Adding a database to your Elastic Beanstalk environment
Elastic Beanstalk provides integration with Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS)
If you haven't used a database instance with your application before, we recommend that you first use the process described in this topic to add a database to a test environment using the Elastic Beanstalk service. By doing this, you can verify that your application can read the environment properties, construct a connection string, and connect to a database instance, without the additional configuration work required for a database external to Elastic Beanstalk.
After you verify that your application works correctly with the database, you may consider moving towards a production environment. At this point you have the option to decouple the database from your Elastic Beanstalk environment to move towards a configuration that offers greater flexibility. The decoupled database can remain operational as an external Amazon RDS database instance. The health of the environment isn't affected by decoupling the database. If you need to terminate the environment, you can do so and also choose the option to keep the database available and operational outside of Elastic Beanstalk.
Using an external database has several advantages. You can connect to the external database from multiple environments, use database types that aren't supported with integrated databases, and perform blue/green deployments. As an alternative to using a decoupled database that Elastic Beanstalk created, you can also create a database instance outside of your Elastic Beanstalk environment. Both options result in a database instance that's external to your Elastic Beanstalk environment and will require additional security group and connection string configuration. For more information, see Using Elastic Beanstalk with Amazon RDS.
Sections
- Database lifecycle
- Adding an Amazon RDS DB instance to your environment using the console
- Connecting to the database
- Configuring an integrated RDS DB instance using the console
- Configuring an integrated RDS DB instance using configuration files
- Decoupling an RDS DB instance using the console
- Decoupling an RDS DB instance using configuration files
Database lifecycle
You can choose what you want to happen to the database after you decouple it from your Elastic Beanstalk environment. The options that you can choose from are collectively referred to as deletion policies. The following deletion policies apply to a database after you decouple it from an Elastic Beanstalk environment or terminate the Elastic Beanstalk environment.
-
Snapshot — Before Elastic Beanstalk terminates the database, it saves a snapshot of it. You can restore a database from a snapshot when you add a DB instance to an Elastic Beanstalk environment or when you create a standalone database. For more information about creating a new standalone DB instance from a snapshot, see Restoring from a DB snapshot in the Amazon RDS User Guide. You might incur charges for storing database snapshots. For more information, see the Backup Storage section of Amazon RDS Pricing
. -
Delete — Elastic Beanstalk terminates the database. After it's terminated, the database instance is no longer available for any operation.
-
Retain — The database instance isn't terminated. It remains available and operational, though decoupled from Elastic Beanstalk. You can then configure one or multiple environments to connect to the database as an external Amazon RDS database instance. For more information, see Using Elastic Beanstalk with Amazon RDS.
Adding an Amazon RDS DB instance to your environment using the console
You can add a DB instance to your environment by using the Elastic Beanstalk console.
To add a DB instance to your environment
Open the Elastic Beanstalk console
, and in the Regions list, select your AWS Region. -
In the navigation pane, choose Environments, and then choose the name of your environment from the list.
Note
If you have many environments, use the search bar to filter the environment list.
In the navigation pane, choose Configuration.
-
In the Database configuration category, choose Edit.
-
Choose a DB engine, and enter a user name and password.
-
To save the changes choose Apply at the bottom of the page.
You can configure the following options:
-
Snapshot – Choose an existing database snapshot. Elastic Beanstalk restores the snapshot and adds it to your environment. The default value is None. When the value is None, you can configure a new database using the other settings on this page.
-
Engine – Choose a database engine.
-
Engine version – Choose a specific version of the database engine.
-
Instance class – Choose the DB instance class. For information about DB instance classes, see https://aws.amazon.com/rds/
. -
Storage – Choose the amount of storage to provision for your database. You can increase allocated storage later, but you can't decrease it. For information about storage allocation, see Features
. -
Username – Enter a user name of your choice using a combination of only numbers and letters.
-
Password – Enter a password of your choice containing 8–16 printable ASCII characters (excluding
/,\, and@). -
Availability – Choose High (Multi-AZ) to run a warm backup in a second Availability Zone for high availability.
-
Database deletion policy – The deletion policy determines what happens to the database after it's decoupled from your environment. It can be set to the following values:
Create Snapshot,Retain, orDelete. These values are described in Database lifecycle in this same topic.
