Regions and Availability Zones
Amazon cloud computing resources are hosted in multiple locations world-wide. These locations are composed of AWS Regions and Availability Zones. Each AWS Region is a separate geographic area. Each AWS Region has multiple, isolated locations known as Availability Zones.
Note
For information about finding the Availability Zones for an AWS Region, see Describe your Availability Zones in the Amazon EC2 documentation.
Amazon operates state-of-the-art, highly-available data centers. Although rare, failures can occur that affect the availability of DB instances that are in the same location. If you host all your DB instances in one location that is affected by such a failure, none of your DB instances will be available.
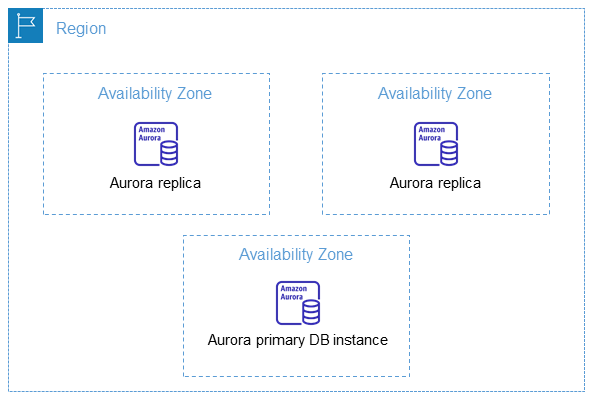
It is important to remember that each AWS Region is completely independent. Any Amazon RDS
activity you initiate (for example, creating database instances or listing available
database instances) runs only in your current default AWS Region. The default AWS Region
can be changed in the console, or by setting the AWS_DEFAULT_REGION environment variable. Or it can be
overridden by using the --region parameter with the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI). For more
information, see Configuring the
AWS Command Line Interface, specifically the sections about environment variables and command
line options.
Amazon RDS supports special AWS Regions called AWS GovCloud (US). These are designed to allow US government agencies and customers to move more sensitive workloads into the cloud. The AWS GovCloud (US) Regions address the US government's specific regulatory and compliance requirements. For more information, see What is AWS GovCloud (US)?
To create or work with an Amazon RDS DB instance in a specific AWS Region, use the corresponding regional service endpoint.
Note
Aurora doesn't support Local Zones.
AWS Regions
Each AWS Region is designed to be isolated from the other AWS Regions. This design achieves the greatest possible fault tolerance and stability.
When you view your resources, you see only the resources that are tied to the AWS Region that you specified. This is because AWS Regions are isolated from each other, and we don't automatically replicate resources across AWS Regions.
Region availability
When you work with an Aurora DB cluster using the command line interface or API operations, make sure that you specify its regional endpoint.
Aurora MySQL Region availability
The following table shows the AWS Regions where Aurora MySQL is currently available and the endpoint for each Region.
| Region Name | Region | Endpoint | Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| US East (Ohio) | us-east-2 | rds.us-east-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| US East (N. Virginia) | us-east-1 | rds.us-east-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| US West (N. California) | us-west-1 | rds.us-west-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| US West (Oregon) | us-west-2 | rds.us-west-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Africa (Cape Town) | af-south-1 | rds.af-south-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Hong Kong) | ap-east-1 | rds.ap-east-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Hyderabad) | ap-south-2 | rds.ap-south-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Jakarta) | ap-southeast-3 | rds.ap-southeast-3.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Malaysia) | ap-southeast-5 | rds.ap-southeast-5.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Melbourne) | ap-southeast-4 | rds.ap-southeast-4.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Mumbai) | ap-south-1 | rds.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (New Zealand) | ap-southeast-6 | rds.ap-southeast-6.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Osaka) | ap-northeast-3 | rds.ap-northeast-3.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Seoul) | ap-northeast-2 | rds.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Singapore) | ap-southeast-1 | rds.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Sydney) | ap-southeast-2 | rds.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Taipei) | ap-east-2 | rds.ap-east-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Thailand) | ap-southeast-7 | rds.ap-southeast-7.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Tokyo) | ap-northeast-1 | rds.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Canada (Central) | ca-central-1 | rds.ca-central-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Canada West (Calgary) | ca-west-1 | rds.ca-west-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Frankfurt) | eu-central-1 | rds.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Ireland) | eu-west-1 | rds.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (London) | eu-west-2 | rds.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Milan) | eu-south-1 | rds.eu-south-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Paris) | eu-west-3 | rds.eu-west-3.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Spain) | eu-south-2 | rds.eu-south-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Stockholm) | eu-north-1 | rds.eu-north-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Zurich) | eu-central-2 | rds.eu-central-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Israel (Tel Aviv) | il-central-1 | rds.il-central-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Mexico (Central) | mx-central-1 | rds.mx-central-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Middle East (Bahrain) | me-south-1 | rds.me-south-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Middle East (UAE) | me-central-1 | rds.me-central-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| South America (São Paulo) | sa-east-1 | rds.sa-east-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| AWS GovCloud (US-East) | us-gov-east-1 | rds.us-gov-east-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| AWS GovCloud (US-West) | us-gov-west-1 | rds.us-gov-west-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
Aurora PostgreSQL Region availability
The following table shows the AWS Regions where Aurora PostgreSQL is currently available and the endpoint for each Region.
