AWS Launch Wizard for SQL Server
AWS Launch Wizard is a service that guides you through the sizing, configuration, and deployment of Microsoft SQL Server applications on AWS, following the AWS Well-Architected Framework. AWS Launch Wizard supports both single instance and high availability (HA) application deployments.
AWS Launch Wizard reduces the time it takes to deploy SQL Server solutions to the cloud. You input your application requirements, including performance, number of nodes, and connectivity, on the service console. AWS Launch Wizard identifies the right AWS resources to deploy and run your SQL Server application. AWS Launch Wizard provides an estimated cost of deployment, and you can modify your resources and instantly view the updated cost assessment. When you approve, AWS Launch Wizard provisions and configures the selected resources in a few hours to create a fully-functioning production-ready SQL Server application. It also creates custom AWS CloudFormation templates, which can be reused and customized for subsequent deployments.
Once deployed, your SQL Server application is ready to use and can be accessed on the EC2 console. You can manage your SQL Server application with AWS SSM.
Supported operating systems and SQL versions
AWS Launch Wizard supports the following operating systems and SQL Server versions:
Deployments on Windows
-
Windows Server 2022/2019/2016/2012 R2
-
Enterprise and Standard Editions of Microsoft SQL Server 2022/2019/2017/2016
Amazon FSx for Failover Clustering (FCI) deployments on Windows
-
Windows Server 2022/2019/2016
-
Enterprise and Standard Editions of Microsoft SQL Server 2022/2019/2017/2016 SP2
CUs are installed at the same time as public AMIs for SQL license-included AMIs. CUs and service packs are not installed for license-included Windows AMIs and BYOL AMIs.
Deployments on Ubuntu
-
Ubuntu 18.04
-
Enterprise and Standard Edition of Microsoft SQL Server 2019
Deployments on RHEL
-
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7.9
-
Enterprise and Standard Edition of Microsoft SQL Server 2019/2017
Features of AWS Launch Wizard
AWS Launch Wizard provides the following features:
Simple application deployment
AWS Launch Wizard makes it easy for you to deploy third-party applications on AWS, such as Microsoft SQL Server. When you input the application requirements, AWS Launch Wizard deploys the necessary AWS resources for a production-ready application. This means that you do not have to manage separate infrastructure pieces or spend time provisioning and configuring your SQL Server application.
AWS resource selection
Launch Wizard considers performance, memory, bandwidth, and other application features to determine the best instance type, EBS volumes, and other resources for your SQL Server application. You can modify the recommended defaults.
Cost estimation
Launch Wizard provides a cost estimate for a complete deployment. The cost estimate is itemized for each individual resource to deploy. The estimated cost automatically updates each time you change a resource type configuration in the wizard. The provided estimates are for general comparisons only. The estimates are based on On-Demand costs and actual costs may be lower.
Reusable code templates
Launch Wizard creates a CloudFormation stack that can be reused to customize and replicate your infrastructure in multiple environments. Code in the template helps you provision resources. You can access and use the templates created by your Launch Wizard deployment from the CloudFormation console. For more information about CloudFormation stacks, see Working with stacks.
SNS notification
You can provide an SNS topic so that Launch Wizard will send you notifications and alerts about the status of a deployment.
Always On Availability Groups (SQL Server)
Always On Availability Groups (AG) is a Microsoft SQL Server feature that is
supported by the AWS SQL Server installation. AG augments the availability of a
set of user databases. An availability group supports a failover environment for a
discrete set of user databases, known as availability databases. If one of these
databases fails, another database takes over its workload with no impact on
availability. Always On Availability improves database availability, enabling more
efficient resource usage. For more information about the concepts and benefits of
Always On Availability, see Always On Availability Groups (SQL Server)
Dedicated Hosts (deployment on Windows)
You can deploy SQL Server Always On Availability Groups (AG) or basic availability groups on your Dedicated Hosts to leverage your existing SQL Server Licenses (BYOL). From the Launch Wizard console, select Dedicated Host tenancy, and then select the Dedicated Hosts for your VPC. For more information about Amazon EC2 Dedicated Hosts, see Dedicated Hosts.
