Getting started with the Espressif ESP32-DevKitC and the ESP-WROVER-KIT
Important
This reference integration is hosted on the Amazon-FreeRTOS repository which is deprecated. We recommend that you start here when you create a new project. If you already have an existing FreeRTOS project based on the now deprecated Amazon-FreeRTOS repository, see the Amazon-FreeRTOS Github Repository Migration Guide.
Note
To explore how to integrate FreeRTOS modular libraries and demos within your own Espressif
IDF project, see our
featured reference integration for ESP32-C3 platform
Follow this tutorial to get started with the Espressif ESP32-DevKitC equipped with ESP32-WROOM-32, ESP32-SOLO-1, or ESP-WROVER modules and the ESP-WROVER-KIT-VB. To purchase one from our partner on the AWS Partner Device catalog, use the following links:
These versions of development boards are supported on FreeRTOS.
For more information about the latest versions of these boards, see
ESP32-DevKitC V4
Note
Currently, the FreeRTOS port for ESP32-WROVER-KIT and ESP DevKitC doesn't support the Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) feature.
Overview
This tutorial guides you through the following steps:
-
Connecting your board to a host machine.
-
Installing software on the host machine for developing and debugging embedded applications for your microcontroller board.
-
Cross compiling a FreeRTOS demo application to a binary image.
-
Loading the application binary image to your board, and then running the application.
-
Interacting with the application running on your board across a serial connection, for monitoring and debugging purposes.
Prerequisites
Before you get started with FreeRTOS on your Espressif board, you must set up your AWS account and permissions.
Sign up for an AWS account
If you do not have an AWS account, complete the following steps to create one.
To sign up for an AWS account
Follow the online instructions.
Part of the sign-up procedure involves receiving a phone call or text message and entering a verification code on the phone keypad.
When you sign up for an AWS account, an AWS account root user is created. The root user has access to all AWS services and resources in the account. As a security best practice, assign administrative access to a user, and use only the root user to perform tasks that require root user access.
AWS sends you a confirmation email after the sign-up process is
complete. At any time, you can view your current account activity and manage your account by
going to https://aws.amazon.com/
Create a user with administrative access
After you sign up for an AWS account, secure your AWS account root user, enable AWS IAM Identity Center, and create an administrative user so that you don't use the root user for everyday tasks.
Secure your AWS account root user
-
Sign in to the AWS Management Console
as the account owner by choosing Root user and entering your AWS account email address. On the next page, enter your password. For help signing in by using root user, see Signing in as the root user in the AWS Sign-In User Guide.
-
Turn on multi-factor authentication (MFA) for your root user.
For instructions, see Enable a virtual MFA device for your AWS account root user (console) in the IAM User Guide.
Create a user with administrative access
-
Enable IAM Identity Center.
For instructions, see Enabling AWS IAM Identity Center in the AWS IAM Identity Center User Guide.
-
In IAM Identity Center, grant administrative access to a user.
For a tutorial about using the IAM Identity Center directory as your identity source, see Configure user access with the default IAM Identity Center directory in the AWS IAM Identity Center User Guide.
Sign in as the user with administrative access
-
To sign in with your IAM Identity Center user, use the sign-in URL that was sent to your email address when you created the IAM Identity Center user.
For help signing in using an IAM Identity Center user, see Signing in to the AWS access portal in the AWS Sign-In User Guide.
Assign access to additional users
-
In IAM Identity Center, create a permission set that follows the best practice of applying least-privilege permissions.
For instructions, see Create a permission set in the AWS IAM Identity Center User Guide.
-
Assign users to a group, and then assign single sign-on access to the group.
For instructions, see Add groups in the AWS IAM Identity Center User Guide.
To provide access, add permissions to your users, groups, or roles:
-
Users and groups in AWS IAM Identity Center:
Create a permission set. Follow the instructions in Create a permission set in the AWS IAM Identity Center User Guide.
-
Users managed in IAM through an identity provider:
Create a role for identity federation. Follow the instructions in Create a role for a third-party identity provider (federation) in the IAM User Guide.
-
IAM users:
-
Create a role that your user can assume. Follow the instructions in Create a role for an IAM user in the IAM User Guide.
-
(Not recommended) Attach a policy directly to a user or add a user to a user group. Follow the instructions in Adding permissions to a user (console) in the IAM User Guide.
