What is Amazon VPC Lattice?
Amazon VPC Lattice is a fully managed application networking service that you use to connect, secure, and monitor the services and resources for your application. You can use VPC Lattice with a single virtual private cloud (VPC) or across multiple VPCs from one or more accounts.
Modern applications can consist of multiple small and modular components which are often called microservices, such as an HTTP API, resources such as databases, and custom resources consisting of DNS and IP address endpoints. While modernization has its advantages, it can also introduce networking complexities and challenges when you connect these microservices and resources. For example, if the developers are spread across different teams, they might build and deploy microservices and resources across multiple accounts or VPCs.
In VPC Lattice, we refer to a microservice as a service and represent a resource only as a resource configuration. These are the terms that you see in the VPC Lattice user guide.
Contents
Key components
To use Amazon VPC Lattice, you should be familiar with its key components.
- Service
-
An independently deployable unit of software that delivers a specific task or function. A service can run on EC2 instances or ECS/EKS/Fargate containers, or as Lambda functions, within an account or a virtual private cloud (VPC). A VPC Lattice service has the following components: target groups, listeners, and rules.
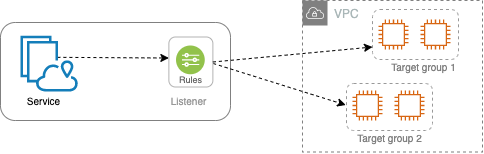
- Target group
-
A collection of resources, also known as targets, that run your application or service. These are similar to the target groups provided by Elastic Load Balancing, but they are not interchangeable. The supported target types include EC2 instances, IP addresses, Lambda functions, Application Load Balancers, Amazon ECS tasks, and Kubernetes Pods.
- Listener
-
A process that checks for connection requests, and routes them to targets in a target group. You configure a listener with a protocol and a port number.
- Rule
-
A default component of a listener that forwards requests to the targets in a VPC Lattice target group. Each rule consists of a priority, one or more actions, and one or more conditions. Rules determines how the listener routes client requests.
- Resource
-
A resource is an entity such as an Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) database, an Amazon EC2 instance, an application endpoint, a domain-name target, or an IP address. You can share a resource in your VPC by creating a resource share in AWS Resource Access Manager (AWS RAM), creating a resource gateway, and defining a resource configuration.
- Resource gateway
-
A resource gateway is a point of ingress into the VPC in which resources reside.
- Resource configuration
-
A resource configuration is a logical object that represents either a single resource or a group of resources. A resource can be an IP address, a domain-name target, or an Amazon RDS database.
- Service network
-
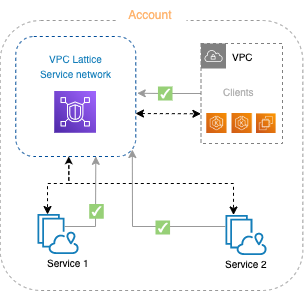
A logical boundary for a collection of services and resource configurations. A client can be in a VPC that is associated with the service network. Clients and services that are associated with the same service network can communicate with each other if they are authorized to do so.
In the following figure, the clients can communicate with both services, because the VPC and services are associated with the same service network.
- Service directory
-
A central registry of all VPC Lattice services that you own or are shared with your account through AWS RAM.
- Auth policies
-
Fine-grained authorization policies that can be used to define access to services. You can attach separate auth policies to individual services or to the service network. For example, you can create a policy for how a payment service running on an auto scaling group of EC2 instances should interact with a billing service running in AWS Lambda.
Auth-policies are not supported on resource configurations. Auth policies of a service-network are not applicable to resource configurations in the service network.
Roles and responsibilities
A role determines who is responsible for the setup and flow of information within Amazon VPC Lattice. There are typically two roles, service network owner and service owner, and their responsibilities can overlap.
Service network owner – The service network owner is usually the network administrator or the cloud administrator in an organization. Service network owners create, share, and provision the service network. They also manage who can access the service network or services within VPC Lattice. The service network owner can define coarse-grained access settings for the services associated with the service network. These controls are used to manage communication between clients and services using authentication and authorization policies. The service network owner can also associate a service or resource configuration with a single or multiple service networks, if the service or resource configuration is shared with the service network owner's account.

Service owner – The service owner is usually a software developer in an organization. Service owners create services within VPC Lattice, define routing rules, and also associate services with the service network. They can also define fine-grained access settings, which can restrict access to only authenticated and authorized services and clients.
Resource owner – The resource owner is usually a software developer in an organization and serves as an admin for a resource such as a database. The resource owner creates a resource configuration for the resource, defines access-settings for the resource configuration, and associates the resource configuration with service networks.

Features
The following are the core features that VPC Lattice provides.
- Service discovery
-
All clients and services in VPCs associated with the service network can communicate with other services within the same service network. DNS directs client-to-service and service-to-service traffic through the VPC Lattice endpoint. When a client wants to send a request to a service, it uses the service’s DNS name. The Route 53 Resolver sends the traffic to VPC Lattice, which then identifies the destination service.
