Migrate Redis workloads to Redis Enterprise Cloud on AWS
Antony Prasad Thevaraj, Amazon Web Services
Srinivas Pendyala, Redis
Summary
This pattern discusses the high-level process for migrating Redis workloads to Redis Enterprise Cloud on Amazon Web Services (AWS). It describes the migration steps, provides information about the selection of tools available, and discusses the advantages, disadvantages, and steps for using each tool. Optionally, if you require additional help in migrating workloads from Redis, you can engage Redis Professional Services.
If you run Redis OSS or Redis Enterprise Software on premises, you’re familiar with the significant administrative overhead and operational complexity of maintaining your Redis databases in your data center. By migrating your workloads to the cloud, you can significantly reduce this operational burden and take advantage of Redis Enterprise Cloud
There are potential applications for Redis Enterprise Cloud in the financial services, retail, healthcare, and gaming sectors, as well as in use cases that require solutions for fraud detection, real-time inventory, claims processing, and session management. You can use Redis Enterprise Cloud to connect to your AWS resources―for example, to an application server that is running on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances, or to a microservice that is deployed as an AWS Lambda service.
Prerequisites and limitations
Assumptions
You are currently operating an on-premises database system that you want to migrate to the cloud.
You have identified the migration requirements for your workloads, including:
Data consistency requirements
Infrastructure and system environment requirements
Data mapping and transformation requirements
Functional testing requirements
Performance testing requirements
Validation requirements
Defined cutover strategy
You have assessed timelines and cost estimates required for the migration.
Your requirements take into consideration the scope of the work and the systems and databases you have identified to be part of the migration.
You have identified the stakeholders along with their roles and responsibilities in a responsible, accountable, consulted, informed (RACI) matrix.
You have received the necessary agreement and approvals from all stakeholders.
Cost
Depending on the technical specifications of your existing source database (for example, memory sizing, throughput, and total data size), a Redis solutions architect can size the target system on Redis Enterprise Cloud. For general pricing information, see Redis Pricing
People and skills
The migration process involves the following roles and responsibilities.
Role | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Migration solutions architect | A technical architect who has expertise in defining, planning, and implementing migration strategies | Technical and application-level understanding of source and target systems; experience with migrating workloads to the cloud |
Data architect | A technical architect who has broad experience in defining, implementing, and delivering data solutions for a wide variety of databases | Data modeling for structured and unstructured data, deep understanding and experience in implementing databases for an enterprise |
Redis solutions architect | A technical architect who can help architect an optimally sized Redis cluster for the appropriate use case | Expertise in architecting and deploying Redis solutions for a wide variety of use cases |
Cloud solutions architect | A technical architect who has a deeper understanding of cloud solutions, especially on AWS | Expertise in architecting solutions for the cloud; workload migration and application modernization experience |
Enterprise architect | A technical architect who has a complete understanding of the technical landscape at your organization, who has a shared vision for the future roadmap, and who practices and establishes standardized architectural best practices across all teams in your organization | Software architecture certifications such as TOGAF, foundational software engineering skills, and solutions architecture and enterprise architecture expertise |
IT or DevOps engineer | An engineer who is responsible for creating and maintaining the infrastructure, including monitoring the infrastructure for issues, performing maintenance tasks, and making updates as needed. | Strong understanding of various technologies, including operating systems, networking, and cloud computing; familiarity with programming languages such as Python, Bash, and Ruby, as well as tools such as Docker, Kubernetes, and Ansible |
Architecture
Migration options
The following diagram shows options for migrating your on-premises (Redis-based or other) data sources to AWS. It shows several migration tools that you can choose from, such as exporting Redis Database (RDB) files to Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), using the Redis replication feature, or using AWS DMS.