| Region Name | Region | Endpoint | Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| US East (Ohio) | us-east-2 | rds.us-east-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| US East (N. Virginia) | us-east-1 | rds.us-east-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| US West (N. California) | us-west-1 | rds.us-west-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| US West (Oregon) | us-west-2 | rds.us-west-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Africa (Cape Town) | af-south-1 | rds.af-south-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Hong Kong) | ap-east-1 | rds.ap-east-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Hyderabad) | ap-south-2 | rds.ap-south-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Jakarta) | ap-southeast-3 | rds.ap-southeast-3.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Malaysia) | ap-southeast-5 | rds.ap-southeast-5.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Melbourne) | ap-southeast-4 | rds.ap-southeast-4.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Mumbai) | ap-south-1 | rds.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (New Zealand) | ap-southeast-6 | rds.ap-southeast-6.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Osaka) | ap-northeast-3 | rds.ap-northeast-3.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Seoul) | ap-northeast-2 | rds.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Singapore) | ap-southeast-1 | rds.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Sydney) | ap-southeast-2 | rds.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Taipei) | ap-east-2 | rds.ap-east-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Thailand) | ap-southeast-7 | rds.ap-southeast-7.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Asia Pacific (Tokyo) | ap-northeast-1 | rds.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Canada (Central) | ca-central-1 | rds.ca-central-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Canada West (Calgary) | ca-west-1 | rds.ca-west-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Frankfurt) | eu-central-1 | rds.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Ireland) | eu-west-1 | rds.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (London) | eu-west-2 | rds.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Milan) | eu-south-1 | rds.eu-south-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Paris) | eu-west-3 | rds.eu-west-3.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Spain) | eu-south-2 | rds.eu-south-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Stockholm) | eu-north-1 | rds.eu-north-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Europe (Zurich) | eu-central-2 | rds.eu-central-2.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Israel (Tel Aviv) | il-central-1 | rds.il-central-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Mexico (Central) | mx-central-1 | rds.mx-central-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Middle East (Bahrain) | me-south-1 | rds.me-south-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| Middle East (UAE) | me-central-1 | rds.me-central-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| South America (São Paulo) | sa-east-1 | rds.sa-east-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| AWS GovCloud (US-East) | us-gov-east-1 | rds.us-gov-east-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
| AWS GovCloud (US-West) | us-gov-west-1 | rds.us-gov-west-1.amazonaws.com | HTTPS |
Availability Zones
An Availability Zone is an isolated location in a given
AWS Region. Each Region has multiple Availability Zones (AZ) designed to provide high
availability for the Region. An AZ is identified by the AWS Region code followed by a
letter identifier (for example, us-east-1a). If you create your
VPC and subnets rather than using the default VPC, you define each subnet in a specific
AZ. When you create an Aurora DB cluster, Aurora creates the primary instance in one of
the subnets in the VPC's DB subnet group. It thus associates that instance with a
specific AZ chosen by Aurora.
Each Aurora DB cluster hosts copies of its storage in three separate AZs selected automatically by Aurora from the AZs in your DB subnet group. Every DB instance in the cluster must be in one of these three AZs.
When you create a DB instance in your cluster, Aurora automatically chooses an appropriate AZ for that instance if you don't specify an AZ.
Use the describe-availability-zones Amazon EC2 command as follows to describe the Availability Zones within the specified Region that are enabled for your account.
aws ec2 describe-availability-zones --regionregion-name
For example, to describe the Availability Zones within the US East (N. Virginia) Region (us-east-1) that are enabled for your account, run the following command:
aws ec2 describe-availability-zones --region us-east-1
To learn how to specify the AZ when you create a cluster or add instances to it, see Configure the network for the DB cluster.
Local time zone for Amazon Aurora DB clusters
By default, the time zone for an Amazon Aurora DB cluster is Universal Time Coordinated (UTC). You can set the time zone for instances in your DB cluster to the local time zone for your application instead.