Early input validation
You can leverage your existing infrastructure (such as VPC or Active Directory) with Launch Wizard. This may lead to deployment failures if your existing infrastructure does not meet certain deployment prerequisites. For example, for a SQL Server Always On deployment in your existing VPC, the VPC must have at least one public subnet and two private subnets. It must also have outbound connectivity to Amazon S3, Systems Manager, and AWS CloudFormation service endpoints. If these requirements are not met, the deployment will fail. If you are in a later stage of a deployment, this failure can take more than an hour to detect. To detect these types of issues early in the application deployment process, Launch Wizard's validation framework verifies key application and infrastructure specifications before provisioning. Verification takes approximately 15 minutes. If necessary, you can take appropriate actions to adjust your VPC configuration.
Launch Wizard performs the following infrastructure validations:
Resource limit validations at the AWS account level:
-
VPC
-
Internet gateway
-
Number of CloudFormation stacks
Additionally, Launch Wizard performs the following application-specific validations:
-
Active Directory credentials (deployment on Windows)
-
Public subnet outbound connectivity
-
Private subnet outbound connectivity
-
Custom Windows AMIs:
-
SQL Server installed and running on instance
-
Compliant versions of Windows and SQL Server
-
-
Dedicated Hosts (deployment on Windows)
-
AMIs are filtered according to the billing code. When you select Dedicated Host tenancy in the application, the AMI selection dropdown list filters out AMIs for which the usage operation is set to include SQL Server Enterprise or SQL Server Standard, per the details and usage operation values. This filtering behavior is the result of restrictions described in the Dedicated Host restrictions page.
-
Supported instance type
-
Sufficient capacity to launch number of nodes and instances
-
Selected subnet and corresponding Dedicated Host are in the same Availability Zone for any additional nodes beyond the primary and first secondary nodes
-
Note
Some validations, for example for valid Active Directory credentials, require
Application Wizard to launch a t2.large EC2 instance in your
account for a few minutes. After it runs the necessary validations, Launch Wizard
terminates the instance.
Application resource groups for easy discoverability
Launch Wizard creates a resource group for all of the AWS resources created for your SQL Server application. You can manage the resources through the EC2 console or with Systems Manager. When you access Systems Manager through Launch Wizard, the resources are automatically filtered for you based on your resource group. You can manage, patch, and maintain your SQL Server applications in Systems Manager.
One-click monitoring
Launch Wizard integrates with CloudWatch Application Insights to provide a one-click monitoring setup experience for deploying SQL Server HA workloads on AWS. When you select the option to set up monitoring and insights with Application Insights on the Launch Wizard console, Application Insights automatically sets up relevant metrics, logs, and alarms on CloudWatch, and starts monitoring newly deployed workloads. You can view automated insights and detected problems, along with the health of your SQL Server HA workloads, on the CloudWatch console.
Counters that you can configure using Application Insights include:
-
Mirrored Write Transaction/sec
-
Recovery Queue Length
-
Transaction delay
-
Windows Event Logs on CloudWatch
You can also get automated insights when a failover event or problem, such as a restricted access to query a target database, is detected on your workload.
Amazon FSx for Failover Clustering (FCI)
Launch Wizard uses Amazon FSx to provide Failover Clustering for SQL Server deployments. Failover Clustering is a high availability solution for SQL that puts all database and log files in shared storage (Amazon FSx). The Amazon FSx file share spans multiple Availability Zones and is highly redundant, which allows for automatic failover between SQL nodes in the event of failure.
Launch Wizard offers two storage options for your FCI deployments: Amazon FSx for Windows or
Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP. If you choose NetApp ONTAP as the storage type for FCI,
License Manager creates the user name FSXAdmin and a password during the
deployment. The user name and password are stored in AWS Secrets Manager to manage
ONTAP.
