Deregister (delete) an AMI
When you deregister an AMI, Amazon EC2 permanently deletes it. Once deregistered, you can't use the AMI to launch new instances. You might consider deregistering an AMI when you have finished using it.
To protect against accidental or malicious deregistering of an AMI, you can turn on deregistration protection. If you accidentally deregister an EBS-backed AMI, you can use the Recycle Bin to restore it only if you restore it within the allowed time period before it is permanently deleted.
Deregistering an AMI has no effect on any instances that were launched from the AMI. You can continue to use these instances. Deregistering an AMI also has no effect on any snapshots that were created during the AMI creation process. You'll continue to incur usage costs for these instances and storage costs for the snapshots. Therefore, to avoid incurring unnecessary costs, we recommend that you terminate any instances and delete any snapshots that you do not need. For more information, see Avoid costs from unused resources.
Contents
Considerations
-
You can't deregister an AMI that is not owned by your account.
-
You can't use Amazon EC2 to deregister an AMI that is managed by the AWS Backup service. Instead, use AWS Backup to delete the corresponding recovery points in the backup vault. For more information, see Deleting backups in the AWS Backup Developer Guide.
Deregister an AMI
Use any of the following methods to deregister an EBS-backed AMI or instance store-backed AMI.
Tip
To avoid incurring unnecessary costs, you should delete any resources that you do not need. For example, for EBS-backed AMIs, if you do not need the snapshots associated with the deregistered AMI, you should delete them. For more information, see Avoid costs from unused resources.
Check when an AMI was last used
LastLaunchedTime is a timestamp that indicates when your AMI was last used to
launch an instance. AMIs that have not been used recently to launch an instance might be good
candidates for deregistering or deprecation.
Note
-
When the AMI is used to launch an instance, there is a 24-hour delay before that usage is reported.
-
lastLaunchedTimedata is available starting April 2017.
Protect an AMI from deregistration
You can turn on deregistration protection on an AMI to prevent accidental or malicious deletion. When you turn on deregistration protection, the AMI can’t be deregistered by any user, regardless of their IAM permissions. If you want to deregister the AMI, you must first turn off the deregistration protection on it.
When you turn on deregistration protection on an AMI, you have the option to include a 24-hour cooldown period. This cooldown period is the time during which deregistration protection remains in effect after you turn it off. During this cooldown period, the AMI can’t be deregistered. When the cooldown period ends, the AMI can be deregistered.
Deregistration protection is turned off by default on all existing and new AMIs.
Turn on deregistration protection
Use any of the following methods to turn on deregistration protection on an AMI. To do this, you must be the owner of the AMI.
Turn off deregistration protection
Use any of the following methods to turn off deregistration protection on an AMI. To do this, you must be the owner of the AMI.
Note
If you chose to include a 24-hour cooldown period when you turned on deregistration protection for the AMI, then, when you turn off deregistration protection, you won’t immediately be able to deregister the AMI. The cooldown period is the 24-hour time period during which deregistration protection remains in effect even after you turn it off. During this cooldown period, the AMI can’t be deregistered. After the cooldown period ends, the AMI can be deregistered.
Avoid costs from unused resources
When you deregister an AMI, you don't delete the resources that are associated with the AMI. These resources include the snapshots for EBS-backed AMIs and the files in Amazon S3 for instance store-backed AMIs. When you deregister an AMI, you also don't terminate or stop any instances launched from the AMI.
You will continue to incur costs for storing the snapshots and files, and you will incur costs for any running instances. For more information, see How you're charged.
To avoid incurring these types of unnecessary costs, we recommend deleting any resources that you don't need.
To determine whether your AMI is EBS-backed or instance store-backed, see Determine the root device type of your AMI.
