Migrate an Oracle database to Aurora PostgreSQL using AWS DMS and AWS SCT
Senthil Ramasamy, Amazon Web Services
Summary
This pattern describes how to migrate an Oracle database to Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition by using AWS Data Migration Service (AWS DMS) and AWS Schema Conversion Tool (AWS SCT).
The pattern covers source Oracle databases that are on premises, Oracle databases that are installed on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances, and Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) for Oracle databases. The pattern converts these databases to Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible.
Prerequisites and limitations
Prerequisites
An active AWS account.
An Oracle database in an on-premises data center or in the AWS Cloud.
SQL clients installed either on a local machine or on an EC2 instance.
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) drivers for AWS SCT connectors, installed on either a local machine or an EC2 instance where AWS SCT is installed.
Limitations
Database size limit: 128 TB
If the source database supports a commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) application or is vendor-specific, you might not be able to convert it to another database engine. Before using this pattern, confirm that the application supports Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible.
Product versions
For self-managed Oracle databases, AWS DMS supports all Oracle database editions for versions 10.2 and later (for versions 10.x), 11g, and up to 12.2, 18c, and 19c. For the latest list of supported Oracle database versions (both self-managed and Amazon RDS for Oracle), see Using an Oracle database as a source for AWS DMS and Using a PostgreSQL database as a target for AWS DMS.
We recommend that you use the latest version of AWS DMS for the most comprehensive version and feature support. For information about Oracle database versions supported by AWS SCT, see the AWS SCT documentation.
Aurora supports the PostgreSQL versions listed in Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL releases and engine versions.
Architecture
Source technology stack
One of the following:
An on-premises Oracle database
An Oracle database on an EC2 instance
An Amazon RDS for Oracle DB instance
Target technology stack
Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible
Target architecture
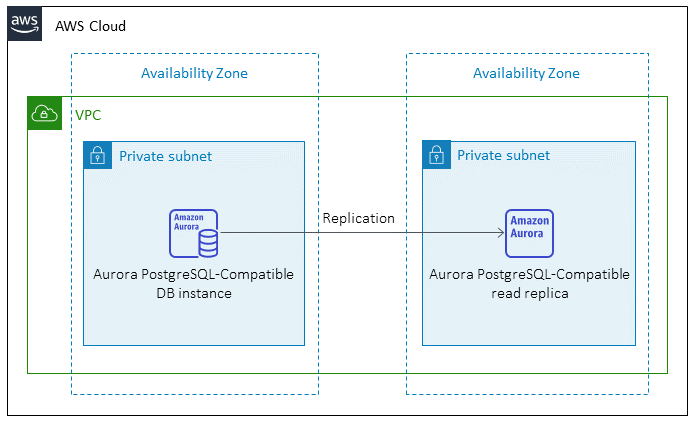
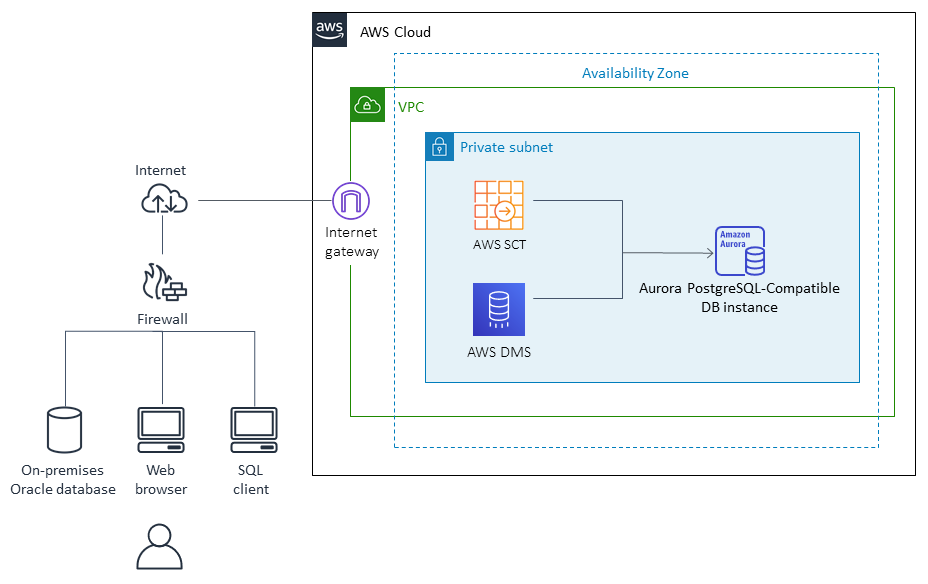
Data migration architecture
From an Oracle database running in the AWS Cloud

From an Oracle database running in an on-premises data center
Tools
AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) helps you migrate data stores into the AWS Cloud or between combinations of cloud and on-premises setups.
AWS Schema Conversion Tool (AWS SCT) supports heterogeneous database migrations by automatically converting the source database schema and a majority of the custom code to a format compatible with the target database.
