Subnet CIDR blocks
The IP addresses for your subnets are represented using Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) notation. The CIDR block of a subnet can be the same as the CIDR block for the VPC (to create a single subnet in the VPC), or a subset of the CIDR block for the VPC (to create multiple subnets in the VPC). If you create more than one subnet in a VPC, the CIDR blocks of the subnets cannot overlap.
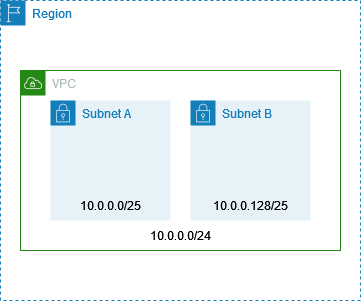
For example, if you create a VPC with CIDR block 10.0.0.0/24, it supports
256 IP addresses. You can break this CIDR block into two subnets, each supporting 128 IP
addresses. One subnet uses CIDR block 10.0.0.0/25 (for addresses
10.0.0.0 - 10.0.0.127) and the other uses CIDR block
10.0.0.128/25 (for addresses 10.0.0.128 -
10.0.0.255).
There are tools available on the internet to help you calculate and create IPv4 and IPv6 subnet CIDR blocks. You can find tools that suit your needs by searching for terms such as 'subnet calculator' or 'CIDR calculator'. Your network engineering group can also help you determine the IPv4 and IPv6 CIDR blocks to specify for your subnets.
Subnet sizing for IPv4
The allowed IPv4 CIDR block size for a subnet is between a /28 netmask and /16 netmask.
The first four IP addresses and the last IP address in each subnet CIDR block are not
available for your use, and they cannot be assigned to a resource, such as an EC2 instance.
For example, in a subnet with CIDR block 10.0.0.0/24, the following five IP
addresses are reserved:
-
10.0.0.0: Network address.
-
10.0.0.1: Reserved by AWS for the VPC router.
-
10.0.0.2: Reserved by AWS. The IP address of the DNS server is the base of the VPC network range plus two. For VPCs with multiple CIDR blocks, the IP address of the DNS server is located in the primary CIDR. We also reserve the base of each subnet range plus two for all CIDR blocks in the VPC. For more information, see Amazon DNS server.
-
10.0.0.3: Reserved by AWS for future use.
-
10.0.0.255: Network broadcast address. We do not support broadcast in a VPC, therefore we reserve this address.
If you create a subnet using a command line tool or the Amazon EC2 API, the CIDR block is automatically modified to its canonical form. For example, if you specify 100.68.0.18/18 for the CIDR block, we create a CIDR block of 100.68.0.0/18.
If you bring an IPv4 address range to AWS using BYOIP, you can use all of the IP addresses in the range, including the first address (the network address) and the last address (the broadcast address).
Subnet sizing for IPv6
If you've associated an IPv6 CIDR block with your VPC, you can associate an IPv6 CIDR
block with an existing subnet in your VPC, or when you create a new subnet. Possible IPv6
netmask lengths are between /44 and /64 in increments of /4.
There are tools available on the internet to help you calculate and create IPv6 subnet CIDR blocks. You can find tools that suit your needs by searching for terms such as 'IPv6 subnet calculator' or 'IPv6 CIDR calculator'. Your network engineering group can also help you determine the IPv6 CIDR blocks to specify for your subnets.
The first four IPv6 addresses and the last IPv6 address in each subnet CIDR block
are not available for your use, and they cannot be assigned to an EC2 instance. For
example, in a subnet with CIDR block 2001:db8:1234:1a00/64, the
following five IP addresses are reserved:
-
2001:db8:1234:1a00:: -
2001:db8:1234:1a00::1: Reserved by AWS for the VPC router. -
2001:db8:1234:1a00::2 -
2001:db8:1234:1a00::3 -
2001:db8:1234:1a00:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff
In addition to the IP address reserved by AWS for the VPC router in the example above, the following IPv6 addresses are reserved for the default VPC router:
A link-local IPv6 address in the FE80::/10 range generated using EUI-64. For more information about link-local addresses, see Link-local address
. The link-local IPv6 address
FE80:ec2::1.
If you need to communicate with the VPC router over IPv6, you can configure your applications to communicate with whichever address best fits your need.