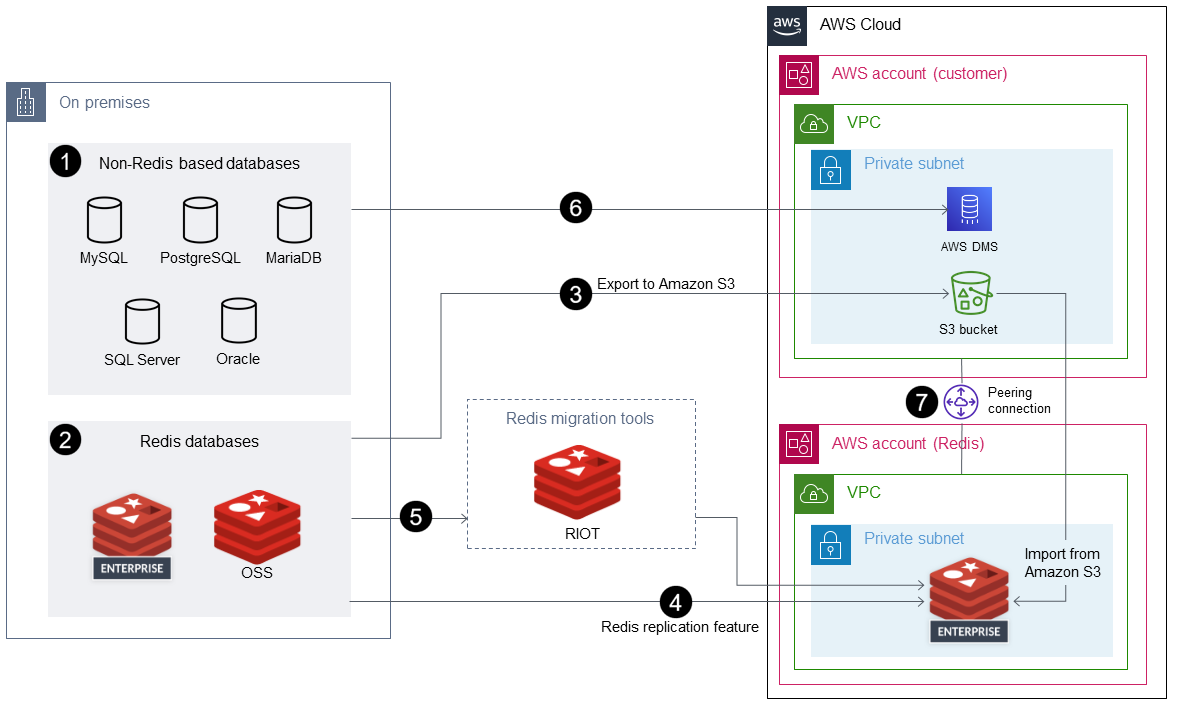
On-premises data sources: Databases that aren’t based on Redis, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, or MariaDB.
On-premises data sources: Redis protocol-based databases such as Redis OSS and Redis Enterprise Software.
The simplest way to migrate data from Redis-based databases is to export RDB files and import them into the target Redis Enterprise Cloud on AWS.
Alternatively, you can migrate the data from source to target by using the replication feature (
ReplicaOf) in Redis.If your data migration requirements include transformation of data, you can employ Redis Input/Output Tools (RIOT) to migrate the data.
Alternatively, you can use AWS Data Migration Service (AWS DMS) to migrate the data from SQL-based databases.
You must use virtual private cloud (VPC) peering for AWS DMS to migrate the data successfully into the target Redis Enterprise Cloud on AWS.
Target architecture
The following diagram shows a typical deployment architecture for Redis Enterprise Cloud on AWS and illustrates how it can be used with key AWS services.
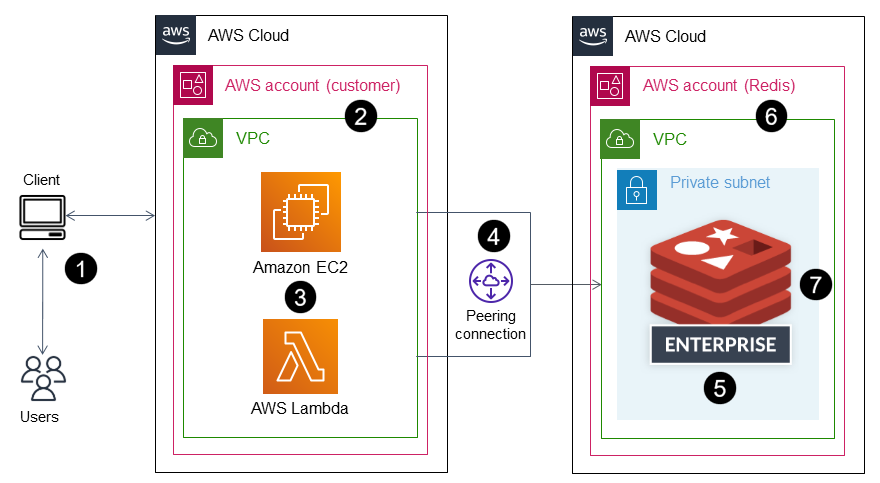
You can connect to the business applications that are backed by Redis Enterprise Cloud on AWS.
