Design principles for developing a secure contact center in Amazon Connect
Security includes the ability to protect information, systems, and assets while delivering business value through risk assessments and mitigation strategies. This section provides an overview of design principles, best practices, and questions surrounding security for Amazon Connect workloads.
Amazon Connect Security Journey
After you’ve made the decision to move your workload to Amazon Connect, in addition to reviewing Security in Amazon Connect and Security Best Practices for Amazon Connect, follow these guidelines and steps to understand and implement your security requirements relative to the following core security areas:

Understanding the AWS Security Model
When you move computer systems and data to the cloud, security responsibilities become shared between you and AWS. AWS is responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure that supports the cloud, and you’re responsible for anything you put on the cloud or connect to the cloud.
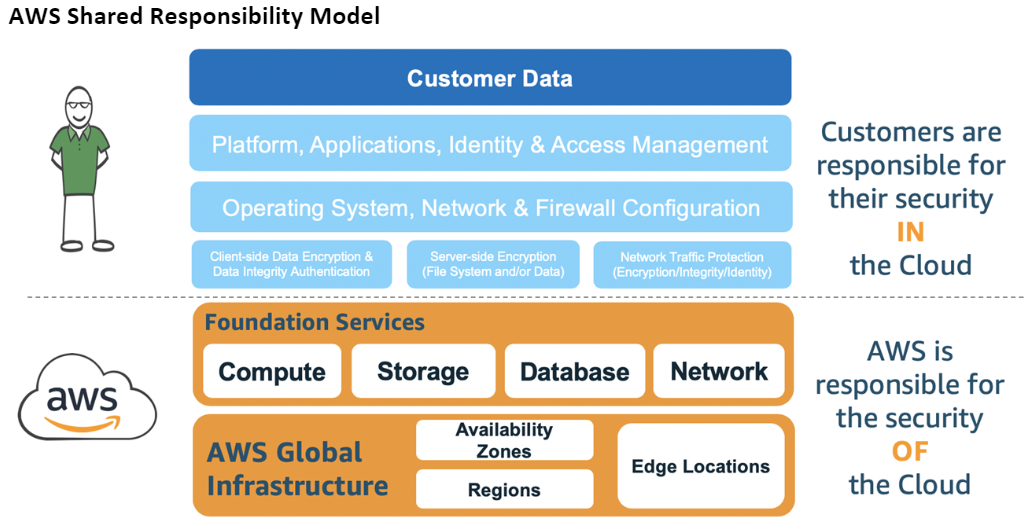
Which AWS services you use will determine how much configuration work you have to perform as part of your security responsibilities. When you use Amazon Connect, the shared model reflects AWS and customer responsibilities at a high-level, as shown in the following diagram.
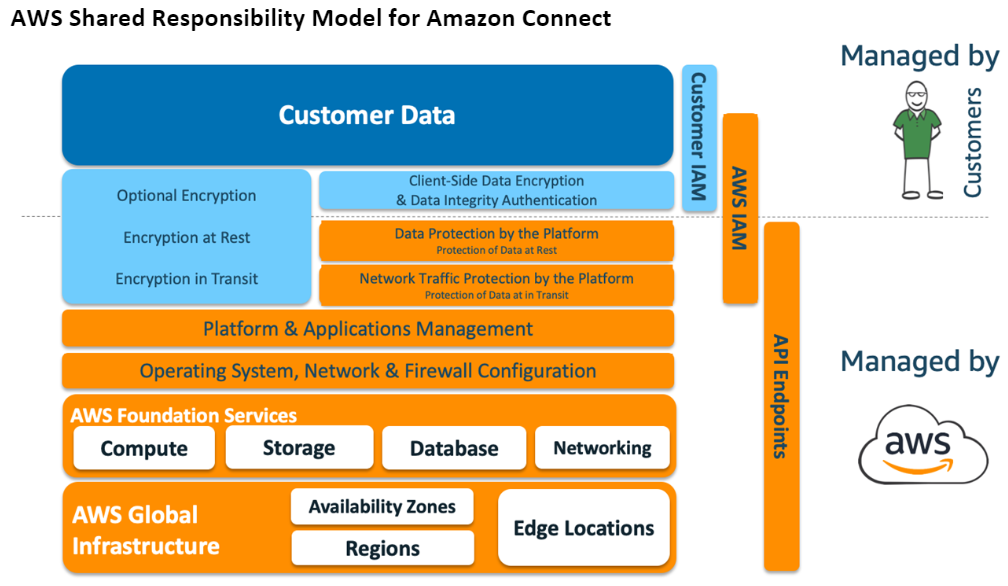
Compliance Foundations
Third-party auditors assess the security and compliance of Amazon Connect as part of
multiple AWS compliance programs. These include SOC
For a list of AWS services in scope of specific compliance programs, see
AWS Services
in Scope by Compliance Program
Region selection
Region selection to host the Amazon Connect instance depends on data sovereignty restrictions and where the contacts and agents are based. After that decision is made, review network requirements for Amazon Connect and ports and protocols that you need to allow. Additionally, to reduce the blast radius use the domain allow list or allowed IP address ranges for your Amazon Connect instance.