-
Get started
Note
The Linux commands in this tutorial require that you use the Bash shell.
-
Set up the Espressif hardware.
-
For information about setting up the ESP32-DevKitC development board hardware, see the ESP32-DevKitC V4 Getting Started Guide
. -
For information about setting up the ESP-WROVER-KIT development board hardware, see the ESP-WROVER-KIT V4.1 Getting Started Guide
.
Important
When you reach the Get Started section of the Espressif guides, stop, and then return to the instructions on this page.
-
-
Download Amazon FreeRTOS from GitHub
. (For instructions, see the README.md file.) -
Set up your development environment.
To communicate with your board, you must install a toolchain. Espressif provides the ESP-IDF to develop software for their boards. Since the ESP-IDF has its own version of the FreeRTOS Kernel integrated as a component, Amazon FreeRTOS includes a custom version of the ESP-IDF v4.2 that has the FreeRTOS Kernel removed. This fixes problems with duplicate files when you compile. To use the custom version of the ESP-IDF v4.2 included with Amazon FreeRTOS, follow the instructions below for your host machine's operating system.
Windows
-
Download ESP-IDF's Universal Online Installer
for Windows. -
Run the Universal Online Installer.
-
When you get to the step Download or use ESP-IDF, select Use an existing ESP-IDF directory and set Choose existing ESP-IDF directory to
freertos/vendors/espressif/esp-idf -
Complete the installation.
macOS
-
Follow the instructions in the Standard Setup of Toolchain prerequisites (ESP-IDF v4.2) for macOS
. Important
When you reach the "Get ESP-IDF" instructions under Next Steps, stop, and then return to the instructions on this page.
-
Open a command line window.
-
Navigate to the FreeRTOS download directory, and then run the following script to download and install the espressif toolchain for your platform.
vendors/espressif/esp-idf/install.sh -
Add the ESP-IDF toolchain tools to your terminal's path with the following command.
source vendors/espressif/esp-idf/export.sh
Linux
-
Follow the instructions in the Standard Setup of Toolchain prerequisites (ESP-IDF v4.2) for Linux
. Important
When you reach the "Get ESP-IDF" instructions under Next Steps, stop, and then return to the instructions on this page.
-
Open a command line window.
-
Navigate to the FreeRTOS download directory, and then run the following script to download and install the Espressif toolchain for your platform.
vendors/espressif/esp-idf/install.sh -
Add the ESP-IDF toolchain tools to your terminal's path with the following command.
source vendors/espressif/esp-idf/export.sh
-
-
Establish a serial connection.
-
To establish a serial connection between your host machine and the ESP32-DevKitC, you must install the CP210x USB to UART Bridge VCP drivers. You can download these drivers from Silicon Labs
. To establish a serial connection between your host machine and the ESP32-WROVER-KIT, you must install the FTDI virtual COM port driver. You can download this driver from FTDI
. -
Follow the steps to Establish Serial Connection with ESP32
. -
After you establish a serial connection, make a note of the serial port for your board's connection. You need it to flash the demo.
-
Configure the FreeRTOS demo applications
For this tutorial, the FreeRTOS configuration file is located at
freertos/vendors/espressif/boards/board-name/aws_demos/config_files/FreeRTOSConfig.hAFR_BOARD espressif.esp32_devkitc is chosen, the configuration file is
located at
freertos/vendors/espressif/boards/esp32/aws_demos/config_files/FreeRTOSConfig.h
-
If you're running macOS or Linux, open a terminal prompt. If you're running Windows, open the "ESP-IDF 4.x CMD" app (if you included this option when you installed the ESP-IDF toolchain), or the "Command Prompt" app otherwise.
-
To verify that you have Python3 installed, run
python --versionThe version installed is displayed. If you don't have Python 3.0.1 or later installed, you can install it from the Python
website. -
You need the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) to run AWS IoT commands. If you're running Windows, use the
easy_install awsclicommand to install the AWS CLI in the "Command" or "ESP-IDF 4.x CMD" app.If you're running macOS or Linux, see Installing the AWS CLI.
-
Run
aws configureand configure the AWS CLI with your AWS access key ID, secret access key, and default AWS Region. For more information, see Configuring the AWS CLI.