Note
Elastic Beanstalk creates a master user for the database using the user name and password you provide. To learn more about the master user and its privileges, see Master User Account Privileges.
It takes about 10 minutes to add a DB instance. When the update is complete the new database is coupled to your environment. The hostname and other connection information for the DB instance are available to your application through the following environment properties.
| Property name | Description | Property value |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The hostname of the DB instance. |
On the Connectivity & security tab on the Amazon RDS console: Endpoint. |
|
|
The port where the DB instance accepts connections. The default value varies among DB engines. |
On the Connectivity & security tab on the Amazon RDS console: Port. |
|
|
The database name, |
On the Configuration tab on the Amazon RDS console: DB Name. |
|
|
The username that you configured for your database. |
On the Configuration tab on the Amazon RDS console: Master username. |
|
|
The password that you configured for your database. |
Not available for reference in the Amazon RDS console. |
Connecting to the database
Use the connectivity information to connect to your database from inside your application through environment variables. For more information about using Amazon RDS with your applications, see the following topics.
-
Java with Tomcat – Connecting to a database (Tomcat platforms)
-
Node.js – Connecting to a database
-
.NET – Connecting to a database
-
Python – Connecting to a database
-
Ruby – Connecting to a database
Configuring an integrated RDS DB instance using the console
You can view and modify configuration settings for your database instance in the Database section on the environment's Configuration page in the Elastic Beanstalk console.
To configure your environment's DB instance in the Elastic Beanstalk console
Open the Elastic Beanstalk console
, and in the Regions list, select your AWS Region. -
In the navigation pane, choose Environments, and then choose the name of your environment from the list.
Note
If you have many environments, use the search bar to filter the environment list.
In the navigation pane, choose Configuration.
-
In the Database configuration category, choose Edit.
You can modify the Instance class, Storage, Password, Availability, and Database deletion policy settings after database creation. If you change the instance class, Elastic Beanstalk re-provisions the DB instance.
If you no longer need Elastic Beanstalk to associate the database to the environment, you can choose to decouple it by selecting Decouple database. It’s important to understand the options and considerations involved with this operation. For more information, see Decoupling an RDS DB instance using the console.
Warning
Don't modify settings on the coupled database instance outside of the functionality that's provided by Elastic Beanstalk (for example, in the Amazon RDS console). If you do, your Amazon RDS DB configuration might be out of sync with your environment's definition. When you update or restart your environment, the settings specified in the environment override any settings you made outside of Elastic Beanstalk.
If you need to modify settings that Elastic Beanstalk doesn't directly support, use Elastic Beanstalk configuration files.
Configuring an integrated RDS DB instance using configuration files
You can configure your environment's database instance using configuration files. Use the options in the aws:rds:dbinstance namespace. The following example modifies the allocated database storage size to 100 GB.
Example .ebextensions/db-instance-options.config
option_settings: aws:rds:dbinstance: DBAllocatedStorage: 100
If you want to configure DB instance properties that Elastic Beanstalk doesn't support, you can still use a configuration file, and specify your settings using
the resources key. The following example sets values to the StorageType and Iops Amazon RDS properties.
Example .ebextensions/db-instance-properties.config
Resources: AWSEBRDSDatabase: Type: AWS::RDS::DBInstance Properties: StorageType:io1 Iops: 1000
Decoupling an RDS DB instance using the console
You can decouple your database from an Elastic Beanstalk environment without affecting the health of the environment. Consider the following requirements before you decouple the database:
-
What should happen to the database after it’s decoupled?
You can choose to create a snapshot of the database and then terminate it, retain the database operational as a standalone database external to Elastic Beanstalk, or permanently delete the database. The Database deletion policy setting determines this result. For a detailed description of the deletion policies, see Database lifecycle in this same topic.
-
Do you need make any changes to the database configuration settings before decoupling it?
If you need to make any configuration changes to the database, you should apply them before decoupling the database. This includes changes to the Database deletion policy. Any pending changes that are submitted simultaneously with the Decouple database setting will be ignored, while only the decouple setting is applied.
To decouple a DB instance from an environment
Open the Elastic Beanstalk console
, and in the Regions list, select your AWS Region. -
In the navigation pane, choose Environments, and then choose the name of your environment from the list.