Related services
The following services are used when you deploy a SQL Server application with AWS Launch Wizard:
AWS CloudFormation
AWS CloudFormation is a service for modeling and setting up your AWS resources, enabling you to spend more time focusing on your applications that run in AWS. You create a template that describes all of the AWS resources that you want to use (for example, Amazon EC2 instances or Amazon RDS DB instances), and AWS CloudFormation takes care of provisioning and configuring those resources for you. With Launch Wizard, you don’t have to sift through CloudFormation templates to deploy your application. Instead, Launch Wizard combines infrastructure provisioning and configuration (with a CloudFormation template) and application configuration (with code that runs on EC2 instances to configure the application) into a unified SSM Automation document. The SSM document is then invoked by Launch Wizard’s backend service to provision a SQL Server application in your account. For more information, see the AWS CloudFormation User Guide.
Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS)
Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) is a highly available, durable, secure, fully managed pub/sub messaging service that provides topics for high-throughput, push-based, many-to-many messaging. Using Amazon SNS topics, your publisher systems can fan out messages to a large number of subscriber endpoints and send notifications to end users using mobile push, SMS, and email. You can use SNS topics for your Launch Wizard deployments to stay up-to-date on deployment progress. For more information, see the Amazon Simple Notification Service Developer Guide.
Amazon CloudWatch Application Insights
Amazon CloudWatch Application Insights facilitates observability for .NET and SQL Server applications. It can help you set up the best monitors for your application resources to continuously analyze data for signs of problems with your applications. Application Insights, which is powered by Sagemaker and other AWS technologies, provides automated dashboards that show potential problems with monitored applications, helping you to quickly isolate ongoing issues with your applications and infrastructure. The enhanced visibility into the health of your applications that Application Insights provides can help you reduce your mean time to repair (MTTR) so that you don't have to pull in multiple teams and experts to troubleshoot your application issues.
Linux-only technologies
The following key technologies are used when you deploy a SQL Server application with Amazon Launch Wizard to the Linux platform.
-
Pacemaker
is an open source cluster resource manager (CRM), which is a system that coordinates managed resources and services made highly available by a cluster. -
Corosync
is an open source program that provides cluster membership and messaging capabilities, often referred to as the messaging layer, to client servers. In contrast to Pacemaker, which allows you to control cluster behavior, Corosync makes it possible for servers to communicate as a cluster. -
Transact-SQL
is an extension to the SQL language. It is used to interact with relational databases. Transact-SQL is platform-agnostic and can be used to configure the AlwaysOn Availability Group and listener. -
Fencing
is used to isolate a malfunctioning server from the cluster in order to protect and secure the synced resources. The recommended solution to use in the case of a malfucntioning server is the "Shoot the other node in the head" (STONITH) method. STONITH is a fencing technique that isolates a failed node so that it does not disrupt a computer cluster. The STONITH method fences failed nodes by resetting or powering down the failed node. Fencing is also used when a clustered service cannot be stopped. In this case, the cluster uses fencing to force the whole node offline, which makes it safe to start the service from a different server. Fencing can be performed at two levels: the node or resource level. Launch Wizard only supports node-level fencing.
Default quotas
Launch Wizard allows for a maximum of 50 active applications (with status in
progress or completed) for any given application type. If you
want to increase this limit, contact Support
AWS Regions
Launch Wizard uses various AWS services during the provisioning of the application's environment. Not every workload is supported in all AWS Regions. For a current list of Regions where the workload can be provisioned, see AWS Launch Wizard workload availability.
Components
Windows
A SQL Server application deployed on Windows with Launch Wizard includes the following components:
-
A virtual private cloud (VPC) configured with public and private subnets across two Availability Zones. A public subnet is a subnet whose traffic is routed to an internet gateway. If a subnet does not have a route to the internet gateway, then it is a private subnet. The VPC provides the network infrastructure for your SQL Server deployment. You can choose an optional third Availability Zone for additional SQL cluster nodes, as shown below.