-
Use the following command to install the AWS SDK for Python (boto3):
-
On Windows, in the "Command" or "ESP-IDF 4.x CMD" app, run
pip install boto3 --userNote
See Boto3 documentation
for details. -
On macOS or Linux, run
pip install tornado nose --userand then run
pip install boto3 --user
FreeRTOS includes the
SetupAWS.pyscript to make it easier to set up your Espressif board to connect to AWS IoT. To configure the script, openfreertos/tools/aws_config_quick_start/configure.jsonafr_source_dir-
The complete path to the
freertos thing_name-
The name that you want to assign to the AWS IoT thing that represents your board.
wifi_ssid-
The SSID of your Wi-Fi network.
wifi_password-
The password for your Wi-Fi network.
wifi_security-
The security type for your Wi-Fi network.
The following are valid security types:
-
eWiFiSecurityOpen(Open, no security) -
eWiFiSecurityWEP(WEP security) -
eWiFiSecurityWPA(WPA security) -
eWiFiSecurityWPA2(WPA2 security)
-
-
-
Run the configuration script.
-
If you're running macOS or Linux, open a terminal prompt. If you're running Windows, open the "ESP-IDF 4.x CMD" or "Command" app.
-
Navigate to the
freertos/tools/aws_config_quick_startpython SetupAWS.py setupThe script does the following:
-
Creates an IoT thing, certificate, and policy.
-
Attaches the IoT policy to the certificate and the certificate to the AWS IoT thing.
-
Populates the
aws_clientcredential.hfile with your AWS IoT endpoint, Wi-Fi SSID, and credentials. -
Formats your certificate and private key and writes them to the
aws_clientcredential_keys.hheader file.
Note
The certificate is hardcoded for demonstration purposes only. Production-level applications should store these files in a secure location.
For more information about
SetupAWS.py, see theREADME.mdin thefreertos/tools/aws_config_quick_start -
-
Monitoring MQTT messages on the cloud
Before you run the FreeRTOS demo project, you can set up the MQTT client in the AWS IoT console to monitor the messages that your device sends to the AWS Cloud.
To subscribe to the MQTT topic with the AWS IoT MQTT client
-
Navigate to the AWS IoT console
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Test, then choose MQTT Test Client.
-
In Subscription topic, enter
your-thing-name/example/topic
When the demo project successfully runs on your device you see "Hello World!" sent multiple times to the topic that you subscribed to.
Build, flash, and run the FreeRTOS demo project using the idf.py script
You can use Espressif's IDF utility (idf.py) to build the project and flash the binaries
onto your device.
Note
Some setups might require that you use the port option "-p port-name" with
idf.py to specify the correct port, as in the following example.
idf.py -p /dev/cu.usbserial-00101301B flash
Build and flash FreeRTOS on Windows, Linux, and macOS (ESP-IDF v4.2)
-
Navigate to the root of your FreeRTOS download directory.
-
In a command line window, enter the following command to add the ESP-IDF tools to your terminal's PATH.
- Windows ("Command" app)
-
vendors\espressif\esp-idf\export.bat - Windows ("ESP-IDF 4.x CMD" app)
-
(This has already been done when you opened the app.)
- Linux / macOS
-
source vendors/espressif/esp-idf/export.sh
-
Configure cmake in the
builddirectory and build the firmware image with the following command.idf.py -DVENDOR=espressif -DBOARD=esp32_wrover_kit -DCOMPILER=xtensa-esp32 buildYou should see output like the following.
Running cmake in directory /path/to/hello_world/build Executing "cmake -G Ninja --warn-uninitialized /path/to/hello_world"... Warn about uninitialized values. -- Found Git: /usr/bin/git (found version "2.17.0") -- Building empty aws_iot component due to configuration -- Component names: ... -- Component paths: ... ... (more lines of build system output) [527/527] Generating hello-world.bin esptool.py v2.3.1 Project build complete. To flash, run this command: ../../../components/esptool_py/esptool/esptool.py -p (PORT) -b 921600 write_flash --flash_mode dio --flash_size detect --flash_freq 40m 0x10000 build/hello-world.bin build 0x1000 build/bootloader/bootloader.bin 0x8000 build/partition_table/partition-table.bin or run 'idf.py -p PORT flash'If there are no errors, the build will generate the firmware binary .bin files.