For more information, see Set up your network to use the Amazon Connect Contact Control Panel (CCP).
AWS services integration
We recommend reviewing each AWS service in your solution against the security requirements of your organization. See the following resources:
Data Security in Amazon Connect
During your security journey, your security teams may require a deeper understanding of how data is handled in Amazon Connect. See the following resources:
Workload diagram
Review your workload diagram and architect an optimum solution on AWS. This includes analyzing and deciding which additional AWS services should be included in your solution and any third-party and on-premises applications that need to be integrated.
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Types of Amazon Connect Personas
There are four types of Amazon Connect personas, based on the activities being performed.
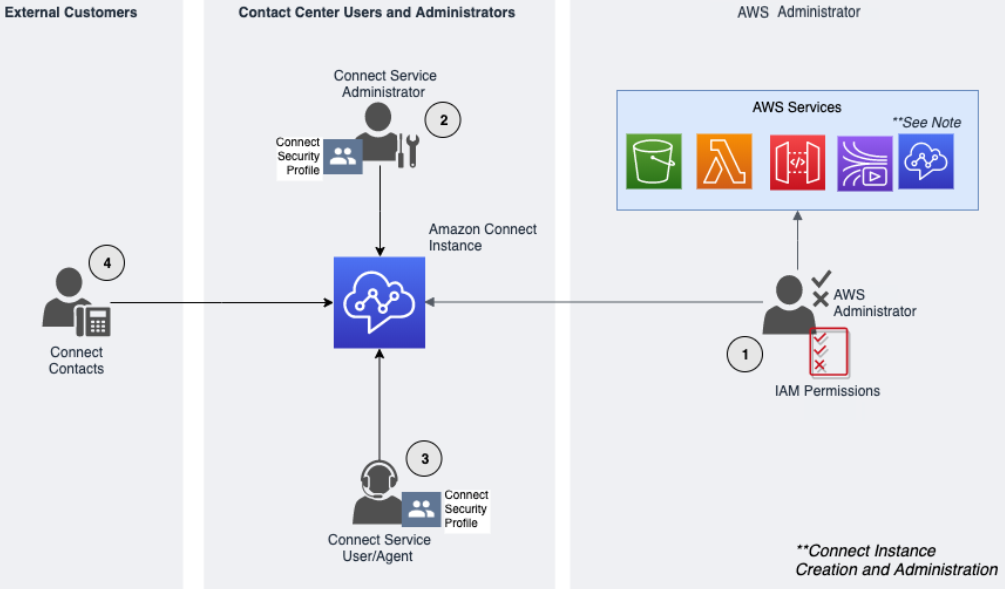
-
AWS administrator – AWS administrators create or modify Amazon Connect resources and may also delegate administrative access to other principals by using the AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) service. The scope of this persona is focused on creating and administering your Amazon Connect instance.