- Connectivity
-
Client-to-service and client-to-resource connectivity is established within the AWS network infrastructure. When you associate a VPC with the service network, any client within the VPC can connect with services and resources (through resource configurations) in the service network, if they have the required access. VPC Lattice supports overlapping CIDR technology.
- On premise access
-
You can enable connectivity to a service network from a VPC using a VPC endpoint (powered by AWS PrivateLink). A VPC endpoint of type service network lets you enable access to services and resources in the service network from on premises networks over Direct Connect and VPN. Traffic that traverses VPC peering or AWS Transit Gateway can also access resources and services over a VPC endpoint.
- Observability
-
VPC Lattice generates metrics and logs for each request and response traversing the service network, to help you monitor and troubleshoot applications. By default, metrics are published to the service owner account. Service owners and resource owners have the option to turn on logging, and receive logs for all client access/requests to their services and resources. Service network owners can also turn on logging on the service network, to log all access/requests to the services and resources from clients in VPCs that are connected to the service network.
VPC Lattice works with the following tools to help you monitor and troubleshoot your services: Amazon CloudWatch log groups, Firehose delivery streams, and Amazon S3 buckets.
- Security
-
VPC Lattice provides a framework that you can use to implement a defense strategy at multiple layers of the network. The first layer is the combination of service, resource configuration, VPC association, and VPC endpoint of type service network. Without a VPC and a service association or a VPC endpoint of type service network, clients cannot access services. Similarly, without a VPC and a resource configuration and a service association or a VPC endpoint of type service network, clients cannot access resources.
The second layer enables users to attach security groups to the association between the VPC and the service network. The third and fourth layers are auth policies that can be applied individually at the service network level and the service level.
Accessing VPC Lattice
You can create, access, and manage VPC Lattice using any of the following interfaces:
-
AWS Management Console – Provides a web interface that you can use to access VPC Lattice.
-
AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) – Provides commands for a broad set of AWS services, including VPC Lattice. The AWS CLI is supported on Windows, MacOS, and Linux. For more information about the CLI, see AWS Command Line Interface
. For more information about the APIs, see Amazon VPC Lattice API Reference. -
VPC Lattice Controller for Kubernetes – Manages VPC Lattice resources for a Kubernetes cluster. For more information about using VPC Lattice with Kubernetes, see the AWS Gateway API Controller User Guide
. -
AWS CloudFormation – Helps you to model and set up your AWS resources. For more information, see the Amazon VPC Lattice resource type reference.
VPC Lattice service endpoints
An endpoint is a URL that serves as an entry point for an AWS web service. VPC Lattice supports the following endpoint types:
-
Dualstack endpoints (support both IPv4 and IPv6)
When you make a request, you can specify the endpoint to use. If you do not specify an endpoint, the IPv4 endpoint is used by default. To use a different endpoint type, you must specify it in your request. For examples of how to do this, see Specifying endpoints. For a table of available endpoints, see Amazon VPC Lattice endpoints.
IPv4 endpoints
IPv4 endpoints support IPv4 traffic only. IPv4 endpoints are available for all Regions.
If you specify the general endpoint, vpc-lattice.amazonaws.com, we use the endpoint for
us-east-1. To use a different Region, specify its associated endpoint. For example, if you
specify vpc-lattice.us-east-2.amazonaws.com as the endpoint, we direct your request to the us-east-2 endpoint.
IPv4 endpoint names use the following naming convention:
-
vpc-lattice.region.amazonaws.com
For example, the IPv4 endpoint name for the eu-west-1 Region is
vpc-lattice.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com.
Dualstack (IPv4 and IPv6) endpoints
Dualstack endpoints support both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic. Dualstack endpoints are available for all Regions. When you make a request to a dualstack endpoint, the endpoint URL resolves to an IPv6 or an IPv4 address, depending on the protocol used by your network and client.
Dual-stack endpoint names use the following naming convention:
-
vpc-lattice.region.api.aws
For example, the dual-stack endpoint name for the eu-west-1 Region is
vpc-lattice.eu-west-1.api.aws.
Specifying endpoints
The following examples show how to specify an endpoint for the
us-east-2 Region using the AWS CLI for vpc-lattice.
-
IPv4
aws vpc-lattice get-service --service-identifier svc-0285b53b2eEXAMPLE --region us-east-2 --endpoint-url https://vpc-lattice.us-east-2.amazonaws.com -
Dualstack
aws vpc-lattice get-service --service-identifier svc-0285b53b2eEXAMPLE --region us-east-2 --endpoint-url https://vpc-lattice.us-east-2.api.aws
Pricing
With VPC Lattice you pay for the time that a service is provisioned, the amount of data
transferred through each service, and the number of requests. As a resource owner, you pay for
the data transferred to and from each resource. As a service network owner, you pay hourly for
resource configurations associated to your service network. As a consumer who has a VPC
associated to a service network, you pay for data transferred to and from resources in the
service network from your VPC. For more information, see Amazon VPC Lattice Pricing