-
Erase your development board's flash memory with the following command.
idf.py erase_flash -
Use the
idf.pyscript to flash the application binary to your board.idf.py flash -
Monitor the output from your board's serial port with the following command.
idf.py monitorNote
You can combine these commands such as in the following example.
idf.py erase_flash flash monitorFor certain host machine setups, you must specify the port when you flash the board such as in the following example.
idf.py erase_flash flash monitor -p /dev/ttyUSB1
Build and Flash FreeRTOS with CMake
In addition to the idf.py script provided by the IDF SDK to build and run your code,
you can also build the project with CMake. Currently, it supports either Unix Makefiles or the Ninja build
system.
To build and flash the project
-
In a command line window, navigate to the root of your FreeRTOS download directory.
-
Run the following script to add the ESP-IDF tools to your shell's PATH.
- Windows
-
vendors\espressif\esp-idf\export.bat - Linux / macOS
-
source vendors/espressif/esp-idf/export.sh
-
Enter the following command to generate the build files.
- With Unix Makefiles
-
cmake -DVENDOR=espressif -DBOARD=esp32_wrover_kit -DCOMPILER=xtensa-esp32 -S . -B ./YOUR_BUILD_DIRECTORY -DAFR_ENABLE_ALL_MODULES=1 -DAFR_ENABLE_TESTS=0 - With Ninja
-
cmake -DVENDOR=espressif -DBOARD=esp32_wrover_kit -DCOMPILER=xtensa-esp32 -S . -B ./YOUR_BUILD_DIRECTORY -DAFR_ENABLE_ALL_MODULES=1 -DAFR_ENABLE_TESTS=0 -GNinja
-
Build the project.
- With Unix Makefiles
-
make -C ./YOUR_BUILD_DIRECTORY -j8 - With Ninja
-
ninja -C ./YOUR_BUILD_DIRECTORY -j8
-
Erase the flash and then flash the board.
- With Unix Makefiles
-
make -C ./YOUR_BUILD_DIRECTORY erase_flashmake -C ./YOUR_BUILD_DIRECTORY flash - With Ninja
-
ninja -C ./YOUR_BUILD_DIRECTORY erase_flashninja -C ./YOUR_BUILD_DIRECTORY flash
Run the Bluetooth Low Energy demos
FreeRTOS supports Bluetooth Low Energy library connectivity.
To run the FreeRTOS demo project across Bluetooth Low Energy, you must run the FreeRTOS Bluetooth Low Energy Mobile SDK Demo Application on an iOS or Android mobile device.
To set up the FreeRTOS Bluetooth Low Energy mobile SDK demo application
-
Follow the instructions in Mobile SDKs for FreeRTOS Bluetooth devices to download and install the SDK for your mobile platform on your host computer.
-
Follow the instructions in FreeRTOS Bluetooth Low Energy Mobile SDK demo application to set up the demo mobile application on your mobile device.
For instructions about how to run the MQTT over Bluetooth Low Energy demo on your board, see MQTT over Bluetooth Low Energy.
For instructions about how to run the Wi-Fi provisioning demo on your board, see Wi-Fi provisioning.
Using FreeRTOS in your own CMake project for ESP32
If you want to consume FreeRTOS in your own CMake project, you can set it up as a subdirectory and build it
together with your application. First, get a copy of FreeRTOS from GitHub
git submodule add -b release https://github.com/aws/amazon-freertos.git freertos
If a later version is released, you can update your local copy with these commands.
# Pull the latest changes from the remote tracking branch. git submodule update --remote -- freertos
# Commit the submodule change because it is pointing to a different revision now. git add freertos
git commit -m "Update FreeRTOS to a new release"
If your project has the following directory structure:
- freertos (the copy that you obtained from GitHub or the AWS IoT console) - src - main.c (your application code) - CMakeLists.txt
Then the following is an example of the top-level CMakeLists.txt file that can be used
to build your application together with FreeRTOS.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.13) project(freertos_examples) # Tell IDF build to link against this target. set(IDF_EXECUTABLE_SRCS "<complete_path>/src/main.c") set(IDF_PROJECT_EXECUTABLE my_app) # Add FreeRTOS as a subdirectory. AFR_BOARD tells which board to target. set(AFR_BOARD espressif.esp32_devkitc CACHE INTERNAL "") add_subdirectory(freertos) # Link against the mqtt library so that we can use it. Dependencies are transitively # linked. target_link_libraries(my_app PRIVATE AFR::core_mqtt)
To build the project, run the following CMake commands. Make sure the ESP32 compiler is in the PATH environment variable.
cmake -S . -B build-directory -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=freertos/tools/cmake/toolchains/xtensa-esp32.cmake -GNinja
cmake --build build-directory
To flash the application to your board, run the following command.
cmake --build build-directory --target flash
Using components from FreeRTOS
After running CMake, you can find all available components in the summary output. It should look something like the following example.