-
Amazon Connect administrator – Service administrators determine which Amazon Connect features and resources employees should access within the Amazon Connect admin website. The service administrator assigns security profiles to determine who can access the Amazon Connect admin website and what tasks they can perform. The scope of this persona is focused on creating and administering your Amazon Connect contact center.
-
Amazon Connect agent – Agents interact with Amazon Connect to perform their job duties. Service users may be contact center agents or supervisors.
-
Amazon Connect Service contact – The customer who interacts with your Amazon Connect contact center.
IAM Administrator Best Practices
IAM Administrative access should be limited to approved personnel within your organization. IAM administrators should also understand what IAM features are available to use with Amazon Connect. For IAM best practices, see Security best practices in IAM in the IAM User Guide. Also see Amazon Connect identity-based policy examples.
Amazon Connect Service Administrator Best Practices
Service administrators are responsible for managing Amazon Connect users, including adding users to Amazon Connect give them their credentials, and assign the appropriate permissions so they can access the features needed to do their job. Administrators should start with a minimum set of permissions and grant additional permissions as necessary.
Security profiles for Amazon Connect and Contact Control Panel (CCP) access help you manage who can access the Amazon Connect dashboard and Contact Control Panel, and who can perform specific tasks. Review the granular permissions granted within the default security profiles available natively. Custom security profiles can be set up to meet specific requirements. For example, a power agent who can take calls but also has access to reports. After this is finalized, users should be assigned to the correct security profiles.
Multi-Factor Authentication
For extra security, we recommend that you require multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all IAM users in your account. MFA can be set up through AWS IAM or your SAML 2.0 identity provider, or Radius server, if that's more applicable for your use case. After MFA is set up, a third text box becomes visible on the Amazon Connect login page to provide the second factor.
Identity Federation
In addition to storing users in Amazon Connect, you can enable single sign-on (SSO) to Amazon Connect by using identity federation. Federation is a recommended practice to allow for employee lifecycle events to be reflected in Amazon Connect when they are made in the source identity provider.
Access to Integrated Applications
Steps within your flows may need credentials to access information in external applications and systems. To provide credentials to access other AWS services in a secure way, use IAM roles. An IAM role is an entity that has its own set of permissions, but that isn't a user or group. Roles also don't have their own permanent set of credentials and are automatically rotated.
Credentials such as API keys should be stored outside of your flow application code, where they can be retrieved programmatically. To accomplish this, you can use AWS Secrets Manager or an existing third-party solution. Secrets Manager enables you to replace hardcoded credentials in your code, including passwords, with an API call to Secrets Manager to retrieve the secret programmatically.
Detective controls
Logging and monitoring are important for the availability, reliability and, performance of contact center. You should log relevant information from Amazon Connect Flows to Amazon CloudWatch and build alerts and notifications based on the same.
You should define log retention requirements and lifecycle policies early on, and plan to move log files to cost-efficient storage locations as soon as practical. Amazon Connect public APIs log to AWS CloudTrail. You should review and automate actions set up based on CloudTrail logs.
Amazon S3 is the best choice for long-term retention and archiving of log data, especially for organizations with compliance programs that require log data to be auditable in its native format. After log data is in an S3 bucket, define lifecycle rules to automatically enforce retention policies and move these objects to other, cost-effective storage classes, such as Amazon S3 Standard - Infrequent Access (Standard - IA) or Amazon S3 Glacier.
The AWS cloud provides flexible infrastructure and tools to support both sophisticated in cooperation with offerings and self-managed centralized-logging solutions. This includes solutions such as Amazon OpenSearch Service and Amazon CloudWatch Logs.
Fraud detection and prevention for incoming contacts can be implemented by customizing Amazon Connect Flows per the customer requirements. As an example, customers can check incoming contacts against previous contact activity in DynamoDB, and then take action, such as disconnecting a contact because they are a blocked contact.
Infrastructure protection
Although there is no infrastructure to manage in Amazon Connect, there could be scenarios where your Amazon Connect instance needs to interact with other components or applications deployed in infrastructure residing on-premises. Consequently, it is important to ensure that networking boundaries are considered under this assumption. Review and implement specific Amazon Connect infrastructure security considerations. Also, review contact center agent and supervisor desktops or VDI solutions for security considerations.