-
An internet gateway to provide access to the internet.
-
In the public subnets, Windows Server-based Remote Desktop Gateway (RDGW) instances and network address translation (NAT) gateways for outbound internet access. If you are deploying in your preexisting VPC, Launch Wizard uses the existing NAT gateway in your VPC. For more information about NAT gateways, see NAT Gateways.
-
Elastic IP addresses associated with the NAT gateway and RDGW instances. For more information about Elastic IP addresses, see Elastic IP addresses.
-
In the private subnets, Active Directory domain controllers.
-
In the private subnets, Windows Server-based instances as Windows Server Failover Clustering (WSFC) nodes. For more information, see Windows Server Failover Clustering with SQL Server
. -
SQL Server Enterprise edition with SQL Server Always On Availability Groups on each WSFC node. This architecture provides redundant databases and a witness server to ensure that a quorum can vote for the node to be promoted to the controlling resource. The default architecture mirrors an on-premises architecture of two SQL Server instances spanning two subnets placed in two different Availability Zones. For more information about SQL Server Always On Availability Groups, see Overview of Always On Availability Groups (SQL Server)
. -
Security groups to ensure the secure flow of traffic between the instances deployed in the VPC. For more information, see Security Groups for Your VPC.
Note
If you choose to deploy SQL Server Always On through Launch Wizard into your existing VPC, there is an additional mandatory check box on the console to indicate whether VPC and public/private subnet requirements have been met.
-
Amazon FSx to provide highly available and redundant storage across Availability Zones for clustering.
Note
Launch Wizard uses two Availability Zones.
You can build a SQL HA installation, as shown in the following diagram.

You can also choose to build an architecture with SQL Server Always On FCI, as shown in the following diagram.

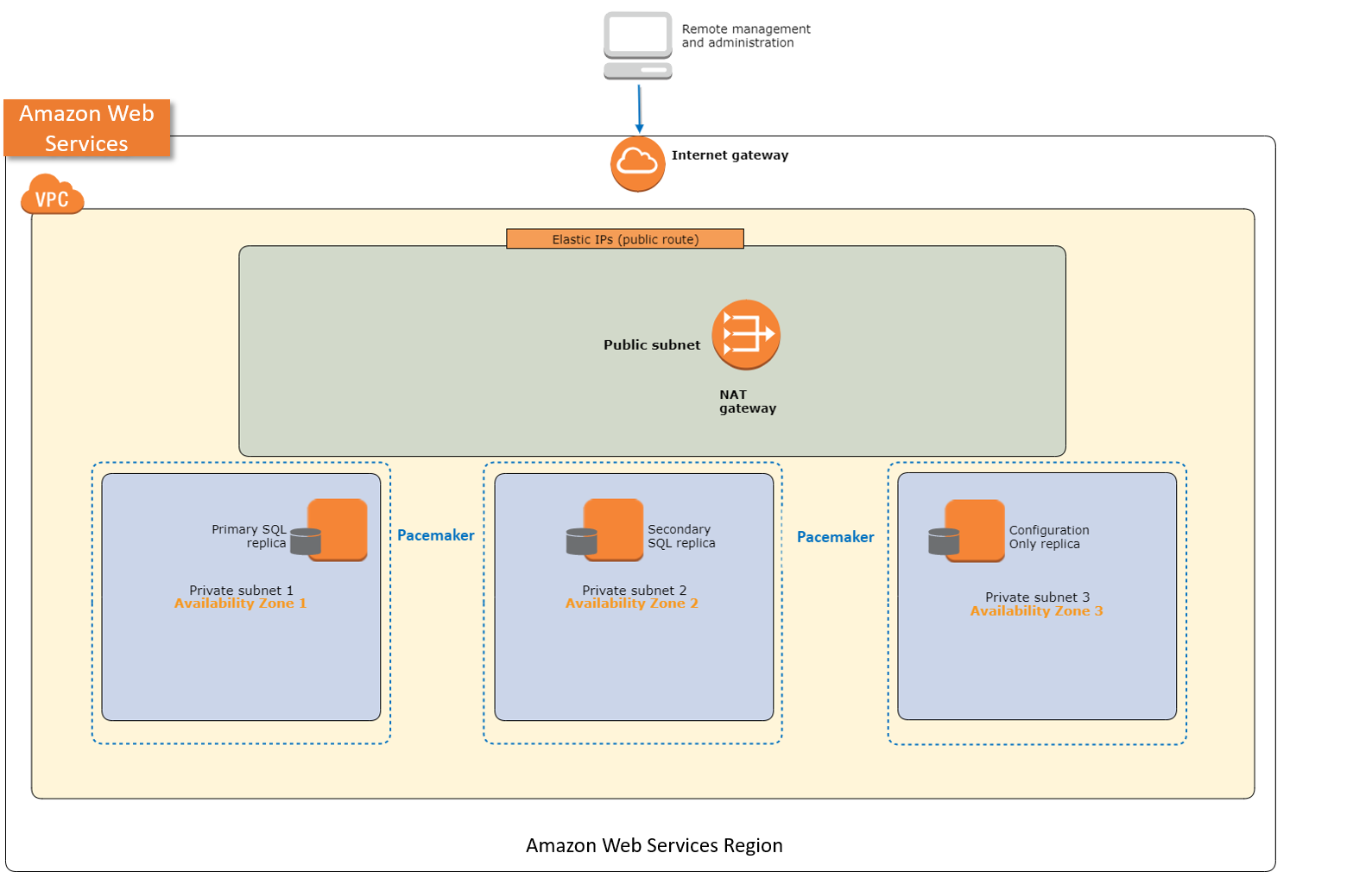
Linux
A SQL Server application deployed on Linux with Launch Wizard includes the following components:
-