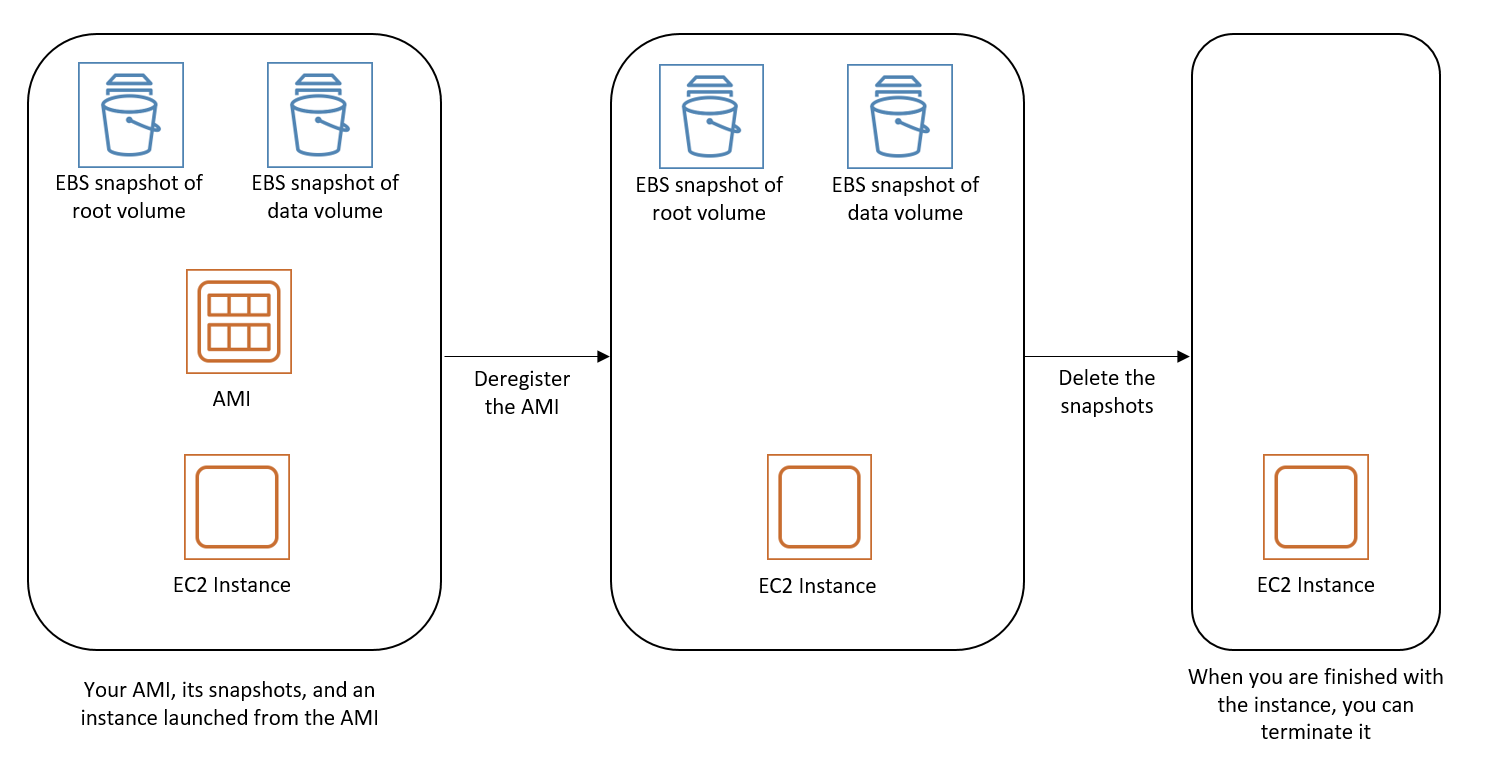
Delete resources associated with your Amazon EBS-backed AMI
Use any of the following methods to delete the resources associated with your EBS-backed AMI.
The following diagram illustrates the flow for you to delete resources associated with an EBS-backed AMI.