You can configure a Lambda function to connect to private subnets in a virtual private cloud (VPC) in your account. Use Amazon Virtual Private Cloud to create a private network for resources such as databases, cache instances, or internal services. Amazon Connect your function to the VPC to access private resources during execution.
Data protection
Customers should analyze the data traversing through and interacting with the contact center solution.
-
Third party and external data
-
On-premises data in hybrid Amazon Connect architectures
After analyzing the scope of the data, data classifications should be performed paying attention to identifying sensitive data. Amazon Connect conforms to the AWS shared responsibility model. Data protection in Amazon Connect includes best practices like using MFA and TLS and the use of other AWS services, including Amazon Macie.
Amazon Connect handles variety of data related to contact centers. This includes phone call media, call recordings, chat transcripts, contact metadata as well as flows, routing profiles and queues. Amazon Connect handles data at rest by segregating data by account ID and instance ID. All data exchanged with Amazon Connect is protected in transit between the user's web browser and Amazon Connect using open standard TLS encryption.
You can specify AWS KMS keys to be used for encryption including bring your own key (BYOK). Additionally, you can use key management options within Amazon S3.
Protecting Data Using Client-Side Encryption
Your use case may require encryption of sensitive data that is collected by flows. For example, to gather appropriate personal information to customize the customer experience when they interact with your IVR. To do this you can use public-key cryptography with the AWS Encryption SDK. The AWS Encryption SDK is a client-side encryption library designed to make it efficient for everyone to encrypt and decrypt data using open standards and best practices.
Input validation
Perform input validation to ensure that only properly formed data is entering the flow. This should happen as early as possible in the flow. For example, when prompting a customer to say or enter a telephone number, they may or may not include the country code.
Amazon Connect security vectors
Amazon Connect security can be divided into three logical layers as illustrated in the following diagram:
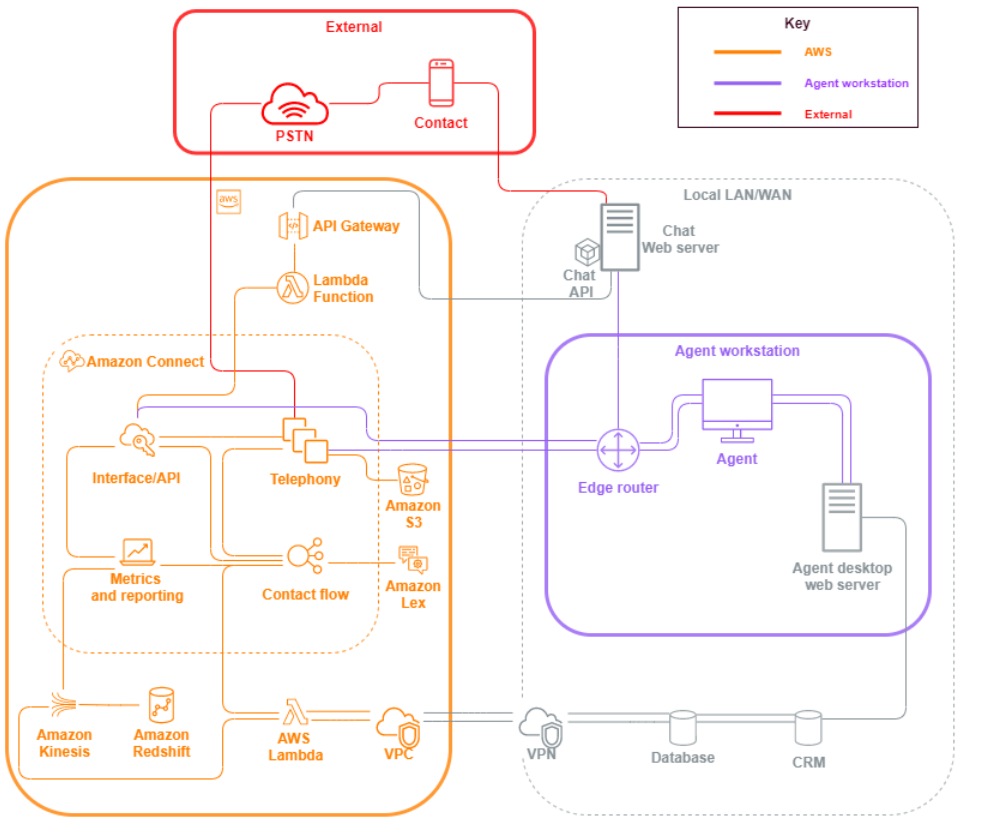
-
Agent workstation. The agent workstation layer is not managed by AWS and consists of any physical equipment and third-party technologies, services, and endpoints that facilitate your agent’s voice, data, and access the Amazon Connect interface layer.