A virtual private cloud (VPC) configured with public and private subnets across three Availability Zones. A public subnet is a subnet whose traffic is routed to an internet gateway. If a subnet does not have a route to the internet gateway, then it is a private subnet. The VPC provides the network infrastructure for your SQL Server deployment.
-
An internet gateway to provide access to the internet.
-
In the public subnets, network address translation (NAT) for outbound internet access. If you are deploying in your preexisting VPC, Launch Wizard uses the existing NAT gateway in your VPC. For more information about NAT gateways, see NAT Gateways.
-
Two of the private subnets each run a SQL Server replica node. One acts as the primary node, and the other as secondary node. The third private subnet is used to run the configuration replica. Launch Wizard deployments on Linux use Pacemaker
as the cluster resource manager. Pacemaker differs from Windows Server Failover Cluster (WSFC), which is used for Windows deployments, in terms of how it handles quorum. For Always On availability groups (AG) on Linux, arbitration happens in SQL Server where the metadata is stored. This is where the configuration-only replica is relevant. In order to maintain quorum and enable automatic failovers, Launch Wizard sets up a third node that acts as the configuration-only replica. -
Security groups to ensure the secure flow of traffic between the instances deployed in the VPC. For more information, see Security Groups for Your VPC.
The high-level architecture of a SQL Server high availability solution on Linux is
similar to the architecture for deployment on Windows. The main differences are the
low-level components and technologies. The architecture for Linux deployments provides
redundant databases and a configuration-only replica node to verify that a quorum can
vote for the node to be promoted to the controlling resource. The default architecture
mirrors an on-premises architecture of two SQL Server instances spanning two subnets
placed in two different Availability Zones. For more information about SQL Server Always
On Availability Groups (AG), see Overview of Always On Availability Groups (SQL Server)