====================Configuration for FreeRTOS==================== Version: 202107.00 Git version: 202107.00-g79ad6defb Target microcontroller: vendor: Espressif board: ESP32-DevKitC description: Development board produced by Espressif that comes in two variants either with ESP-WROOM-32 or ESP32-WROVER module family: ESP32 data ram size: 520KB program memory size: 4MB Host platform: OS: Linux-4.15.0-66-generic Toolchain: xtensa-esp32 Toolchain path: /opt/xtensa-esp32-elf CMake generator: Ninja FreeRTOS modules: Modules to build: backoff_algorithm, common, common_io, core_http, core_http_demo_dependencies, core_json, core_mqtt, core_mqtt_agent, core_mqtt_agent_demo_dependencies, core_mqtt_demo_dependencies, crypto, defender, dev_mode_key_ provisioning, device_defender, device_defender_demo_ dependencies, device_shadow, device_shadow_demo_dependencies, freertos_cli_plus_uart, freertos_plus_cli, greengrass, http_demo_helpers, https, jobs, jobs_demo_dependencies, kernel, logging, mqtt, mqtt_agent_interface, mqtt_demo_ helpers, mqtt_subscription_manager, ota, ota_demo_ dependencies, ota_demo_version, pkcs11, pkcs11_helpers, pkcs11_implementation, pkcs11_utils, platform, secure_sockets, serializer, shadow, tls, transport_interface_secure_sockets, wifi Enabled by user: common_io, core_http_demo_dependencies, core_json, core_mqtt_agent_demo_dependencies, core_mqtt_demo_ dependencies, defender, device_defender, device_defender_demo_ dependencies, device_shadow, device_shadow_demo_dependencies, freertos_cli_plus_uart, freertos_plus_cli, greengrass, https, jobs, jobs_demo_dependencies, logging, ota_demo_dependencies, pkcs11, pkcs11_helpers, pkcs11_implementation, pkcs11_utils, platform, secure_sockets, shadow, wifi Enabled by dependency: backoff_algorithm, common, core_http, core_mqtt, core_mqtt_agent, crypto, demo_base, dev_mode_key_provisioning, freertos, http_demo_helpers, kernel, mqtt, mqtt_agent_ interface, mqtt_demo_helpers, mqtt_subscription_manager, ota, ota_demo_version, pkcs11_mbedtls, serializer, tls, transport_interface_secure_sockets, utils 3rdparty dependencies: jsmn, mbedtls, pkcs11, tinycbor Available demos: demo_cli_uart, demo_core_http, demo_core_mqtt, demo_core_mqtt_ agent, demo_device_defender, demo_device_shadow, demo_greengrass_connectivity, demo_jobs, demo_ota_core_http, demo_ota_core_mqtt, demo_tcp Available tests: =========================================================================
You can reference any components from the Modules to build list. To link them into your
application, put the AFR:: namespace in front of the name, for example,
AFR::core_mqtt, AFR::ota, and so on.
Add custom components using ESP-IDF
You can add more components while using ESP-IDF. For example, assuming you want to add a
component called example_component, and your project looks like this:
- freertos - components - example_component - include - example_component.h - src - example_component.c - CMakeLists.txt - src - main.c - CMakeLists.txt
The following is an example of the CMakeLists.txt file for your
component.
add_library(example_componentsrc/example_component.c) target_include_directories(example_componentPUBLIC include)
Then, in the top level CMakeLists.txt file, add the component by
inserting the following line just after add_subdirectory(freertos).
add_subdirectory(component/example_component)
Then, modify target_link_libraries to include your component.
target_link_libraries(my_app PRIVATE AFR::core_mqtt PRIVATEexample_component)
This component is now automatically linked to your application code by default. You can now include its header files and call the functions it defines.
