AWS CloudFormation
AWS CloudFormation
AWS CloudFormation offers granular control over the provisioning and management of all application infrastructure components, from low-level components such as route tables or subnet configurations, to high-level components such as CloudFront distributions. AWS CloudFormation is commonly used with other AWS deployment services or third-party tools, combining AWS CloudFormation with more specialized deployment services to manage deployments of application code onto infrastructure components.
AWS offers extensions to the CloudFormation service in addition to its base features:
-
AWS Cloud Development Kit (AWS CDK)
is an open source software development kit (SDK) to programmatically model AWS infrastructure with TypeScript, JavaScript, Python, Java, or C#/.NET. -
AWS Serverless Application Model
(AWS SAM) is an open source framework to simplify building serverless applications on AWS. It provides shorthand syntax to express functions, APIs, databases, and event source mappings.
Table 1: AWS CloudFormation deployment features
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Provision |
CloudFormation will automatically create and update infrastructure components that are defined in a template. Refer to AWS CloudFormation Best Practices for more details on creating infrastructure using AWS CloudFormation templates. |
| Configure |
AWS CloudFormation templates offer extensive flexibility to customize and update all infrastructure components. Refer to AWS CloudFormation Template Anatomy for more details on customizing templates. |
| Deploy |
Update your AWS CloudFormation templates to alter the resources in a stack. Depending on your application architecture, you might need an additional deployment service to update the application version running on your infrastructure. Refer to Deploying Applications on Amazon EC2 with AWS CloudFormation for more details on how AWS CloudFormation can be used as a deployment solution. |
| Scale | AWS CloudFormation will not automatically handle infrastructure scaling on your behalf; however, you can configure auto scaling policies for your resources in a AWS CloudFormation template. |
| Monitor |
AWS CloudFormation provides native monitoring of the success or failure of updates to infrastructure defined in a template, as well as drift detection to monitor when resources defined in a template do not meet specifications. Additional monitoring solutions will need to be in place for application-level monitoring and metrics. Refer to Monitoring the Progress of a Stack Update for more details on how AWS CloudFormation monitors infrastructure updates. |
The following diagram shows a common use case for AWS CloudFormation. Here, AWS CloudFormation templates are created to define all infrastructure components necessary to create a simple three-tier web application. In this example, we are using bootstrap scripts defined in AWS CloudFormation to deploy the latest version of our application onto Amazon EC2 instances; however, it is also a common practice to combine additional deployment services with AWS CloudFormation (using AWS CloudFormation only for its infrastructure management and provisioning capabilities). Note that more than one AWS CloudFormation template is used to create the infrastructure. In the diagram, AWS CloudFormation is used to create all infrastructure components including IAM roles, VPCs, subnets, route tables, security groups, and Amazon S3 bucket policies. Separate AWS CloudFormation templates are used to build each domain of the application architecture.
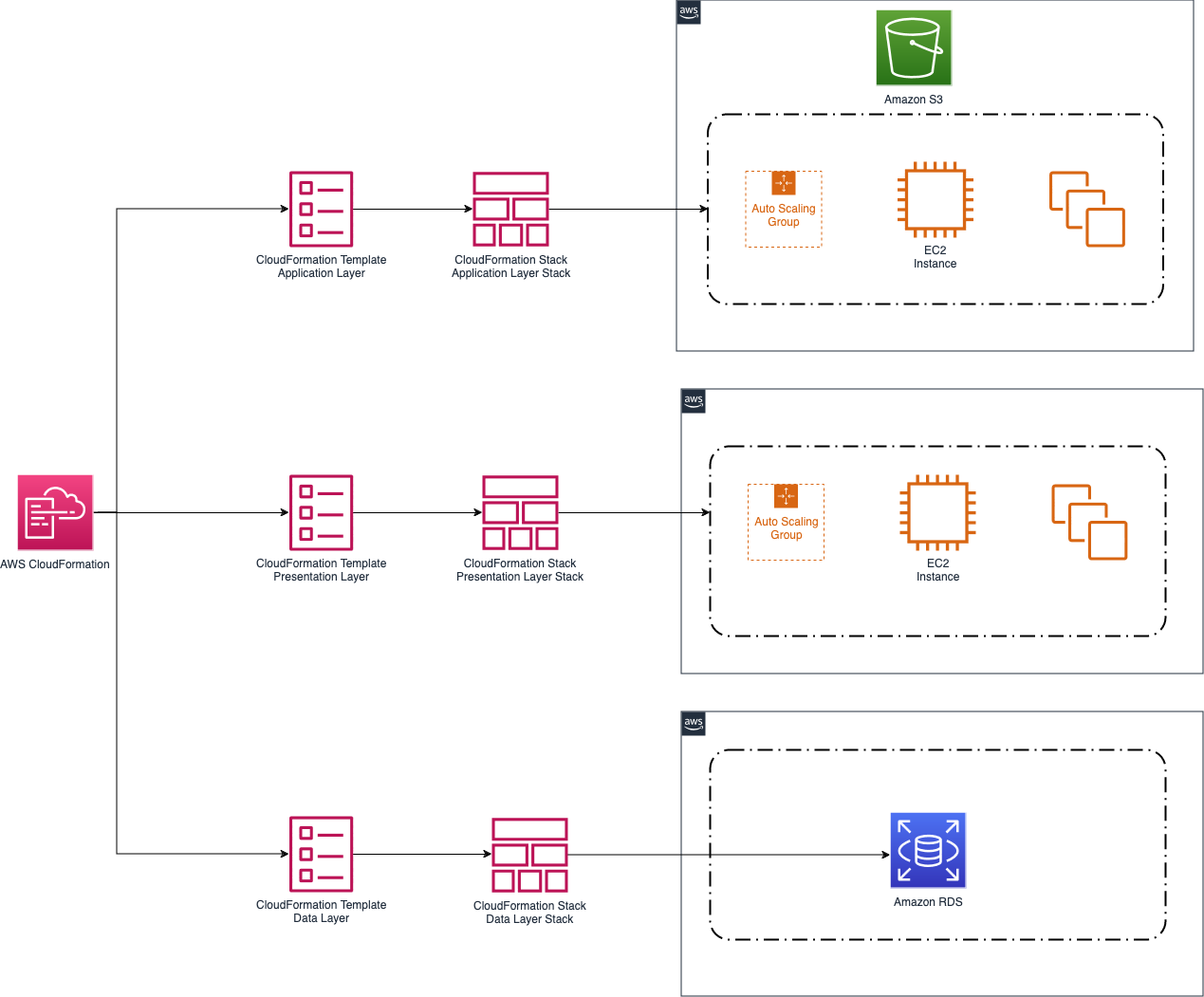
AWS CloudFormation use case