Migrate from Oracle 8i or 9i to Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL using materialized views and AWS DMS
Kumar Babu P G and Pragnesh Patel, Amazon Web Services
Summary
This pattern describes how to migrate an on-premises legacy Oracle 8i or 9i database to Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) for PostgreSQL or Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition.
AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) doesn't support Oracle 8i or 9i as a source, so this pattern uses an intermediate Oracle database instance that's compatible with AWS DMS, such as Oracle 10g or 11g. It also uses the materialized views feature to migrate data from the source Oracle 8i/9i instance to the intermediate Oracle 10g/11g instance.
AWS Schema Conversion Tool (AWS SCT) converts the database schema, and AWS DMS migrates the data to the target PostgreSQL database.
This pattern helps users who want to migrate from legacy Oracle databases with minimum database downtime. In this implementation, the downtime would be limited to the length of time it takes to create or validate all the foreign keys, triggers, and sequences on the target database.
The pattern uses Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances with an Oracle 10g/11g database installed to help AWS DMS stream the data. You can temporarily pause streaming replication from the on-premises Oracle database to the intermediate Oracle instance to enable AWS DMS to catch up on data validation or to use another data validation tool. The PostgreSQL DB instance and intermediate Oracle database will have the same data when AWS DMS has finished migrating current changes.
Prerequisites and limitations
Prerequisites
An active AWS account
A source Oracle 8i or 9i database in an on-premises data center
AWS Direct Connect configured between the on-premises data center and AWS
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) drivers for AWS SCT connectors installed either on a local machine or on the EC2 instance where AWS SCT is installed
Familiarity with using an Oracle database as an AWS DMS source
Familiarity with using a PostgreSQL database as an AWS DMS target
Limitations
The database size limit is 64 TB
Product versions
Oracle 8i or 9i for the source database
Oracle 10g or 11g for the intermediate database
PostgreSQL 10.17 or later
Architecture
Source technology stack
Oracle 8i or 9i database
Target technology stack
Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL or Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible
Target architecture
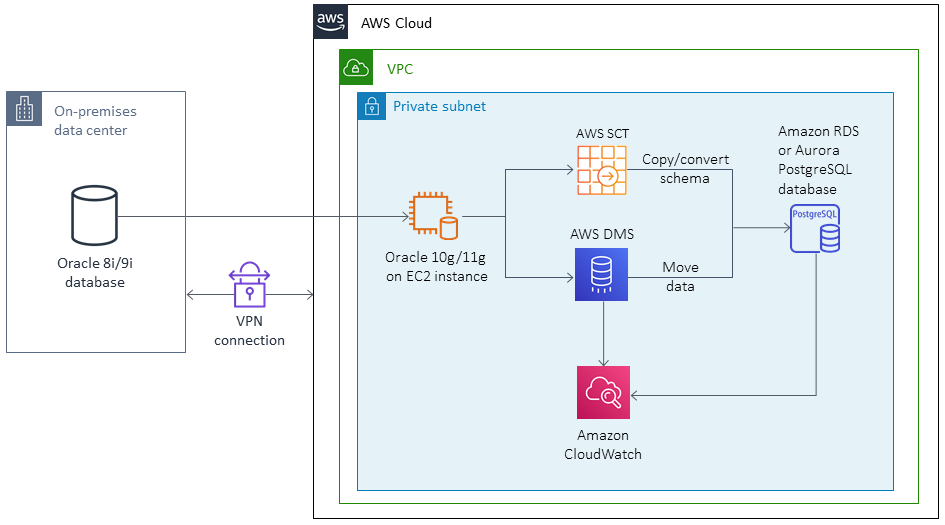
Tools
AWS DMS helps migrate databases quickly and securely. The source database remains fully operational during the migration, minimizing downtime to applications that rely on the database. AWS DMS can migrate your data to and from the most widely used commercial and open-source databases.
AWS SCT automatically converting the source database schema and a majority of the database code objects, including views, stored procedures, and functions, to a format compatible with the target database. Objects that cannot be automatically converted are clearly marked so that they can be manually converted to complete the migration. AWS SCT can also scan your application source code for embedded SQL statements and convert them as part of a database schema conversion project. During this process, AWS SCT performs cloud-native code optimization by converting legacy Oracle and SQL Server functions to their AWS equivalents, to help you modernize your applications while migrating your databases. When schema conversion is complete, AWS SCT can help migrate data from a range of data warehouses to Amazon Redshift by using built-in data migration agents.