Override the configurations for FreeRTOS
There's currently no well-defined approach to redefining the configs outside of the FreeRTOS source tree.
By default, CMake will look for the
freertos/vendors/espressif/boards/esp32/aws_demos/config_files/freertos/demos/include/
- freertos - freertos-configs - aws_clientcredential.h - aws_clientcredential_keys.h - iot_mqtt_agent_config.h - iot_config.h - components - src - CMakeLists.txt
The files under freertos-configs are copied from the
freertos/vendors/espressif/boards/esp32/aws_demos/config_files/freertos/demos/include/CMakeLists.txt file, add this line before add_subdirectory(freertos)
so that the compiler will search this directory first.
include_directories(BEFORE freertos-configs)
Providing your own sdkconfig for ESP-IDF
In case you want to provide your own sdkconfig.default, you can set the CMake variable
IDF_SDKCONFIG_DEFAULTS, from the command line:
cmake -S . -B build-directory -DIDF_SDKCONFIG_DEFAULTS=path_to_your_sdkconfig_defaults -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=freertos/tools/cmake/toolchains/xtensa-esp32.cmake -GNinja
If you don't specify a location for your own sdkconfig.default file, FreeRTOS uses
the default file located at
freertos/vendors/espressif/boards/esp32/aws_demos/sdkconfig.defaults
For more information, see Project
Configuration
Summary
If you have a project with a component called example_component, and you want to override some
configurations, here's a complete example of the top level CMakeLists.txt file.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.13) project(freertos_examples) set(IDF_PROJECT_EXECUTABLE my_app) set(IDF_EXECUTABLE_SRCS "src/main.c") # Tell IDF build to link against this target. set(IDF_PROJECT_EXECUTABLE my_app) # Add some extra components. IDF_EXTRA_COMPONENT_DIRS is a variable used by ESP-IDF # to collect extra components. get_filename_component( EXTRA_COMPONENT_DIRS "components/example_component" ABSOLUTE ) list(APPEND IDF_EXTRA_COMPONENT_DIRS ${EXTRA_COMPONENT_DIRS}) # Override the configurations for FreeRTOS. include_directories(BEFORE freertos-configs) # Add FreeRTOS as a subdirectory. AFR_BOARD tells which board to target. set(AFR_BOARD espressif.esp32_devkitc CACHE INTERNAL "") add_subdirectory(freertos) # Link against the mqtt library so that we can use it. Dependencies are transitively # linked. target_link_libraries(my_app PRIVATE AFR::core_mqtt)
Troubleshooting
-
If you're running macOS and the operating system doesn't recognize your ESP-WROVER-KIT, make sure you don't have the D2XX drivers installed. To uninstall them, follow the instructions in the FTDI Drivers Installation Guide for macOS X
. -
The monitor utility provided by ESP-IDF (and invoked using make monitor) helps you decode addresses. For this reason, it can help you get some meaningful backtraces in the event the application stops working. For more information, see Automatic Address Decoding
on the Espressif website. -
It's also possible to enable GDBstub for communication with gdb without requiring any special JTAG hardware. For more information, see Launching GDB with GDBStub
on the Espressif website. -
For information about setting up an OpenOCD-based environment if JTAG hardware-based debugging is required, see JTAG Debugging
on the Espressif website. -
If
pyserialcan't be installed usingpipon macOS, download it from the pyserial website. -
If the board resets continuously, try erasing the flash by entering the following command on the terminal.
make erase_flash -
If you see errors when you run
idf_monitor.py, use Python 2.7. -
Required libraries from ESP-IDF are included in FreeRTOS, so there is no need to download them externally. If the
IDF_PATHenvironment variable is set, we recommend that you clear it before you build FreeRTOS. -
On Windows, it can take 3-4 minutes for the project to build. To reduce the build time, you can use the
-j4switch on the make command.make flash monitor -j4 -
If your device has trouble connecting to AWS IoT, open the
aws_clientcredential.hfile, and verify that the configuration variables are properly defined in the file.clientcredentialMQTT_BROKER_ENDPOINT[]should look like1234567890123-ats.iot.us-east-1.amazonaws.com. -
If you're following the steps in Using FreeRTOS in your own CMake project for ESP32 and you see undefined reference errors from the linker, it's usually because of missing dependent libraries or demos. To add them, update the
CMakeLists.txtfile (under the root directory) using the standard CMake functiontarget_link_libraries. -
ESP-IDF v4.2 supports the use of the xtensa\-esp32\-elf\-gcc 8\.2\.0\. toolchain. If you're using an earlier version of the Xtensa toolchain, download the required version.
