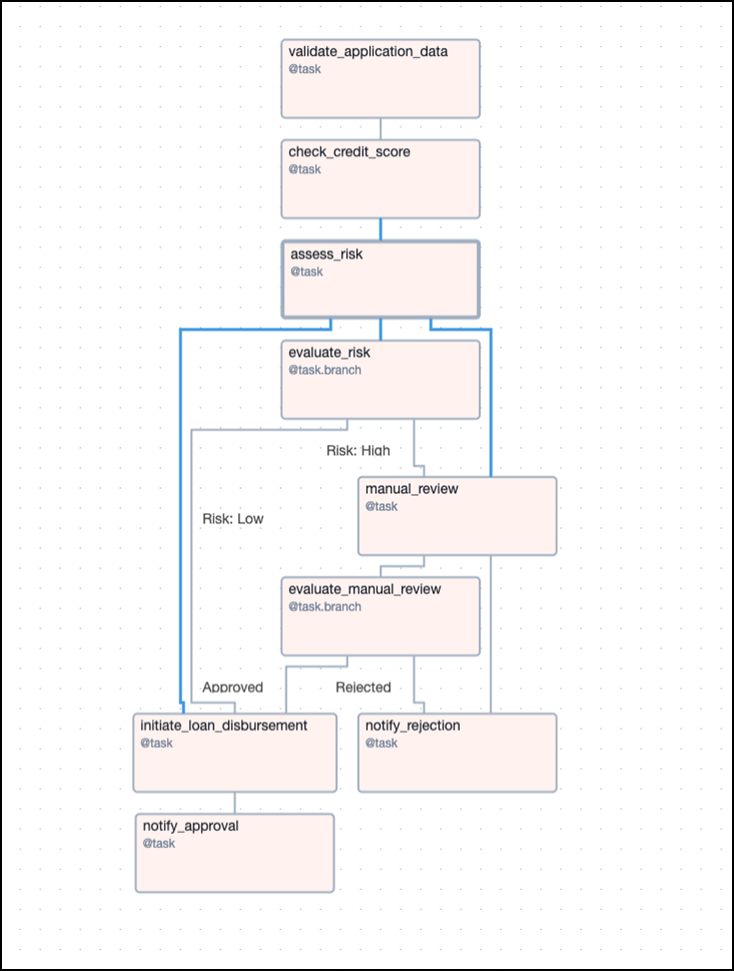
For information about working with DAGs, see the Amazon MWAA documentation.
Key differences between Step Functions and Amazon MWAA
-
Step Functions is a fully-managed serverless service, so there is no infrastructure to pre-provision and no need to schedule a maintenance window. Amazon MWAA must be deployed ahead of time, and you choose the size and number of nodes in your cluster.
-
In Step Functions, you can author state machines in a variety of ways, including Workflow Studio, directly as JSON, or using the AWS Cloud Development Kit (AWS CDK). Apache Airflow DAGs are written in Python.
-
With Step Functions, you incur no cost when there are no workflows running. With Amazon MWAA, you will incur costs even when no DAGs are running.