You can run business applications in your own AWS account, in a VPC within that account.
You can use Redis Enterprise Cloud database endpoints to connect to your applications. Examples include an application server running on EC2 instances, a microservice deployed as an AWS Lambda service, an Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) application, or an Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) application.
Business applications running in your VPC require a VPC peer connection to the Redis Enterprise Cloud VPC. This enables the business applications to connect securely over private endpoints.
Redis Enterprise Cloud on AWS is an in-memory NoSQL database platform deployed as a DBaaS on AWS and is fully managed by Redis.
Redis Enterprise Cloud is deployed within a VPC in a standard AWS account that is created by Redis.
For security reasons, Redis Enterprise Cloud is deployed in a private subnet that can be accessed at both private and public endpoints. We recommend that you connect your client applications to Redis on private endpoints. If you plan to use a public endpoint, we strongly recommend that you enable TLS
to encrypt the data between your client applications and Redis Enterprise Cloud.
The Redis migration methodology aligns with the AWS migration methodology, which is illustrated in Mobilize your organization to accelerate large-scale migrations on the AWS Prescriptive Guidance website.
Automation and scale
The environment setup tasks for the migration can be automated through AWS Landing Zone and infrastructure as code (IaC) templates for automation and scale. These are discussed in the Epics section of this pattern.
Tools
Based on your data migration requirements, you can choose from a selection of technological options to migrate your data to Redis Enterprise Cloud on AWS. The following table describes and compares these tools.
Tool | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
RDB export | You export the data from the source (for example, Redis OSS or Redis Enterprise Software) database in the form of RDB files. If your database is provided through a Redis OSS Cluster, you export each master shard to an RDB. You then import all the RDB files in one step. If your source database is based on an OSS Cluster but your target database isn't using the OSS Cluster API, you have to change your application source code to use a standard Redis client library. Data transformation requirements or logical database merges require a more complex process, which is explained under Logical database merge later in this table. |
|
|
Redis replication feature | You can continuously replicate data from a Redis OSS, Enterprise Software, or Enterprise Cloud database to a Redis Enterprise Cloud database. After the initial synchronization, the Redis replication feature ( The Redis replication feature is intended to be used in an active-passive way. The target is assumed to be passive and gets fully resynchronized (flushed and synchronized from the source database). Therefore, switching between the source and the target is somewhat more complicated. It’s possible to replicate from a Redis OSS Cluster to a standard clustered Redis Enterprise Cloud database by specifying all the master shards of the OSS Cluster as sources. However, the Redis replication feature allows a maximum of 32 source databases. |
|
|
You can use AWS DMS to migrate data from any supported source database to a target Redis data store with minimal downtime. For more information, see Using Redis as a target for AWS DMS in the AWS DMS documentation. |
|
| |
Logical database merge | Special database merge requirements might require a custom data migration solution. For example, you might have four logical databases ( |
|
|
In addition, you can use the following tools and services from AWS.