To set the local time zone for a DB cluster, set the time zone parameter to one of the supported values. You set this parameter in the cluster parameter group for your DB cluster.
-
For Aurora MySQL, the name of this parameter is
time_zone. For information on best practices for setting thetime_zoneparameter, see Optimizing timestamp operations. -
For Aurora PostgreSQL, the name of this parameter is
timezone.
When you set the time zone parameter for a DB cluster, all instances in the DB cluster change to use the new local time zone. In some cases, other Aurora DB clusters might be using the same cluster parameter group. If so, all instances in those DB clusters change to use the new local time zone also. For information on cluster-level parameters, see Amazon Aurora DB cluster and DB instance parameters.
After you set the local time zone, all new connections to the database reflect the change. In some cases, you might have open connections to your database when you change the local time zone. If so, you don't see the local time zone update until after you close the connection and open a new connection.
If you are replicating across AWS Regions, the replication source DB cluster and the replica use different parameter groups. Parameter groups are unique to an AWS Region. To use the same local time zone for each instance, make sure to set the time zone parameter in the parameter groups for both the replication source and the replica.
When you restore a DB cluster from a DB cluster snapshot, the local time zone is set to UTC. You can update the time zone to your local time zone after the restore is complete. In some cases, you might restore a DB cluster to a point in time. If so, the local time zone for the restored DB cluster is the time zone setting from the parameter group of the restored DB cluster.
The following table lists some of the values to which you can set your local time zone. To list all of the available time zones, you can use the following SQL queries:
-
Aurora MySQL:
select * from mysql.time_zone_name; -
Aurora PostgreSQL:
select * from pg_timezone_names;
Note
For some time zones, time values for certain date ranges can be reported incorrectly as noted in the table. For Australia time zones, the time zone abbreviation returned is an outdated value as noted in the table.
|
Time zone |
Notes |
|---|---|
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 28 Feb 1903 21:49:40 GMT to 28 Feb 1903 21:55:48 GMT. |
|
|
|
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 31 Dec 1939 21:30:00 GMT to 31 Dec 1959 21:15:15 GMT. |
|
|
|
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 23 Nov 1914 04:56:16 GMT to 23 Nov 1914 04:56:20 GMT. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In some cases, for a DB cluster in the South America (Sao Paulo)
Region, time doesn't show correctly for a recently changed Brazil
time zone. If so, reset the DB cluster's time zone parameter to
|
|
|
|
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 27 Oct 1918 05:00:00 GMT to 31 Oct 1918 05:00:00 GMT. |
|
|
If your DB cluster is in the South America (Cuiaba) time zone and the
expected time doesn't show correctly for the recently changed Brazil
time zone, reset the DB cluster's time zone parameter to
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 31 Dec 1919 20:05:36 GMT to 31 Dec 1919 20:05:40 GMT. |
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 13 Mar 1947 20:53:08 GMT to 31 Dec 1949 20:53:08 GMT. |
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 30 Nov 1904 15:30:00 GMT to 07 Sep 1945 15:00:00 GMT. |
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 31 Dec 1927 15:54:08 GMT to 02 Jun 1940 16:00:00 GMT. |
|
|
|
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 30 Sep 1937 16:00:00 GMT to 29 Sep 1979 15:00:00 GMT. |
|
|
|
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 30 Sep 1937 15:00:00 GMT to 31 Dec 1937 15:00:00 GMT. |
|
|
|
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 24 May 1911 01:54:32 GMT to 01 Jan 1912 01:54:32 GMT. |
|
|
The abbreviation for this time zone is returned as CST instead of ACDT/ACST. |
|
|
The abbreviation for this time zone is returned as EST instead of AEDT/AEST. |
|
|
The abbreviation for this time zone is returned as CST instead of ACDT/ACST. |
|
|
The abbreviation for this time zone is returned as EST instead of AEDT/AEST. |
|
|
The abbreviation for this time zone is returned as WST instead of AWDT/AWST. |
|
|
The abbreviation for this time zone is returned as EST instead of AEDT/AEST. |
|
|
|
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 27 Oct 1918 08:00:00 GMT to 31 Oct 1918 08:00:00 GMT. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 30 Apr 1921 22:20:08 GMT to 30 Apr 1921 22:20:11 GMT. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 21 May 1933 11:30:00 GMT to 30 Sep 1945 11:30:00 GMT. |
|
|
This time zone setting can return incorrect values from 01 Jan 1911 11:22:48 GMT to 01 Jan 1950 11:30:00 GMT. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|