Epics
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Prepare the source database. | To prepare the source database, see Using Oracle Database as a source for AWS SCT in the AWS SCT documentation. | DBA |
Create an EC2 instance for AWS SCT. | Create and configure an EC2 instance for AWS SCT, if required. | DBA |
Download AWS SCT. | Download the latest version of AWS SCT and associated drivers. For more information, see Installing, verifying, and updating AWS SCT in the AWS SCT documentation. | DBA |
Add users and permissions. | Add and validate the prerequisite users and permissions in the source database. | DBA |
Create an AWS SCT project. | Create an AWS SCT project for the workload, and connect to the source database. For instructions, see Creating an AWS SCT project and Adding database servers in the AWS SCT documentation. | DBA |
Evaluate feasibility. | Generate an assessment report, which summarizes action items for schemas that can’t be converted automatically and provides estimates for manual conversion efforts. For more information, see Creating and reviewing the database migration assessment report in the AWS SCT documentation. | DBA |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Create a target Amazon RDS DB instance. | Create a target Amazon RDS DB instance, using Amazon Aurora as the database engine. For instructions, see Creating an Amazon RDS DB instance in the Amazon RDS documentation. | DBA |
Extract users, roles, and permissions. | Extract the list of users, roles, and permissions from the source database. | DBA |
Map users. | Map the existing database users to the new database users. | App owner |
Create users. | Create users in the target database. | DBA, App owner |
Apply roles. | Apply roles from the previous step to the target database. | DBA |
Check options, parameters, network files, and database links. | Review the source database for options, parameters, network files, and database links, and then evaluate their applicability to the target database. | DBA |
Apply settings. | Apply any relevant settings to the target database. | DBA |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Configure AWS SCT connectivity. | Configure AWS SCT connectivity to the target database. | DBA |
Convert the schema using AWS SCT. | AWS SCT automatically converts the source database schema and most of the custom code to a format that is compatible with the target database. Any code that the tool cannot convert automatically is clearly marked so that you can convert it manually. | DBA |
Review the report. | Review the generated SQL report and save any errors and warnings. | DBA |
Apply automated schema changes. | Apply automated schema changes to the target database or save them as a .sql file. | DBA |
Validate objects. | Validate that AWS SCT created the objects on the target. | DBA |
Handle items that weren't converted. | Manually rewrite, reject, or redesign any items that failed to convert automatically. | DBA, App owner |
Apply role and user permissions. | Apply the generated role and user permissions and review any exceptions. | DBA |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Determine the method. | Determine the method for migrating data. | DBA |
Create a replication instance. | Create a replication instance from the AWS DMS console. For more information, see Working with an AWS DMS replication instance in the AWS DMS documentation. | DBA |
Create the source and target endpoints. | To create endpoints, follow the instructions in Creating source and target endpoints in the AWS DMS documentation. | DBA |
Create a replication task. | To create a task, see Working with AWS DMS tasks in the AWS DMS documentation. | DBA |
Start the replication task and monitor the logs. | For more information about this step, see Monitoring AWS DMS tasks in the AWS DMS documentation. | DBA |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Analyze and convert SQL items in the application code. | Use AWS SCT to analyze and convert the SQL items in the application code. When you convert your database schema from one engine to another, you also need to update the SQL code in your applications to interact with the new database engine instead of the old one. You can view, analyze, edit, and save the converted SQL code. | App owner |
Create application servers. | Create the new application servers on AWS. | App owner |
Migrate the application code. | Migrate the application code to the new servers. | App owner |
Configure the application servers. | Configure the application servers for the target database and drivers. | App owner |
Fix code. | Fix any code that’s specific to the source database engine in your application. | App owner |
Optimize code. | Optimize your application code for the target database engine. | App owner |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Cut over to the target database. | Perform the cutover to the new database. | DBA |
Lock the application. | Lock the application from any further changes. | App owner |
Validate changes. | Validate that all changes were propagated to the target database. | DBA |
Redirect to the target database. | Point the new application servers to the target database. | App owner |
Check everything. | Perform a final, comprehensive system check. | App owner |
Go live. | Complete final cutover tasks. | App owner |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Shut down temporary resources. | Shut down the temporary AWS resources such as the AWS DMS replication instance and the EC2 instance used for AWS SCT. | DBA, App owner |
Update feedback. | Update feedback on the AWS DMS process for internal teams. | DBA, App owner |
Revise process and templates. | Revise the AWS DMS process and improve the template if necessary. | DBA, App owner |
Validate documents. | Review and validate the project documents. | DBA, App owner |
Gather metrics. | Gather metrics to evaluate the time to migrate, percent of manual versus tool cost savings, and so on. | DBA, App owner |
Close the project. | Close the migration project and provide feedback to stakeholders. | DBA, App owner |
Related resources
References
Using a PostgreSQL Database as a Target for AWS Database Migration Service
Oracle Database 11g/12c to Amazon Aurora with PostgreSQL Compatibility (9.6.x) Migration Playbook
Oracle Database 19c to Amazon Aurora with PostgreSQL Compatibility (12.4) Migration Playbook
Migrating an Amazon RDS for Oracle database to Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition
Tutorials and videos
Additional information
.