-
If you see an error log like the following about python dependencies that are not being met for ESP-IDF v4.2:
The following Python requirements are not satisfied: click>=5.0 pyserial>=3.0 future>=0.15.2 pyparsing>=2.0.3,<2.4.0 pyelftools>=0.22 gdbgui==0.13.2.0 pygdbmi<=0.9.0.2 reedsolo>=1.5.3,<=1.5.4 bitstring>=3.1.6 ecdsa>=0.16.0 Please follow the instructions found in the "Set up the tools" section of ESP-IDF Getting Started GuideInstall the python dependencies on your platform using the following Python command:
root/vendors/espressif/esp-idf/requirements.txt
For more troubleshooting information, see Troubleshooting getting started.
Debugging
Debugging code on Espressif ESP32-DevKitC and ESP-WROVER-KIT (ESP-IDF v4.2)
This section shows you how to debug Espressif hardware using ESP-IDF v4.2. You need a JTAG to USB cable.
We use a USB to MPSSE cable (for example, the
FTDI C232HM-DDHSL-0
- ESP-DevKitC JTAG setup
-
For the FTDI C232HM-DDHSL-0 cable, these are the connections to the ESP32 DevkitC.
| C232HM-DDHSL-0 Wire Color | ESP32 GPIO Pin | JTAG Signal Name | | ------------------------- | -------------- | ---------------- | | Brown (pin 5) | IO14 | TMS | | Yellow (pin 3) | IO12 | TDI | | Black (pin 10) | GND | GND | | Orange (pin 2) | IO13 | TCK | | Green (pin 4) | IO15 | TDO | - ESP-WROVER-KIT JTAG setup
-
For the FTDI C232HM-DDHSL-0 cable, these are the connections to the ESP32-WROVER-KIT.
| C232HM-DDHSL-0 Wire Color | ESP32 GPIO Pin | JTAG Signal Name | | ------------------------- | -------------- | ---------------- | | Brown (pin 5) | IO14 | TMS | | Yellow (pin 3) | IO12 | TDI | | Orange (pin 2) | IO13 | TCK | | Green (pin 4) | IO15 | TDO |These tables were developed from the FTDI C232HM-DDHSL-0 datasheet
. For more information, see the section "C232HM MPSSE Cable Connection and Mechanical Details in the data sheet. To enable JTAG on the ESP-WROVER-KIT, place jumpers on the TMS, TDO, TDI, TCK, and S_TDI pins as shown here.
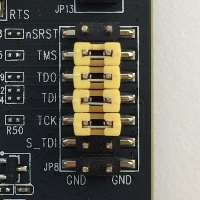
- Debugging on Windows (ESP-IDF v4.2)
-
To set up for debugging on Windows
-
Connect the USB side of the FTDI C232HM-DDHSL-0 to your computer and the other side as described in Debugging code on Espressif ESP32-DevKitC and ESP-WROVER-KIT (ESP-IDF v4.2). The FTDI C232HM-DDHSL-0 device should appear in Device Manager under Universal Serial Bus Controllers.
-
Under the list of universal serial bus devices, right-click the C232HM-DDHSL-0 device, and then choose Properties.
Note
The device might be listed as USB Serial Port.
To see the properties of the device, in the properties window, choose the Details tab. If the device isn't listed, install the Windows driver for FTDI C232HM-DDHSL-0
. -
On the Details tab, choose Property, and then choose Hardware IDs. You should see something like this in the Value field.
FTDIBUS\COMPORT&VID_0403&PID_6014In this example, the vendor ID is 0403 and the product ID is 6014.
Verify these IDs match the IDs in
projects/espressif/esp32/make/aws_demos/esp32_devkitj_v1.cfg. The IDs are specified in a line that begins withftdi_vid_pidfollowed by a vendor ID and a product ID.ftdi_vid_pid 0x0403 0x6014 -
Download OpenOCD for Windows
. -
Unzip the file to
C:\and addC:\openocd-esp32\binto your system path. -
OpenOCD requires libusb, which is not installed by default on Windows. To install libusb:
-
Download zadig.exe
. -
Run
zadig.exe. From the Options menu, choose List All Devices. -
From the dropdown menu, choose C232HM-DDHSL-0.