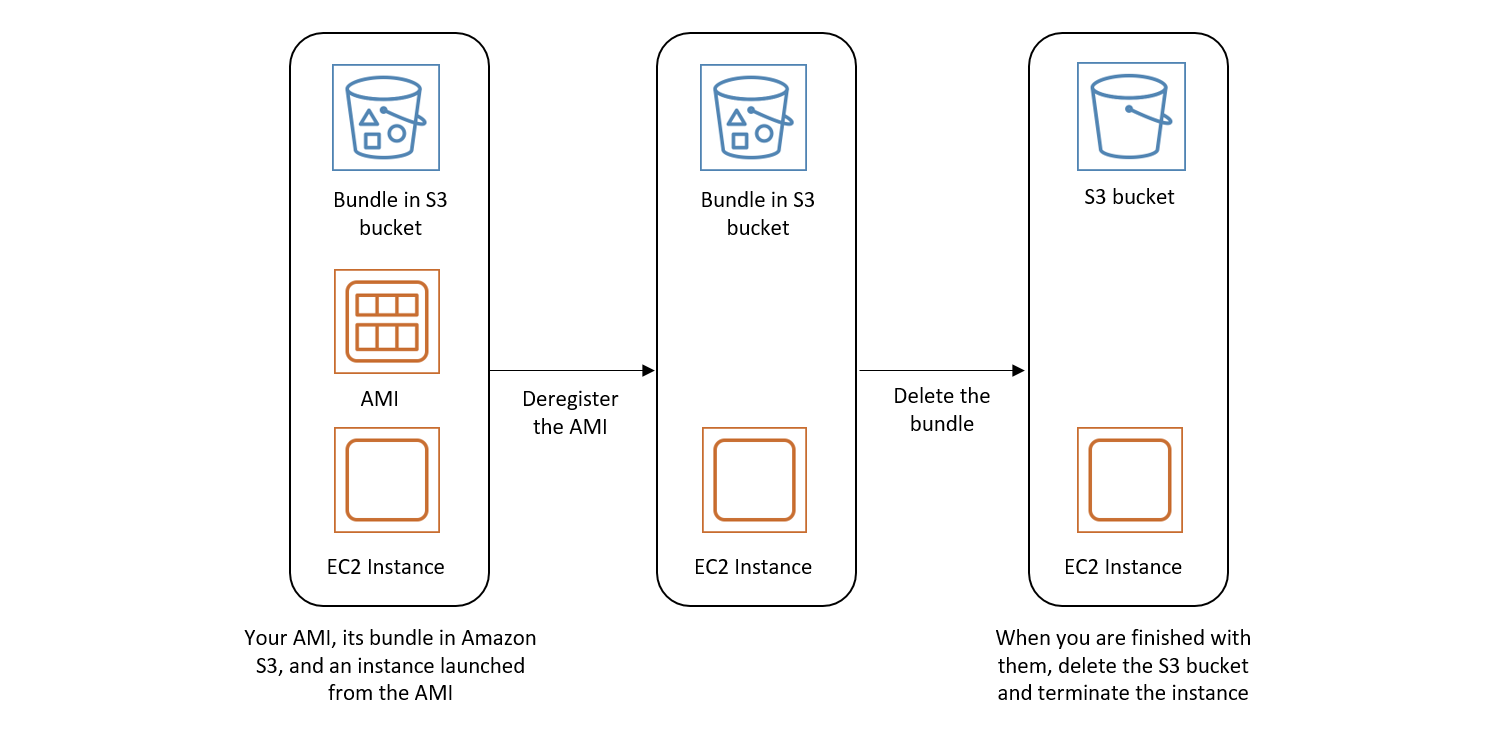
Delete resources associated with your instance store-backed AMI
Use the following method to delete the resources associated with your instance store-backed AMI.
To delete resources associated with your instance store-backed AMI
-
Deregister the AMI by using the deregister-image command.
aws ec2 deregister-image --image-idami-0123456789example -
Delete the bundle in Amazon S3 by using the ec2-delete-bundle (AMI tools) command.
ec2-delete-bundle -bmyawsbucket/myami-ayour_access_key_id-syour_secret_access_key-pimage -
Terminate instances that you don't need by using the terminate-instances command.
aws ec2 terminate-instances --instance-idsi-0123456789example -
If you are finished with the Amazon S3 bucket that you uploaded the bundle to, you can delete the bucket. To delete an Amazon S3 bucket, open the Amazon S3 console, select the bucket, choose Actions, and then choose Delete.
The following diagram illustrates the flow for you to delete resources associated with your instance store-backed AMI.