Assessment and discovery tools:
Application and server migration tools:
Migration management:
AWS Partner solutions:
Epics
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Identify workloads. | Identify the suitable candidate workloads that you want to migrate. Consider the following before you choose a workload for migration:
Ideally, choose a workload that has maximum business impact with minimum risks involved. Keep the overall process iterative and migrate in small increments. | Data architect, Business champions, Migration project sponsors |
Identify data sources and requirements; design data model. | Redis runs a workshop to accelerate discovery and to define migration planning for the project. As a part of this workshop, Redis teams identify the data sources and source data model requirements, and analyze how these can be remodeled in Redis Enterprise Cloud. The Redis migration team (Professional Services) performs a detailed data model design exercise with your organization. As a part of this exercise, the Redis team:
| Redis solutions architect |
Identify the characteristics of the source database. | Identify the Redis product that is used in the source and target environments. For example:
| Data architect |
Gather current system SLA and other sizing metrics. | Determine the current service-level agreements (SLAs) expressed in terms of throughput (operations per second), latency, overall memory size per database, and high availability (HA) requirements. | Data architect |
Identify the characteristics of the target system. | Determine the answers to these questions:
| Data architect, Redis solutions architect (optional) |
Identify dependencies. | Identify the upstream and downstream dependencies of the current system to be migrated. Make sure that the migration work is in alignment with other dependent system migrations. For example, if you’re planning to migrate other business applications from on premises to the AWS Cloud, identify these applications and align them based on project goals, timelines, and stakeholders. | Data architect, enterprise architect |
Identify migration tools. | Depending on your data migration requirements (such as source data or downtime requirements), you can use any of the tools described previously in the Tools section. In addition, you can use: | Migration solutions architect, Redis solutions architect |
Create a contingency plan. | Establish a contingency plan to roll back, in case you encounter problems during migration. | Project management, Technical teams, including architect |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Secure the Redis administration console. | To secure the administration console, follow the instructions in the Redis documentation | IT infrastructure administrator |
Secure the Redis database. | See the following pages in the Redis documentation to: | |
Secure Redis Cloud APIs. | When you enable the API | IT infrastructure administrator |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Set up a new environment on AWS. | This task includes:
| IT or DevOps engineer |
Deploy the migration architecture. |
You are now ready to run the actual data migration pipelines and test them. | IT or DevOps engineer |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Establish connectivity. | Establish connectivity between the on-premises infrastructure and AWS Cloud resources. Use security groups, AWS Direct Connect, and other resources to achieve this functionality. For more information, see Connect Your Data Center to AWS | IT or DevOps engineer |
Set up VPC peering. | Establish VPC peering between the VPCs that run business applications (or the EC2 instances that run migration tools or the AWS DMS replication server) and the VPC that runs Redis Enterprise Cloud. For instructions, see Get started with Amazon VPC in the Amazon VPC documentation, and Enable VPC peering | IT or DevOps engineer |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Choose a data migration tool. | Review the table in the Tools section to see descriptions, advantages, and disadvantages of these tools:
The following rows describe the data migration tasks associated with each tool. | Migration solutions architect |
Option 1: Use RDB export and import. |
For more information, see the Redis documentation | Migration solutions architect, Redis solutions architect |
Option 2: Use the Redis replication feature (active-passive). |
For more information, see the Redis documentation | Migration solutions architect, Redis solutions architect |
Option 3: Use AWS DMS. |
| Migration solutions architect, Redis solutions architect |
Option 4: Use logical database merge. | This option involves using a migration script or ETL tool that can transform the source database’s physical data model and generating an RDB file. Redis Professional Services can help with this step, if needed. | Migration solutions architect, Redis solutions architect |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Align project management timelines and goals. | Align the migration project goals, milestones, and timelines of the application layer with that of the Redis data migration project. | Project management |
Align testing activities. | After the application layer is migrated and modernized in the AWS Cloud, point the application layer to the newly migrated Redis Enterprise Cloud on AWS for testing. | Testing |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Implement test plans. | Run the data migration routines and the scripts that were developed during the implementation phase in a testing environment, per test requirements, at your site. | Testing |
Test data quality. | Test data quality after you migrate the data. | Testing |
Test functionality. | Test data queries and the application layer to ensure that the application is performing at the same level as in the source system. | Testing |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Make the cutover decision. | After all application-level and database-level testing is complete, the executive leadership team and stakeholders make the final decision regarding whether to cut over to the new environment on AWS based on the final results confirmed by the testing teams. | Project management, Business champions |
Cut over to the AWS Cloud. | When you have confirmed that everything is in place, point the application layer to the newly migrated data and point clients to the new application layer that is running based on the new Redis Enterprise Cloud system on AWS. | IT or DevOps engineer, Data architect, Migration solutions architect, Redis solutions architect |
Related resources
Redis resources
RIOT
tool (GitHub repository) Terraform Provider
(download)
AWS resources
Additional information
For standard security requirements for migrating Redis workloads to the AWS Cloud, see the Best Practices for Security, Identity, and Compliance