-
In the target driver field, to the right of the green arrow, choose WinUSB.
-
For the list under the target driver field, choose the arrow, and then choose Install Driver. Choose Replace Driver.
-
-
Open a command prompt, navigate to the root of your FreeRTOS download directory, and run the following command.
idf.py openocdLeave this command prompt open.
-
Open a new command prompt, navigate to the root of your FreeRTOS download directory, and run
idf.py flash monitor -
Open another command prompt, navigate to the root of your FreeRTOS download directory, and wait until the demo starts running on your board. When it does, run
idf.py gdbThe program should stop in the
mainfunction.Note
The ESP32 supports a maximum of two break points.
-
- Debugging on macOS (ESP-IDF v4.2)
-
-
Download the FTDI driver for macOS
. -
Download OpenOCD
. -
Extract the downloaded .tar file and set the path in
.bash_profiletoOCD_INSTALL_DIR/openocd-esp32/bin. -
Use the following command to install
libusbon macOS.brew install libusb -
Use the following command to unload the serial port driver.
sudo kextunload -b com.FTDI.driver.FTDIUSBSerialDriver -
Use the following command to unload the serial port driver.
sudo kextunload -b com.FTDI.driver.FTDIUSBSerialDriver -
If you're running a macOS version later than 10.9, use the following command to unload the Apple FTDI driver.
sudo kextunload -b com.apple.driver.AppleUSBFTDI -
Use the following command to get the product ID and vendor ID of the FTDI cable. It lists the attached USB devices.
system_profiler SPUSBDataTypeThe output from
system_profilershould look like the following.DEVICE: Product ID: product-ID Vendor ID: vendor-ID (Future Technology Devices International Limited) -
Open the
projects/espressif/esp32/make/aws_demos/esp32_devkitj_v1.cfgfile. The vendor ID and product ID for your device are specified in a line that begins withftdi_vid_pid. Change the IDs to match the IDs from thesystem_profileroutput in the previous step. -
Open a terminal window, navigate to the root of your FreeRTOS download directory, and use the following command to run OpenOCD.
idf.py openocdLeave this terminal window open.
-
Open a new terminal, and use the following command to load the FTDI serial port driver.
sudo kextload -b com.FTDI.driver.FTDIUSBSerialDriver -
Navigate to the root of your FreeRTOS download directory, and run
idf.py flash monitor -
Open another new terminal, navigate to the root of your FreeRTOS download directory, and run
idf.py gdbThe program should stop at
main.
-
- Debugging on Linux (ESP-IDF v4.2)
-
-
Download OpenOCD
. Extract the tarball and follow the installation instructions in the readme file. -
Use the following command to install libusb on Linux.
sudo apt-get install libusb-1.0 -
Open a terminal and enter ls -l /dev/ttyUSB* to list all USB devices connected to your computer. This helps you check if the board's USB ports are recognized by the operating system. You should see output like the following.
$ls -l /dev/ttyUSB* crw-rw---- 1 root dialout 188, 0 Jul 10 19:04 /dev/ttyUSB0 crw-rw---- 1 root dialout 188, 1 Jul 10 19:04 /dev/ttyUSB1 -
Sign off and then sign in and cycle the power to the board to make the changes take effect. In a terminal prompt, list the USB devices. Make sure the group owner has changed from
dialouttoplugdev.$ls -l /dev/ttyUSB* crw-rw---- 1 root plugdev 188, 0 Jul 10 19:04 /dev/ttyUSB0 crw-rw---- 1 root plugdev 188, 1 Jul 10 19:04 /dev/ttyUSB1The
/dev/ttyUSBninterface with the lower number is used for JTAG communication. The other interface is routed to the ESP32's serial port (UART) and is used for uploading code to the ESP32's flash memory. -
In a terminal window, navigate to the root of your FreeRTOS download directory, and use the following command to run OpenOCD.
idf.py openocd -
Open another terminal, navigate to the root of your FreeRTOS download directory, and run the following command.
idf.py flash monitor -
Open another terminal, navigate the root of your FreeRTOS download directory, and run the following command:
idf.py gdbThe program should stop in
main().
-