Note
If you have many environments, use the search bar to filter the environment list.
In the navigation pane, choose Configuration.
-
In the Database configuration category, choose Edit.
-
Review all of the configurations values in the Database settings section, especially the Database deletion policy, which determines what happens to the database after it's decoupled.
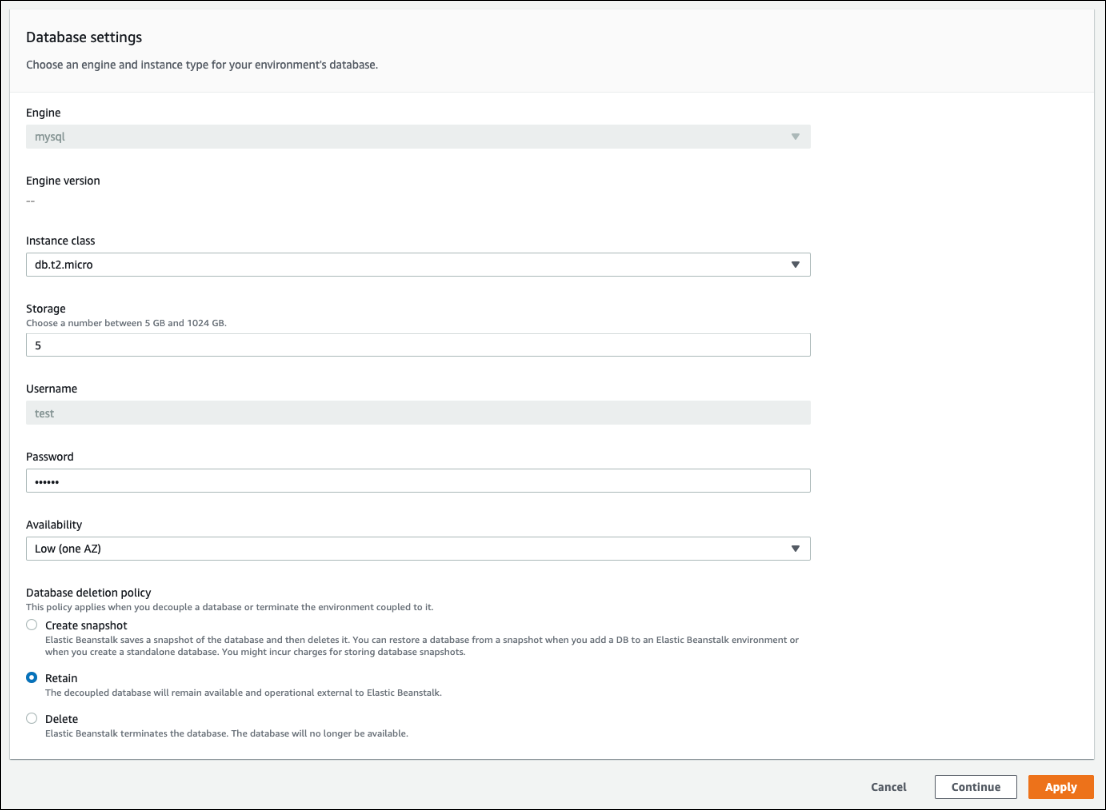
If all of the other configuration settings are correct, skip to Step 6 to decouple the database.
Warning
It’s important to apply the Database deletion policy setting separately from Decouple database. If you select Apply with the intent to save both Decouple database and a newly selected Database deletion policy, the new deletion policy that you chose will be ignored. Elastic Beanstalk will decouple the database following the prior-set deletion policy. If the prior-set deletion policy is
DeleteorCreate Snapshot, you risk losing the database instead of following the intended pending policy.If any of the configuration settings require updates do the following:
-
Make the required modifications in the Database settings panel.
-
Choose Apply. It will take a few minutes to save the configuration changes for your database.
-
Go back to Step 3 and choose Configuration from the navigation pane.
-
-
Go to the Database connection section of the pane.