Best practices
For best practices for refreshing materialized views, see the following Oracle documentation:
Epics
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Set up the network for the EC2 instance. | Create the virtual private cloud (VPC), subnets, internet gateway, route tables, and security groups. | AWS SysAdmin |
Create the EC2 instance. | Select the Amazon Machine Image (AMI) for the EC2 instance. Choose the instance size and configure instance details: the number of instances (1), the VPC and subnet from the previous step, auto-assign public IP, and other options. Add storage, configure security groups, and launch the instance. When prompted, create and save a key pair for the next step. | AWS SysAdmin |
Install Oracle on the EC2 instance. | Acquire the licenses and the required Oracle binaries, and install Oracle 10g or 11g on the EC2 instance. | DBA |
Configure Oracle networking. | Modify or add entries in | DBA |
Create materialized views. | Identify the database objects to replicate in the source Oracle 8i/9i database, and then create materialized views for all the objects by using the database link. | DBA |
Deploy scripts to refresh materialized views at required intervals. | Develop and deploy scripts to refresh materialized views at required intervals on the Amazon EC2 Oracle 10g/11g instance. Use the incremental refresh option to refresh materialized views. | DBA |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Set up AWS SCT. | Create a new report, and then connect to Oracle as the source and PostgreSQL as the target. In project settings, open the SQL Scripting tab. Change the target SQL script to Multiple Files. (AWS SCT doesn't support Oracle 8i/9i databases, so you have to restore the schema-only dump on the intermediate Oracle 10g/11g instance and use it as a source for AWS SCT.) | DBA |
Convert the Oracle database schema. | On the Action tab, choose Generate Report, Convert Schema, and then Save as SQL. | DBA |
Modify the SQL scripts. | Make modifications based on best practices. For example, switch to suitable data types and develop PostgreSQL equivalents for Oracle-specific functions. | DBA, DevDBA |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Create the Amazon RDS DB instance. | In the Amazon RDS console, create a new PostgreSQL DB instance. | AWS SysAdmin, DBA |
Configure the DB instance. | Specify the DB engine version, DB instance class, Multi-AZ deployment, storage type, and allocated storage. Enter the DB instance identifier, a master user name, and a master password. | AWS SysAdmin, DBA |
Configure network and security. | Specify the VPC, subnet group, public accessibility, Availability Zone preference, and security groups. | DBA, SysAdmin |
Configure database options. | Specify the database name, port, parameter group, encryption, and master key. | DBA, AWS SysAdmin |
Configure backups. | Specify the backup retention period, backup window, start time, duration, and whether to copy tags to snapshots. | AWS SysAdmin, DBA |
Configure monitoring options. | Enable or disable enhanced monitoring and performance insights. | AWS SysAdmin, DBA |
Configure maintenance options. | Specify auto minor version upgrade, maintenance window, and the start day, time, and duration. | AWS SysAdmin, DBA |
Run the pre-migration scripts from AWS SCT. | On the target Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL instance, create the database schema by using the SQL scripts from AWS SCT with other modifications. These might include running multiple scripts and including user creation, database creation, schema creation, tables, views, functions, and other code objects. | AWS SysAdmin, DBA |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Create a replication instance in AWS DMS. | Complete the fields for the name, instance class, VPC (same as for the EC2 instance), Multi-AZ, and public accessibility. In the advanced configuration section, specify allocated storage, subnet group, Availability Zone, VPC security groups, and AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) key. | AWS SysAdmin, DBA |
Create the source database endpoint. | Specify the endpoint name, type, source engine (Oracle), server name (the EC2 instance's private DNS name), port, SSL mode, user name, password, SID, VPC (specify the VPC that has the replication instance), and replication instance. To test the connection, choose Run Test, and then create the endpoint. You can also configure the following advanced settings: maxFileSize and numberDataTypeScale. | AWS SysAdmin, DBA |
Connect AWS DMS to Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL. | Create a migration security group for connections across VPCs, if your PostgreSQL database is in another VPC. | AWS SysAdmin, DBA |
Create the target database endpoint. | Specify the endpoint name, type, source engine (PostgreSQL), server name (Amazon RDS endpoint), port, SSL mode, user name, password, database name, VPC (specify the VPC that has the replication instance), and replication instance. To test the connection, choose Run Test, and then create the endpoint. You can also configure the following advanced settings: maxFileSize and numberDataTypeScale. | AWS SysAdmin, DBA |
Create the AWS DMS replication task. | Specify the task name, replication instance, source and target endpoints, and replication instance. For migration type, choose Migrate existing data and replicate ongoing changes. Clear the Start task on create check box. | AWS SysAdmin, DBA |
Configure the AWS DMS replication task settings. | For target table preparation mode, choose Do nothing. Stop the task after full load completes (to create primary keys). Specify limited or full LOB mode, and enable control tables. Optionally, you can configure the CommitRate advanced setting. | DBA |
Configure the table mappings. | In the Table mappings section, create an Include rule for all tables in all schemas included in the migration, and then create an Exclude rule. Add three transformation rules to convert the schema, table, and column names to lowercase, and add any other rules you need for this specific migration. | DBA |
Start the task. | Start the replication task. Make sure that the full load is running. Run | DBA |
Run the mid-migration scripts from AWS SCT. | In Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL, run the following scripts: | DBA |
Resume the task to continue change data capture (CDC). | Run | DBA |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Check the AWS DMS logs and validation tables. | Check and fix any replication or validation errors. | DBA |
Stop using the on-premises Oracle database and its dependencies. | Stop all Oracle dependencies, shut down listeners on the Oracle database, and run | DBA |
Run the post-migration scripts from AWS SCT. | In Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL, run these scripts: | DBA |
Complete additional Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL steps. | Increment sequences to match Oracle if needed, run | DBA |
Open the connections to Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL. | Remove the AWS DMS security groups from Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL, add production security groups, and point your applications to the new database. | DBA |
Clean up the AWS DMS objects. | Remove the endpoints, replication tasks, replication instances, and the EC2 instance. | SysAdmin, DBA |