Follow your security best practices for this layer with special attention to the following:
-
Plan identity management keeping in mind best practices noted in Security Best Practices for Amazon Connect.
-
Mitigate insider threat and compliance risk associated with workloads that handle sensitive information, by creating a secure IVR solution that enables you to bypass agent access to sensitive information. By encrypting contact input in your flows, you’re able to capture information securely without exposing it to your agents, their workstations, or their operating environments. For more information, see Encrypt sensitive customer input in Amazon Connect.
-
You are responsible for maintaining the allowlist of AWS IP addresses, ports, and protocols needed to use Amazon Connect.
-
-
AWS: The AWS layer includes Amazon Connect and AWS integrations including AWS Lambda, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon API Gateway, Amazon S3, and other services. Follow the security pillar guidelines for AWS services, with special attention to the following:
-
Plan identity management, keeping in mind best practices noted in Security Best Practices for Amazon Connect.
-
Integrations with other AWS services: Identify each AWS service in the use case as well as any third-party integration points applicable for this use case.
-
Amazon Connect can integrate with AWS Lambda functions that run inside of a customer VPC through the VPC endpoints for Lambda.
-
-
External: The External layer includes contact points including chat, click-to-call endpoints, and the PSTN for voice calls, integrations you may have with legacy contact center solutions in a Hybrid contact center architecture, and integrations you may have with other third-party solutions. Any entry point or exit point for a third party in your workload is considered the external layer.
This layer also covers integrations customers may have with other third-party solutions and applications such as CRM systems, work force management (WFM), and reporting and visualization tools and applications, such as Tableau and Kibana. You should consider the following areas when securing the external layer:
-
You can create contact filters for repeat and fraudulent contacts
using AWS Lambda to write contact details to DynamoDB from within your flow, including ANI, IP address for click-to-dial and chat endpoints, and any other identifying information to track how many contact requests occur during a given period of time. This approach allows you to query and add contacts to deny lists, automatically disconnecting them if they exceed reasonable levels. -
ANI Fraud detection solutions using Amazon Connect telephony metadata and partner solutions
can be used to protect against caller ID spoofing. -
Amazon Connect Voice ID and other voice biometric partner solutions can be used to enhance and streamline the authentication process. Active voice biometric authentication allows contacts the option to speak specific phrases and use those for voice signature authentication. Passive voice biometrics allow contacts to register their unique voiceprint and use their voiceprint to authenticate with any voice input that meets sufficient length requirements for authentication.
-
Maintain the application integration section in the Amazon Connect console for adding any third-party application or integration points to your allowlist, and remove unused endpoints.
-
Send only the data necessary to meet minimum requirements to external systems that handle sensitive data. For example, if you have only one business unit using your call recording analytics solution, you can set an AWS Lambda trigger in your S3 bucket to process contact records, check for the business unit’s specific queues in the contact record data, and if it is a queue that belongs to the unit, send only that call recording to the external solution. With this approach, you only send the data necessary and avoid the cost and overhead associated with processing unnecessary recordings.
For an integration that enables Amazon Connect to communicate with Amazon Kinesis and Amazon Redshift to enable the streaming of contact records, see Amazon Connect integration: Data streaming
.
-
Resources
Documentation
Articles
Videos