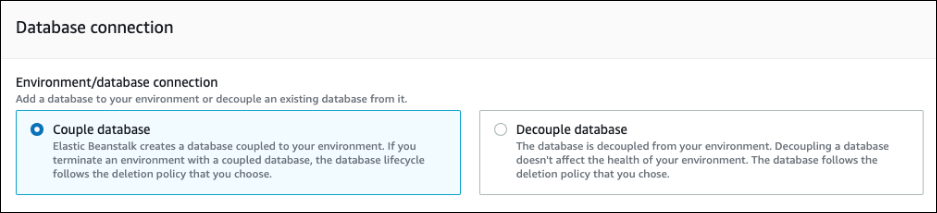
-
Choose Decouple database.
-
Choose Apply to initiate the database decoupling operation.
The deletion policy setting determines the outcome for the database and the length of time that's required to decouple the database.
-
If the deletion policy is set to
Delete, the database is deleted. The operation can take approximately 10-20 minutes, depending on the size of database. -
If the deletion policy is set to
Snapshot, a snapshot of the database is created. Then, the database is deleted. The length of time required for this process varies according to the size of the database. -
If the deletion policy is set to
Retain, the database remains operational external to the Elastic Beanstalk environment. It usually takes less than five minutes to decouple a database.
If you decided to retain the database external to your Elastic Beanstalk environment, you'll need to take additional steps to configure it. For more information, see Using Elastic Beanstalk with Amazon RDS. If you plan to use the database that you decouple for a production environment, verify the storage type that the database uses is suitable for your workload. For more information, see DB Instance Storage and Modifying a DB instance in the Amazon RDS User Guide.
Decoupling an RDS DB instance using configuration files
You can decouple your DB instance from an Elastic Beanstalk environment without affecting the health of the environment. The database instance follows the database deletion policy that was applied when the database was decoupled.
Both of the options required to decouple the database are in the aws:rds:dbinstance namespace. They are as follows:
-
The
DBDeletionPolicyoption sets the deletion policy. It can be set to the following values:Snapshot,Delete, orRetain. These values are described in Database lifecycle in this same topic. -
The
HasCoupledDatabaseoption determines if your environment has a coupled database.-
If toggled to
true, Elastic Beanstalk creates a new DB instance coupled to your environment. -
If toggled to
false, Elastic Beanstalk starts decoupling the DB instance from your environment.
-
If you want to change your database configuration before you decouple it, apply any configuration changes first, in a separate operation. This
includes changing the DBDeletionPolicy configuration. After your changes are applied, run a separate command to set the decoupling option. If
you submit other configuration settings and the decouple setting at the same time, the other configuration option settings are ignored while the decouple
setting is applied.
Warning
It’s important that you run the commands to apply the DBDeletionPolicy and HasCoupledDatabase settings as two separate
operations. If the active deletion policy is already set to Delete or Snapshot, you risk losing the database. The database
follows the deletion policy that's currently active, rather than the pending deletion policy that you intended.
To decouple a DB instance from an environment
Follow these steps to decouple the database from your Elastic Beanstalk environment. You can use the EB CLI or the AWS CLI to complete the steps. For more information, see Advanced environment customization with configuration files.
-
If you want to change the deletion policy, set up a configuration file in the following format. In this example, the deletion policy is set to retain.
option_settings: aws:rds:dbinstance: DBDeletionPolicy:Retain -
Run the command using your preferred tool to complete the configuration update.
-
Set up a configuration file to set
HasCoupledDatabasetofalse.option_settings: aws:rds:dbinstance: HasCoupledDatabase:false -
Run the command using your preferred tool to complete the configuration update.
The deletion policy setting determines the outcome for the database and the length of time that's required to decouple the database.
-
If the deletion policy is set to
Delete, the database is deleted. The operation can take approximately 10-20 minutes, depending on the size of database. -
If the deletion policy is set to
Snapshot, a snapshot of the database is created. Then, the database is deleted. The length of time required for this process varies according to the size of the database. -
If the deletion policy is set to
Retain, the database remains operational external to the Elastic Beanstalk environment. It usually takes less than five minutes to decouple a database.
If you decided to retain the database external to your Elastic Beanstalk environment, you'll need to take additional steps to configure it. For more information, see Using Elastic Beanstalk with Amazon RDS. If you plan to use the database that you decouple for a production environment, verify the storage type that the database uses is suitable for your workload. For more information, see DB Instance Storage and Modifying a DB instance in the Amazon RDS User Guide.